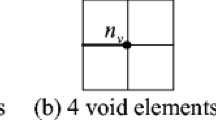
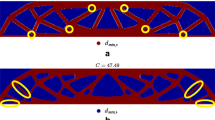
Abstract
Minimum length scale control on real and void material phases in topology optimization is an important topic of research with direct implications on numerical stability and solution manufacturability. And it also is a challenge area of research due to serious conflicts of both the solid and the void phase element densities in phase mixing domains of the topologies obtained by existing methods. Moreover, there is few work dealing with controlling distinct minimum feature length scales of real and void phase materials used in topology designs. A new method for solving the minimum length scale controlling problem of real and void material phases, is proposed. Firstly, we introduce two sets of coordinating design variable filters for these two material phases, and two distinct smooth Heaviside projection functions to destroy the serious conflicts in the existing methods (e.g. Guest Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(14):123–135, 2009). Then, by introducing an adaptive weighted 2-norm aggregation constraint function, we construct a coordinating topology optimization model to ensure distinct minimum length scale controls of real and void phase materials for the minimum compliance problem. By adopting a varied volume constraint limit scheme, this coordinating topology optimization model is transferred into a series of coordinating topology optimization sub-models so that the structural topology configuration can stably and smoothly changes during an optimization process. The structural topology optimization sub-models are solved by the method of moving asymptotes (MMA). Then, the proposed method is extended to the compliant mechanism design problem. Numerical examples are given to demonstrate that the proposed method is effective and can obtain a good 0/1 distribution final topology.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendsøe, M.P., Kikuchi, N.: Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 71(2), 197–224 (1988)
Bendsøe, M.P., Sigmund, O.: Topology optimization: theory, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Eschenauer, H.A., Olhoff, N.: Topology optimization of continuum structures: a review. Appl. Mech. Rev. 54(4), 331–390 (2001)
Sigmund, O., Maute, K.: Topology optimization approaches. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48(6), 1031–1055 (2013)
Deaton, J.D., Grandhi, R.V.: A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 49(1), 1–38 (2014)
Yoely, Y.M., Amir, O., Hanniel, I.: Topology and shape optimization with explicit geometric constraints using a spline-based representation and a fixed grid. Procedia Manuf. 21, 189–196 (2018)
Sun, J.L., Tian, Q., Hu, H.Y., et al.: Simultaneous topology and size optimization of a 3D variable-length structure described by the ALE–ANCF. Mech. Mach. Theory 129, 80–105 (2018)
Suzuki, K., Kikuchi, N.: A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 93(3), 291–318 (1991)
Bendsøe, M.P.: Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct. Optim. 1(4), 193–202 (1989)
Zhou, M., Rozvany, G.: The COC algorithm, Part II: topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 89(1–3), 309–336 (1991)
Allaire, G., Jouve, F., Toader, A.M.: A level-set method for shape optimization. C.R. Math. 334(12), 1125–1130 (2002)
Guo, X., Zhang, W., Zhong, W.: Explicit feature control in structural topology optimization via level set method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 272, 354–378 (2014)
Xie, Y.M., Steven, G.P.: A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput. Struct. 49(5), 885–896 (1993)
Rong, J., Xie, Y., Yang, X.: An improved method for evolutionary structural optimisation against buckling. Comput. Struct. 79(3), 253–263 (2001)
Xu, B., Zhao, L., Xie, Y.M., et al.: Topology optimization of continuum structures with uncertain-but-bounded parameters for maximum non-probabilistic reliability of frequency requirement. J. Vib. Control 23(16), 2557–2566 (2017)
Nabaki, K., Shen, J.H., Huang, X.D.: Evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures considering fatigue failure. Mater. Des. 166, 107586 (2019)
Guo, X., Zhang, W., Zhong, W.: Doing topology optimization explicitly and geometrically—a new moving morphable components based framework. J. Appl. Mech. 81(8), 081009 (2014)
Guo, X., Zhou, J., Zhang, W., et al.: Self-supporting structure design in additive manufacturing through explicit topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 323, 27–63 (2017)
