Abstract
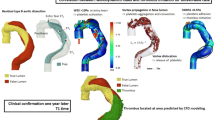
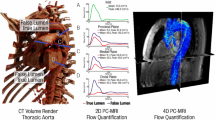
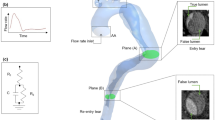
Progressive false lumen aneurysmal degeneration in type B aortic dissection (TBAD) is a complex process with a multi-factorial etiology. Patient-specific computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations provide spatial and temporal hemodynamic quantities that facilitate understanding this disease progression. A longitudinal study was performed for a TBAD patient, who was diagnosed with the uncomplicated TBAD in 2006 and treated with optimal medical therapy but received surgery in 2010 due to late complication. Geometries of the aorta in 2006 and 2010 were reconstructed. With registration algorithms, we accurately quantified the evolution of the false lumen, while with CFD simulations we computed several hemodynamic indexes, including the wall shear stress (WSS), and the relative residence time (RRT). The numerical fluid model included large eddy simulation (LES) modeling for efficiently capturing the flow disturbances induced by the entry tears. In the absence of complete patient-specific data, the boundary conditions were based on a specific calibration method. Correlations between hemodynamics and the evolution field in time obtained by registration of the false lumen are discussed. Further testing of this methodology on a large cohort of patients may enable the use of CFD to predict whether patients, with originally uncomplicated TBAD, develop late complications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CFD:
-
Computational fluid dynamics
- AD:
-
Aortic dissection
- TBAD:
-
Type B AD
- uTBAD:
-
Uncomplicated TBAD
- FL:
-
False lumen
- TL:
-
True lumen
- OMT:
-
Optimal medical therapy
- WSS:
-
Wall shear stress
- TAWSS:
-
Time averaged WSS
- RRT:
-
Relative residence time
- OSI:
-
Oscillatory shear index
- 3WK:
-
3 Element windkessel model
References
Afifi, R. O., H. K. Sandhu, S. S. Leake, V. Kumar, A. Azizzadeh, K. M. Charlton-Ouw, T. C. Nguyen, C. C. Miller, H. J. Safi, and A. L. Estrera. Outcomes of patients with acute type B (DeBakey III) aortic dissection: a 13 year single center experience. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.015302.
Akutsu, K., J. Nejima, K. Kiuchi, K. Sasaki, M. Ochi, K. Tanaka, and T. Takano. Effects of the patent false lumen on the long-term outcome of type B acute aortic dissection. Eur. J. Cardio-Thor. Surg. 26:359–366, 2004.
Alimohammadi, M., O. Agu, S. Balabani, and V. Díaz-Zuccarini. Development of a patient-specific simulation tool to analyse aortic dissections: assessment of mixed patient-specific flow and pressure boundary conditions. Med. Eng. Phys. 36:275–284, 2014.
Bertagna, L., A. Quaini, and A. Veneziani. Deconvolution-based nonlinear filtering for incompressible flows at moderately large Reynolds numbers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 81:463–488, 2016.
Chen, D., M. Müller-Eschner, D. Kotelis, D. Böckler, Y. Ventikos, and H. von Tengg-Kobligk. A longitudinal study of type-B aortic dissection and endovascular repair scenarios: computational analyses. Med. Eng. Phys. 35:1321–1330, 2013.
Cheng, Z., C. Riga, J. Chan, M. Hamady, N. B. Wood, N. J. Cheshire, Y. Xu, and R. G. Gibbs. Initial findings and potential applicability of computational simulation of the aorta in acute type B dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 57:35S–43S, 2013.
Cheng, Z., F. Tan, C. Riga, C. Bicknell, M. Hamady, R. Gibbs, N. Wood, and X. Xu. Analysis of flow patterns in a patient-specific aortic dissection model. J. Biomech. Eng. 132:051007, 2010.
Cheng, Z., N. B. Wood, R. G. Gibbs, and X. Y. Xu. Geometric and flow features of type B aortic dissection: initial findings and comparison of medically treated and stented cases. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:177–189, 2015.
Evangelista, A., V. Galuppo, D. Gruosso, H. Cuéllar, G. Teixidó, and J. Rodríguez-Palomares. Role of entry tear size in type B aortic dissection. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 3:403, 2014.
Hebballi, R., and J. Swanevelder. Diagnosis and management of aortic dissection. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 9:14–18, 2009.
Kim, H. J., I. E. Vignon-Clementel, C. A. Figueroa, J. F. LaDisa, K. E. Jansen, J. A. Feinstein, and C. A. Taylor. On coupling a lumped parameter heart model and a three-dimensional finite element aorta model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37:2153–2169, 2009.
Lobato, A., and P. Puech-Leao. Predictive factors for rupture of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 27:446–453, 1998.
Modersitzki, J. Numerical Methods for Image Registration. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2004.
Moireau, P., N. Xiao, M. Astorino, C. A. Figueroa, D. Chapelle, C. Taylor, and J.-F. Gerbeau. External tissue support and fluid–structure simulation in blood flows. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 11:1–18, 2012.
Morbiducci, U., R. Ponzini, D. Gallo, C. Bignardi, and G. Rizzo. Inflow boundary conditions for image-based computational hemodynamics: impact of idealized versus measured velocity profiles in the human aorta. J. Biomech. 46:102–109, 2013.
Myronenko, A., and X. Song. Point set registration: coherent point drift. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32:2262–2275, 2010.
