Abstract
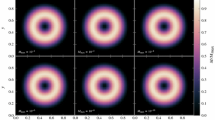
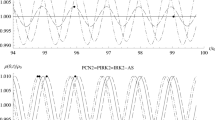
Many all-speed Roe schemes have been proposed to improve performance in terms of low speeds. Among them, the F-Roe and T-D-Roe schemes have been found to get incorrect density fluctuation in low Mach flows, which is expected to be with the square of Mach number. Asymptotic analysis presents the mechanism of how the density fluctuation problem relates to the incorrect order of terms in the energy equation \({{\tilde{\rho }} {\tilde{a}} {\tilde{U}}\varDelta U}\). It is known that changing the upwind scheme coefficients of the pressure-difference dissipation term \(D^P\) and the velocity-difference dissipation term in the momentum equation \(D^{\rho U}\) to the order of \(O(c^{-1})\) and \(O(c^{0})\) can improve the level of pressure and velocity accuracy at low speeds. This paper shows that corresponding changes in energy equation can also improve the density accuracy in low speeds. We apply this modification to a recently proposed scheme, TV-MAS, to get a new scheme, TV-MAS2. Unsteady Gresho vortex flow, double shear-layer flow, low Mach number flows over the inviscid cylinder, and NACA0012 airfoil show that energy equation modification in these schemes can obtain the expected square Ma scaling of density fluctuations, which is in good agreement with corresponding asymptotic analysis. Therefore, this density correction is expected to be widely implemented into all-speed compressible flow solvers.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng, X., Zhou, S., Hou, A., et al.: Separation control using synthetic vortex generator jets in axial compressor cascade. Acta Mech. Sin. 22, 521–527 (2006)
Xu, G., Jiang, X., Liu, G.: Delayed detached eddy simulations of fighter aircraft at high angle of attack. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 588–603 (2016)
Zheng, W., Yan, C., Liu, H., et al.: Comparative assessment of SAS and DES turbulence modeling for massively separated flows. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 12–21 (2016)
Fang, J., Lu, L.-P., Shao, L.: Heat transport mechanisms of low Mach number turbulent channel flow with spanwise wall oscillation. Acta Mech. Sin. 26, 391–399 (2010)
Turkel, E.: Preconditioning techniques in computational fluid dynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 31, 385–416 (1999)
Weiss, J., Smith, W.: Preconditioning applied to variable and constant density flows. AIAA J. 33, 2050–2057 (1995)
Guillard, H., Viozat, C.: On the behaviour of upwind schemes in the low Mach number limit. Comput. Fluids 28, 63–86 (1999)
Roe, P.L., Pike, J.: Efficient construction and utilisation of approximate Riemann solutions. In: Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, VI, North Holland, 499–518 (1984)
Boniface, J.-C.: Rescaling of the Roe scheme in low Mach-number flow regions. J. Comput. Phys. 328, 177–199 (2017)
Li, X.-S., Gu, C.-W.: Mechanism of Roe-type schemes for all-speed flows and its application. Comput. Fluids 86, 56–70 (2013)
Li, X., Gu, C.: An all-speed Roe-type scheme and its asymptotic analysis of low Mach number behaviour. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 5144–5159 (2008)
Li, X.-S., Gu, C.-W., Xu, J.-Z.: Development of Roe-type scheme for all-speed flows based on preconditioning method. Comput. Fluids 38, 810–817 (2009)
Thornber, B.J.R., Drikakis, D.: Numerical dissipation of upwind schemes in low Mach flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 56, 1535–1541 (2008)
Rieper, F.: A low-Mach number fix for Roe’s approximate Riemann solver. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 5263–5287 (2011)
Fillion, P., Chanoine, A., Dellacherie, S., et al.: FLICA-OVAP: a new platform for core thermalhydraulic studies. Nucl. Eng. Des. 241, 4348–4358 (2011)
Li, X.-S.: Uniform algorithm for all-speed shock-capturing schemes. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 28, 329–338 (2014)
Qu, F., Yan, C., Sun, D., et al.: A new Roe-type scheme for all speeds. Comput. Fluids 121, 11–25 (2015)
Sun, D., Yan, C., Qu, F., et al.: A robust flux splitting method with low dissipation for all-speed flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 84, 3–18 (2016)
Liou, M.-S., Steffen, C.J.: A new flux splitting scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 107, 23–39 (1993)
