Abstract
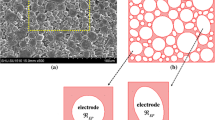
A new model of porous electrodes based on the Gibbs free energy is developed, in which lithium-ion (Li-ion) diffusion, diffusion-induced stress (DIS), Butler–Volmer (BV) reaction kinetics, and size polydispersity of electrode particles are considered. The influence of BV reaction kinetics and concentration-dependent exchange current density (ECD) on concentration profile and DIS evolution are numerically investigated. BV reaction kinetics leads to a decrease in Li-ion concentration and DIS. In addition, concentration-dependent ECD results in a decrease in Li-ion concentration and an increase in DIS. Size polydispersity of electrode particles significantly affects the concentration profile and DIS. Optimal macroscopic state of charge (SOC) should consider the influence of the microscopic SOC values and mass fractions of differently sized particles.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dunn, B., Kamath, H., Tarascon, J.M.: Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices. Science 334, 928–935 (2011)
Palacin, M.R., de Guibert, A.: Why do batteries fail? Science 351, 1253292 (2016)
Shpigel, N., Levi, M.D., Sigalov, S., et al.: In situ hydrodynamic spectroscopy for structure characterization of porous energy storage electrodes. Nat. Mater. 15, 570–575 (2016)
Liu, H., Strobridge, F.C., Borkiewiez, O.J., et al.: Capturing metastable structures during high-rate cycling of LiFePO\(_4\) nanoparticle electrodes. Science 344, 1252817 (2014)
Banerjee, J., Dutta, K.: Materials for electrodes of Li-ion batteries: issues related to stress development. Crit. Rev. Solid State 42, 218–238 (2017)
Prussin, S.: Generation and distribution of dislocations by solute diffusion. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 1876–1881 (1961)
Malavé, V., Berger, J.R., Zhu, H., et al.: A computational model of the mechanical behavior within reconstructed Li\(_{x}\)CoO\(_{2}\) Li-ion battery cathode particles. Electrochim. Acta 130, 707–717 (2014)
Verbrugge, M.W., Cheng, Y.T.: Stress and strain-energy distributions within diffusion-controlled insertion-electrode particles subjected to periodic potential excitations. J. Electrochem. Soc. 156, A927–A937 (2009)
Li, Y., Zhang, K., Zheng, B.: Interaction between diffusion and stresses in composition-gradient electrodes. Solid State Ion. 283, 103–108 (2015)
Di Leo, C.V., Rejovitzky, E., Anand, L.: A Cahn–Hilliard-type phase-field theory for species diffusion coupled with large elastic deformations: application to phase-separating Li-ion electrode materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 70, 1–29 (2014)
Stein, P., Xu, B.: 3D Isogeometric analysis of intercalation-induced stresses in Li-ion battery electrode particles. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. 268, 225–244 (2014)
Zuo, P., Zhao, Y.P.: A phase field model coupling lithium diffusion and stress evolution with crack propagation and application in lithium ion batteries. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 287–297 (2015)
Zuo, P., Zhao, Y.P.: Phase field modeling of lithium diffusion, finite deformation, stress evolution and crack propagation in lithium ion battery. Extreme Mech. Lett. 9, 467–479 (2016)
Woodford, W.H., Chiang, Y.M., Carter, W.C.: “Electrochemical shock” of intercalation electrodes: a fracture mechanics analysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, A1052–A1059 (2010)
Woodford, W.H., Carter, W.C., Chiang, Y.M.: Strategies to avert electrochemical shock and their demonstration in spinels. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, F3005–F3009 (2014)
Vanimisetti, S.K., Ramakrishnan, N.: Effect of the electrode particle shape in Li-ion battery on the mechanical degradation during charge–discharge cycling. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 226, 2192–2213 (2011)
Zhang, T., Guo, Z.: Effects of electrode properties and fabricated pressure on Li ion diffusion and diffusion-induced stresses in cylindrical Li-ion batteries. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. 22, 025016 (2014)
