Abstract
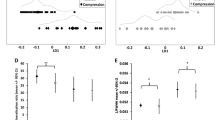
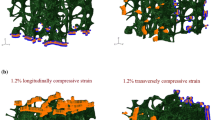
The load-transfer pathway in trabecular bone is largely determined by its architecture. However, the influence of variations in mineralization is not known. The goal of this study was to examine the influence of inhomogeneously distributed degrees of mineralization (DMB) on intratrabecular stresses and strains. Cubic mandibular condylar bone specimens from fetal and newborn pigs were used. Finite element models were constructed, in which the element tissue moduli were scaled to the local DMB. Disregarding the observed distribution of mineralization was associated with an overestimation of average equivalent strain and underestimation of von Mises equivalent stress. From the surface of trabecular elements towards their core the strain decreased irrespective of tissue stiffness distribution. This indicates that the trabecular elements were bent during the compression experiment. Inhomogeneously distributed tissue stiffness resulted in a low stress at the surface that increased towards the core. In contrast, disregarding this tissue stiffness distribution resulted in high stress at the surface which decreased towards the core. It was concluded that the increased DMB, together with concurring alterations in architecture, during development leads to a structure which is able to resist increasing loads without an increase in average deformation, which may lead to damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourne B. C., M. C. H. van der Meulen. Finite element models predict cancellous apparent modulus when tissue modulus is scaled from specimen CT-attenuation. J. Biomech. 37: 613–621, 2004
Burger E. H., J. Klein-Nulend, J. P. Veldhuijzen. Modulation of osteogenesis in fetal bone rudiments by mechanical stress in vitro. J. Biomech. 24: 101–109, 1991
Camacho D. L., R. H. Hopper, G. M. Lin, B. S. Myers. An improved method for finite element mesh generation of geometrically complex structures with application to the skullbase. J. Biomech. 30: 1067–1070, 1997
Ciarelli T. E., D. P. Fyhrie, A. M. Parfitt. Effects of vertebral bone fragility and bone formation rate on the mineralization levels of cancellous bone from white females. Bone 32: 311–315, 2003
Currey J. D. Effects of differences in mineralization on the mechanical properties of bone. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 304: 509–518, 1984
Currey J. D. The effect of porosity and mineral content on the Young’s modulus of elasticity of compact bone. J. Biomech. 21: 131–139, 1988
Currey J. D. What determines the bending strength of compact bone? J. Exp. Biol. 202: 2495–2503, 1999
de Vries J. I. P., G. H. A. Visser, H. F. R. Prechtl. The emergence of fetal behaviour. II. Quantitative aspects. Early Hum. Dev. 12: 99–120, 1985
Evans H. E., W. O. Sack. Prenatal development of domestic and laboratory mammals: Growth curves, external features and selected references. Zentralbl. Veterinarmed. [C] 2: 11–45, 1973
Fyhrie D. P., M. B. Schaffler. Failure mechanisms in human vertebral cancellous bone. Bone 15: 105–109, 1994
Guldberg R. E., S. J. Hollister, G. T. Charras. The accuracy of digital image-based finite element models. J. Biomech. Eng. 120: 289–295, 1998
Homminga J., B. van Rietbergen, E. M. Lochmüller, H. Weinans, F. Eckstein, R. Huiskes. The osteoporotic vertebral structure is well adapted to the loads of daily life, but not to infrequent “error” loads. Bone 34: 510–516, 2004
Jaasma M. J., H. H. Bayraktar, G. L. Niebur, T. M. Keaveny. Biomechanical effects of intraspecimen variation in tissue modulus for trabecular bone. J. Biomech. 35: 237–246, 2002
Kabel J., B. van Rietbergen, M. Dalstra, A. Odgaard, R. Huiskes. The role of an effective isotropic tissue modulus in the elastic properties of cancellous bone. J. Biomech. 32: 673–80, 1999
Keaveny T. M., X. E. Guo, E. F. Wachtel, T. A. McMahon, W. C. Hayes. Trabecular bone exhibits fully linear elastic behaviour and yields at low strains. J. Biomech. 27: 1127–1136, 1994
Mori S., R. Harruf, W. Ambrosius, D. B. Burr. Trabecular bone volume and microdamage accumulation in the femoral heads of women with and without femoral neck fractures. Bone 21: 521–526, 1997
Mulder L., J. H. Koolstra, T. M. G. J. van Eijden. Accuracy of microCT in the quantitative determination of the degree and distribution of mineralization in developing bone. Acta Radiol. 45: 769–777, 2004