Liou, M.S.: A sequel to \(\{\text{ AUSM: } \text{ AUSM }\}^+\). J. Computat. Phys. 129, 364–382 (1996)
Liou, M.: A sequel to AUSM, part II: AUSM+-up for all speeds. J. Comput. Phys. 214, 137–170 (2006)
Shima, E., Kitamura, K.: Parameter-free simple low-dissipation AUSM-family scheme for all speeds. AIAA J. 49, 1693–1709 (2011)
Kitamura, K., Shima, E., Fujimoto, K., et al.: Performance of low-dissipation euler fluxes and preconditioned LU-SGS at low speeds. Commun. Comput. Phys. 10, 90–119 (2011)
Shima, E., Kitamura, K.: New approaches for computation of low Mach number flows. Comput. Fluids 85, 143–152 (2013)
Yao, S.B., Sun, Z.X., Guo, D.L., et al.: Numerical study on wake characteristics of high-speed trains. Acta Mech. Sin. 29, 811–822 (2013)
Guo, D., Shang, K., Zhang, Y., et al.: Influences of affiliated components and train length on the train wind. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 191–205 (2016)
Xiao, Z., Fu, S.: Studies of the unsteady supersonic base flows around three afterbodies. Acta Mech. Sin. 25, 471–479 (2009)
Qu, F., Yan, C., Sun, D.: Investigation into the influences of the low speed’s accuracy on the hypersonic heating computations. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 70, 53–58 (2016)
Qu, F., Sun, D., Shi, Y., et al.: Investigation into the influences of the low speeds’ accuracy on RANS simulations. In: 21st AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonics Technologies Conference, Xiamen, China, 1–14 (2017)
Zha, G., Bilgen, E.: Numerical solutions of Euler equations by using a new flux vector splitting scheme. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 17, 115–144 (1993)
Toro, E.F., Vazquez-Cendon, M.E.: Flux splitting schemes for the Euler equations. Comput. Fluids 70, 1–12 (2012)
Qu, F., Yan, C., Yu, J., et al.: A new flux splitting scheme for the Euler equations. Comput. Fluids 102, 203–214 (2014)
Kapen, P.T., Tchuen, G.: An extension of the TV-HLL scheme for multi-dimensional compressible flows. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 29, 303–312 (2015)
Xie, W., Li, H., Tian, Z., et al.: A low diffusion flux splitting method for inviscid compressible flows. Comput. Fluids 112, 83–93 (2015)
Toro, E.F.: Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Sun, M., Takayama, K.: An artificially upstream flux vector splitting scheme for the Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 189, 305–329 (2003)
Tong, B.G., Kong, X.Y., Deng, G.H.: Gas Dynamics, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing (2012). (in Chinese)
Gresho, P.M.: On the theory of semi-implicit projection methods for viscous incompressible flow and its implementation via a finite element method that also introduces a nearly consistent mass matrix. Part 1: theory. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 11, 620–687 (1990)
Gresho, P.M., Chan, S.T.: On the theory of semi-implicit projection methods for viscous incompressible flow and its implementation via a finite element method that also introduces a nearly consistent mass matrix. Part 2: implementation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 11, 621–659 (1990)
Gottlieb, S.: On high order strong stability preserving Runge–Kutta and multi step time discretizations. J. Sci. Comput. 25, 105–128 (2005)
Ishiko, K., Ohnishi, N., Sawada, K.: Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Turbulence Using Shock Capturing Monotone Scheme. In: 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, Nevada, 1–12 (2006)
Kitamura, K., Hashimoto, A.: Reduced dissipation AUSM-family fluxes: HR-SLAU2 and HR-AUSM+-up for high resolution unsteady flow simulations. Comput. Fluids 126, 41–57 (2016)
Yoon, S., Jamesont, A.: Lower-upper symmetric-Gauss-Seidel method for the Euler and Navier-Stokes equations. AIAA J. 26, 1025–1026 (1988)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support for this work provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 11402016), and all the authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, BX., Yan, C. & Chen, SS. Density enhancement mechanism of upwind schemes for low Mach number flows. Acta Mech. Sin. 34, 431–445 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-017-0737-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-017-0737-9