Deshpande, R., Cheng, Y.T., Verbrugge, M.W., et al.: Diffusion induced stresses and strain energy in a phase-transforming spherical electrode particle. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158, A718–A724 (2011)
Lim, C., Yan, B., Yin, L.: Simulation of diffusion-induced stress using reconstructed electrodes particle structures generated by micro/nano-CT. Electrochim. Acta 75, 279–287 (2012)
Heubner, C., Schneider, M., Michaelis, A.: Investigation of charge transfer kinetics of Li-Intercalation in LiFePO\(_{4}\). J. Power Sources 288, 115–120 (2015)
Guo, Y., Smith, R.B., Yu, Z., et al.: Li intercalation into graphite: direct optical imaging and Cahn–Hilliard reaction dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 2151–2156 (2016)
Kuzmin, R.N., Maximov, D.S., Savenkova, N.P., et al.: Mathematical modeling of hysteresis in porous electrodes. J. Math. Chem. 50, 2471–2477 (2012)
Golmon, S., Maute, K., Lee, S.H., et al.: Stress generation in silicon particles during lithium insertion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 033111 (2010)
Jagannathan, M., Chandran, K.S.R.: Analytical modeling and simulation of electrochemical charge/discharge behavior of Si thin film negative electrodes in Li-ion cells. J. Power Sources 247, 667–675 (2014)
Swamy, T., Chiang, Y.M.: Electrochemical charge transfer reaction kinetics at the silicon–liquid electrolyte interface. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, A7129–A7134 (2015)
Richardson, G., Denuault, G., Please, C.P.: Multiscale modelling and analysis of lithium-ion battery charge and discharge. J. Eng. Math. 72, 41–72 (2011)
Liu, S., Jiang, J., Shi, W., et al.: Butler–Volmer-equation-based electrical model for high-power lithium titanate batteries used in electric vehicles. IEEE. Trans. Ind. Electron. 62, 7557–7568 (2015)
Hess, A., Roode-Gutzmer, Q., Heubner, C., et al.: Determination of state of charge-dependent asymmetric Butler–Volmer kinetics for LixCoO\(_{2}\) electrode using GITT measurements. J. Power Sources 299, 156–161 (2015)
Gwak, Y., Moon, J., Cho, M.: Multi-scale analysis of an electrochemical model including coupled diffusion, stress, and nonideal solution in a silicon thin film anode. J. Power Sources 307, 856–865 (2016)
Zhang, Q., Guo, Q., White, R.E.: A new kinetic equation for intercalation electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 153, A301–A309 (2006)
Latz, A., Zausch, J.: Thermodynamic derivation of a Butler-Volmer model for intercalation in Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 110, 358–362 (2013)
Ferguson, T.R., Bazant, M.Z.: Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of porous electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, A1967–A1985 (2012)
Lee, J.K., Yoon, W.Y., Kim, B.K.: Kinetics of reaction products of silicon monoxide with controlled amount of Li-ion insertion at various current densities for Li-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, A927–A933 (2014)
Bazant, M.Z.: Theory of chemical kinetics and charge transfer based on nonequilibrium thermodynamics. Accounts Chem. Res. 46, 1144–1160 (2013)
Levi, M.D., Aurbach, D.: Kinetics of electrochemically induced phase transitions in ion-insertion electrodes and the chemical diffusion coefficient. J. Solid State Electr. 12, 409–420 (2007)
Bates, A., Mukherjee, S., Schuppert, N., et al.: Modeling and simulation of 2D lithium-ion solid state battery. Int. J. Energy Res. 39, 1505–1518 (2015)
Okajima, Y., Shibuta, Y., Suzuki, T.: A phase-field model for electrode reactions with Butler–Volmer kinetics. Comput. Mater. Sci. 50, 118–124 (2010)
Zhao, Y., Xu, B.X., Stein, P., et al.: Phase-field study of electrochemical reactions at exterior and interior interfaces in Li-ion battery electrode particles. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 312, 428–446 (2016)