Zhang, W., Chen, J., Zhu, X., et al.: Explicit three dimensional topology optimization via Moving Morphable Void (MMV) approach. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 322, 590–614 (2017)
Chang, K.H., Tang, P.S.: Integration of design and manufacturing for structural shape optimization. Adv. Eng. Softw. 32(7), 555–567 (2001)
Li, F., Liu, J., Wen, G., et al.: Extending SORA method for reliability-based design optimization using probability and convex set mixed models. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 59(4), 1163–1179 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Liu, S.: Design of conducting paths based on topology optimization. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 44(10), 1217–1227 (2008)
Zhu, J.H., Guo, W.J., Zhang, W.H., et al.: Integrated layout and topology optimization design of multi-frame and multi-component fuselage structure systems. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 56, 21–45 (2017)
Harzheim, L., Graf, G.: Topshape: an attempt to create design proposals including manufacturing constraints. Int. J. Vehicle Des. 28(4), 389–409 (2002)
Harzheim, L., Graf, G.: A review of optimization of cast parts using topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 31(5), 388–399 (2006)
Andreassen, E., Lazarov, B.S., Sigmund, O.: Design of manufacturable 3D extremal elastic microstructure. Mech. Mater. 69(1), 1–10 (2014)
Zhang, W.H., Zhou, L.: Topology optimization of self-supporting structures with polygon features for additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 334, 56–78 (2018)
Froes, F.H., Boyer, R., Dutta, B.: Additive manufacturing for aerospace applications-part I. Adv. Mater. Process. 175(5), 36–40 (2017)
Liu, J.K., Gaynor, A.T., Chen, S.K., et al.: Current and future trends in topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 57(6), 2457–2483 (2018)
Zhang, K.Q., Cheng, G.D., Xu, L.: Topology optimization considering overhang constraint in additive manufacturing. Comput. Struct. 212, 86–100 (2019)
Guest, J.K., Prévost, J.H., Belytschko, T.: Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 61(2), 238–254 (2004)
Guest, J.K.: Topology optimization with multiple phase projection. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(1–4), 123–135 (2009)
Almeida, S.R.M., Paulino, G.H., Silva, E.C.N.: A simple and effective inverse projection scheme for void distribution control in topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 39(4), 359–371 (2009)
Sigmund, O.: Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 33(4–5), 401–424 (2007)
Sigmund, O.: Manufacturing tolerant topology optimization. Acta. Mech. Sin. 25(2), 227–239 (2009)
Guest, J.K.: Imposing maximum length scale in topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 37(5), 463–473 (2009)
Guest, J.K., Asadpoure, A., Ha, S.H.: Eliminating beta-continuation from heaviside projection and density filter algorithms. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 44(4), 443–453 (2011)
Schevenels, M., Lazarov, B.S., Sigmund, O.: Robust topology optimization accounting for spatially varying manufacturing errors. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200(49–52), 3613–3627 (2011)
Svanberg, K., Svärd, H.: Density filters for topology optimization based on the Pythagorean means. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48(5), 859–875 (2013)
Lazarov, B.S., Wang, F., Sigmund, O.: Length scale and manufacturability in density-based topology optimization. Arch. Appl. Mech. 86(1–2), 189–218 (2016)
Liu, J., Ma, Y.: A survey of manufacturing oriented topology optimization methods. Adv. Eng. Softw. 100, 161–175 (2016)
Van, D.V.E., Maas, R., Ayas, C., et al.: Continuous front propagation-based overhang control for topology optimization with additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 57(5), 2075–2091 (2018)
Vatanabe, S.L., Lippi, T.N., De, L.C.R., et al.: Topology optimization with manufacturing constraints: a unified projection-based approach. Adv. Eng. Softw. 100, 97–112 (2016)
Wang, F., Lazarov, B.S., Sigmund, O.: On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 43(6), 767–784 (2011)
Zhou, M., Lazarov, B.S., Wang, F., et al.: Minimum length scale in topology optimization by geometric constraints. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 293, 266–282 (2015)
Carstensen, J.V., Guest, J.K.: Projection-based two-phase minimum and maximum length scale control in topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 58(5), 1845–1860 (2018)