Nerem, R. M., D. G. Harrison, R. W. Taylor, and W. R. Alexander. Hemodynamics and vascular endothelial biology. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 21:S6–S10, 1993.
Nienaber, C. A., and R. E. Clough. Management of acute aortic dissection. Lancet 385:800–811, 2015.
Nienaber, C. A., S. Kische, H. Rousseau, H. Eggebrecht, T. C. Rehders, G. Kundt, A. Glass, D. Scheinert, M. Czerny, and T. Kleinfeldt. Endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection. Circulation 6:407–416, 2013.
Onitsuka, S., H. Akashi, K. Tayama, T. Okazaki, K. Ishihara, S. Hiromatsu, and S. Aoyagi. Long-term outcome and prognostic predictors of medically treated acute type B aortic dissections. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 78:1268–1273, 2004.
Pape, L. A., M. Awais, E. M. Woznicki, T. Suzuki, S. Trimarchi, A. Evangelista, T. Myrmel, M. Larsen, K. M. Harris, and K. Greason. Presentation, diagnosis, and outcomes of acute aortic dissection: 17 year trends from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 66:350–358, 2015.
Passerini, T., A. Quaini, U. Villa, A. Veneziani, and S. Canic. Validation of an open source framework for the simulation of blood flow in rigid and deformable vessels. Int. J. Num. Methods Biomed. Eng. 29:1192–1213, 2013.
Pirola, S., Z. Cheng, O. Jarral, D. O’Regan, J. Pepper, T. Athanasiou, and X. Xu. On the choice of outlet boundary conditions for patient-specific analysis of aortic flow using computational fluid dynamics. J. Biomech. 60:15–21, 2017.
Quarteroni, A., A. Veneziani, and C. Vergara. Geometric multiscale modeling of the cardiovascular system, between theory and practice. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 302:193–252, 2016.
Rayz, V., L. Boussel, L. Ge, J. Leach, A. Martin, M. Lawton, C. McCulloch, and D. Saloner. Flow residence time and regions of intraluminal thrombus deposition in intracranial aneurysms. Ann. Biomed Eng. 38:3058–3069, 2010.
Shang, E. K., D. P. Nathan, R. M. Fairman, J. E. Bavaria, R. C. Gorman, J. H. Gorman, and B. M. Jackson. Use of computational fluid dynamics studies in predicting aneurysmal degeneration of acute type B aortic dissections. J. Vasc. Surg. 62:279–284, 2015.
Song, J.-M., S.-D. Kim, J.-H. Kim, M.-J. Kim, D.-H. Kang, J. B. Seo, T.-H. Lim, J. W. Lee, M.-G. Song, and J.-K. Song. Long-term predictors of descending aorta aneurysmal change in patients with aortic dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 50:799–804, 2007.
Sueyoshi, E., I. Sakamoto, K. Hayashi, T. Yamaguchi, and T. Imada. Growth rate of aortic diameter in patients with type B aortic dissection during the chronic phase. Circulation 110:II-256–II-261, 2004.
Svensson, L. G., N. T. Kouchoukos, D. C. Miller, J. E. Bavaria, J. S. Coselli, M. A. Curi, H. Eggebrecht, J. A. Elefteriades, R. Erbel, and T. G. Gleason. Expert consensus document on the treatment of descending thoracic aortic disease using endovascular stent-grafts. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 85:S1–S41, 2008.
Tsai, T. T., A. Evangelista, C. A. Nienaber, T. Myrmel, G. Meinhardt, J. V. Cooper, D. E. Smith, T. Suzuki, R. Fattori, and A. Llovet. Partial thrombosis of the false lumen in patients with acute type B aortic dissection. N Engl. J. Med. 357:349–359, 2007.
Tse, K. M., P. Chiu, H. P. Lee, and P. Ho. Investigation of hemodynamics in the development of dissecting aneurysm within patient-specific dissecting aneurismal aortas using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. J. Biomech. 44:827–836, 2011.
Xiang, J., S. K. Natarajan, M. Tremmel, D. Ma, J. Mocco, L. N. Hopkins, A. H. Siddiqui, E. I. Levy, and H. Meng. Hemodynamic–morphologic discriminants for intracranial aneurysm rupture. Stroke 42:144–152, 2011.
Xiao, N., J. D. Humphrey, and C. A. Figueroa. Multi-scale computational model of three-dimensional hemodynamics within a deformable full-body arterial network. J. Comput. Phys. 244:22–40, 2013.
Xu, H., Z. Li, H. Dong, Y. Zhang, J. Wei, P. N. Watton, W. Guo, D. Chen, and J. Xiong. Hemodynamic parameters that may predict false-lumen growth in type-B aortic dissection after endovascular repair: a preliminary study on long-term multiple follow-ups. Med. Eng. Phys. 50:12–21, 2017.
Zamir, M., P. Sinclair, and T. H. Wonnacott. Relation between diameter and flow in major branches of the arch of the aorta. J. Biomech. 25:1303–1310, 1992.
Acknowledgments
US-NSF Project DMS 162040 and NSF-XSEDE TG-ASC160069. The authors thank Professor R. Nerem for many fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Umberto Morbiducci oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Piccinelli, M., Leshnower, B.G. et al. Coupled Morphological–Hemodynamic Computational Analysis of Type B Aortic Dissection: A Longitudinal Study. Ann Biomed Eng 46, 927–939 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2012-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2012-z