Mulder L., J. H. Koolstra, W. A. Weijs, T. M. G. J. van Eijden. Architecture and mineralization of developing trabecular bone in the pig mandibular condyle. Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 285: 659–667, 2005
Mulder L., J. H. Koolstra, H. W. de Jonge, T. M. G. J. van Eijden. Architecture and mineralization of developing cortical and trabecular bone of the mandible. Anat. Embryol. 211: 71–78, 2006
Mulder, L., L. J. van Ruijven, J. H. Koolstra, T. M. G. J. van Eijden. Biomechanical consequences of developmental changes in trabecular architecture and mineralization of the pig mandibular condyle. J. Biomech. 40:1575–1582, 2007
Nuzzo S., C. Meneghini, P. Braillon, R. Bouvier, S. Mobilio, F. Peyrin. Microarchitectural and physical changes during fetal growth in human vertebral bone. J. Bone Miner. Res. 18: 760–768, 2003
Ouyang J., G. T. Yang, W. Z. Wu, Q. A. Zhu, S. Z. Zhong. Biomechanical characteristics of human trabecular bone. Clin. Biomech. 12: 522–524, 1997
Pidaparti R. M., C. H. Turner. Cancellous bone architecture: advantages of nonorhtogonal trabecular alignment under multidirectional joint loading. J. Biomech. 26: 111–119, 1997
Pistoia W., B. van Rietbergen, E. M. Lochmüller, C. A. Lill, F. Eckstein, P. Rüegsegger. Estimation of distal radius failure load with micro-finite element analysis models based on three-dimensional peripheral quantitative computed tomography images. Bone 30: 842–848, 2002
Rho J. Y., T. Y. Tsui, G. M. Pharr. Elastic properties of human cortical and trabecular lamellar bone measured by nanoindentation. Biomaterials 18: 1325–1330, 1997
Roy M. E., J. Y. Rho, T. Y. Tsui, N. D. Evans, G. M. Pharr. Mechanical and morphological variation of the human lumbar vertebral cortical and trabecular bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 44: 191–197, 1999
van der Linden J. C., D. H. Birkenhäger-Frenkel, J. A. N. Verhaar, H. Weinans. Trabecular bone’s mechanical properties are affected by its non-uniform mineral distribution. J. Biomech. 34: 1573–1580, 2001
van Eijden T. M. G. J., L. J. van Ruijven, E. B. W. Giesen. Bone tissue stiffness in the mandibular condyle is dependent on the direction and density of the cancellous structure. Calcif. Tissue Int. 75: 502–508, 2004
van Rietbergen B., H. Weinans, R. Huiskes, A. Odgaard. A new method to determine trabecular bone elastic properties and loading using micromechanical finite-element models. J. Biomech. 28: 69–81, 1995
van Rietbergen B., R. Müller, D. Ulrich, P. Rüegsegger, R. Huiskes. Tissue stresses and strain in trabeculae of a canine proximal femur can be quantified from computer reconstructions. J. Biomech. 32: 165–173, 1999
van Rietbergen B., R. Huiskes, F. Eckstein, P. Rüegsegger. Trabecular bone tissue strains in healthy and osteoporotic human femur. J. Bone Miner. Res. 18: 1781–1788, 2003
van Ruijven L. J., E. B. W. Giesen, M. Farella, T. M. G. J. van Eijden. Prediction of mechanical properties of the cancellous bone of the mandibular condyle. J. Dent. Res. 82: 819–823, 2003
van Ruijven L. J., L. Mulder, T. M. G. J. van Eijden. Variations in mineralization affect the stress and strain distributions in cortical and trabecular bone. J. Biomech. 40: 1211–1218, 2007
Verhulp E., B. van Rietbergen, R. Huiskes. Comparison of micro-level and continuum-level voxel models of the proximal femur. J. Biomech. 39:2951–2957, 2006
Zioupos P., J. D. Currey. The extent of microcracking and the morphology of microcracks in damaged bone. J. Mater. Sci. 29: 978–986, 1994
Acknowledgements
Appreciation goes out to Bert van Rietbergen from the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, for his assistance with the inhomogeneous finite element models. The authors would also like to thank Geerling Langenbach for critically reading the manuscript. This research was institutionally supported by the Inter-University Research School of Dentistry, through the Academic Centre for Dentistry Amsterdam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulder, L., van Ruijven, L., Koolstra, J. et al. The Influence of Mineralization on Intratrabecular Stress and Strain Distribution in Developing Trabecular Bone. Ann Biomed Eng 35, 1668–1677 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-007-9345-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-007-9345-3