Bruns, T.E., Tortorelli, D.A.: Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190(26–27), 3443–3459 (2001)
Petersson, J., Sigmund, O.: Slope constrained topology optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 41(8), 1417–1434 (1998)
Sigmund, O., Petersson, J.: Numerical instabilities in topology optimization: a survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima. Struct. Optim. 16(1), 68–75 (1998)
Xu, S., Cai, Y., Cheng, G.: Volume preserving nonlinear density filter based on heaviside functions. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 41(4), 495–505 (2010)
Rong, J.H., Xiao, T.T., Yu, L.H., et al.: Continuum structural topological optimizations with stress constraints based on an active constraint technique. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 108(4), 326–360 (2016)
Chu, S., Gao, L., Xiao, M.: Stress-based multi-material topology optimization of compliant mechanisms. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 113(7), 1021–1044 (2018)
Pereira, A.A., Cardoso, E.L.: On the influence of local and global stress constraint and filtering radius on the design of hinge-free compliant mechanisms. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 58(2), 641–655 (2018)
Silva, G.A.D., Beck, A.T., Sigmund, O.: Stress-constrained topology optimization considering uniform manufacturing uncertainties. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 344, 512–537 (2019)
Svanberg, K.: A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J. Optim. 12(2), 555–573 (2002)
Rong, J.H., Tang, Z.L., Xie, Y.M., et al.: Topological optimization design of structures under random excitations using SQP method. Eng. Struct. 56, 2098–2106 (2013)
Buhl, T., Pedersen, C.B., Sigmund, O.: Stiffness design of geometrically nonlinear structures using topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 19(2), 93–104 (2000)
Li, L., Khandelwal, K.: Volume preserving projection filters and continuation methods in topology optimization. Eng. Struct. 85, 144–161 (2015)
Rojas-Labanda, S., Stolpe, M.: Automatic penalty continuation in structural topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 52(6), 1205–1221 (2015)
Watada, R., Ohsaki, M.: Continuation approach for investigation of non-uniqueness of optimal topology for minimum compliance. In: Proceedings of 8th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, (2009)
Watada, R., Ohsaki, M., Kanno, Y.: Non-uniqueness and symmetry of optimal topology of a shell for minimum compliance. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 43(4), 459–471 (2011)
Stolpe, M., Svanberg, K.: On the trajectories of penalization methods for topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 21(2), 128–139 (2001)
Rong, J., Yi, J.: A structural topological optimization method for multi-displacement constraints and any initial topology configuration. Acta. Mech. Sin. 26(5), 735–744 (2010)
Rong, J.H., Yu, L., Rong, X.P., et al.: A novel displacement constrained optimization approach for black and white structural topology designs under multiple load cases. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 56(4), 865–884 (2017)
Rong, J.H., Liu, X.H., Yi, J.J., et al.: An efficient structural topological optimization method for continuum structures with multiple displacement constraints. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 47(8), 913–921 (2011)
Luo, Z., Chen, L., Yang, J., et al.: Compliant mechanism design using multi-objective topology optimization scheme of continuum structures. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 30(2), 142–154 (2005)
Wang, L.P., Jiang, Y., Li, T.M.: Analytical compliance modeling of serial flexure-based compliant mechanism under arbitrary applied load. Int. J. Mech. Eng. 30(4), 951–962 (2017)
Liu, K., Tovar, A.: An efficient 3D topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 50(6), 1175–1196 (2014)
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11772070 and 11372055) and the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2019JJ40296). Very thanks reviewers for their comments on the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, X., Rong, J., Zhao, S. et al. New method for controlling minimum length scales of real and void phase materials in topology optimization. Acta Mech. Sin. 36, 805–826 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-020-00932-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-020-00932-9