Xu, B.X., Zhao, Y., Stein, P.: Phase field modeling of electrochemically induced fracture in Li-ion battery with large deformation and phase segregation. GAMM-Mitt. 39, 92–109 (2016)
Newman, J., Tobias, C.: Theoretical analysis of current distribution in porous electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 109, 1183–1191 (1962)
Newman, J., Tiedemann, W.: Porous-electrode theory with battery applications. AIChE. J. 21, 25–41 (1975)
Christensen, J.: Modeling diffusion-induced stress in Li-ion cells with porous electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, A366–A380 (2010)
Lai, W., Ciucci, F.: Mathematical modeling of porous battery electrodes—Revisit of Newman’s model. Electrochim. Acta 56, 4369–4377 (2011)
Landstorfer, M., Jacob, T.: Mathematical modeling of intercalation batteries at the cell level and beyond. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 3234–3252 (2013)
Zheng, J.P., Crain, D.J., Roy, D.: Kinetic aspects of Li intercalation in mechano-chemically processed cathode materials for lithium ion batteries: electrochemical characterization of ball-milled LiMn\(_{2}\)O\(_{4}\). Solid State Ion. 196, 48–58 (2011)
Chung, D.W., Shearing, P.R., Brandon, N.P., et al.: Particle size polydispersity in Li-ion bateries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, A422–A430 (2014)
Wu, W., Xiao, X., Wang, M., et al.: A microstructural resolved model for the stress analysis of lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, A803–A813 (2014)
Jokar, A., Rajabloo, B., Désilets, M., et al.: Review of simplified pseudo-two-dimensional models of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 327, 44–55 (2016)
Aberg, S.: A simple model for the measurement of charge transfer resistances of reactions with slow kinetics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 439, 63–71 (1997)
Zhang, X., Shyy, W., Sastry, A.M.: Numerical simulation of intercalation-induced stress in Li-ion battery electrode particles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, A910–A916 (2007)
Zhang, X., Sastry, A.M., Shyy, W.: Intercalation-induced stress and heat generation within single lithium-ion battery cathode particles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 155, A542–A552 (2008)
Guo, Z., Zhu, J., Feng, J., et al.: Direct in situ observation and explanation of lithium dendrite of commercial graphite electrodes. RSC Adv. 5, 69514–69521 (2015)
Yang, L., Yan, Y., Ran, Z., et al.: A new method for generating random fibre distributions for fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 76, 14–20 (2013)
Takahashi, K., Srinivasan, V.: Examination of graphite particle cracking as a failure mode in lithium-ion batteries: a model-experimental study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, A635–A645 (2015)
Takahashi, K., Higa, K., Mair, S., et al.: Mechanical degradation of graphite/PVDF composite electrodes: a model-experimental study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, A385–A395 (2016)
Orvananos, B., Malik, R., Yu, H.C., et al.: Architecture dependence on the dynamics of nano-LiFePO\(_4\) electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 137, 245–257 (2014)
Elul, S., Cohen, Y., Aurbach, D.: The influence of geometry in 2D simulation on the charge/discharge processes in Li-ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 682, 53–65 (2012)
Jung, S., Jung, H.Y.: Charge/discharge characteristics of Li-ion batteries with two-phase active materials: a comparative study of LiFePO\(_{4}\) and LiCoO\(_{2}\) cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 40, 1541–1555 (2016)
Lim, C., Yan, B., Kang, H., et al.: Analysis of geometric and electrochemical characteristics of lithium cobalt oxide electrode with different packing densities. J. Power Sources 328, 46–55 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 11472165, 11332005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, L., Guo, Z. Analytical modeling and simulation of porous electrodes: Li-ion distribution and diffusion-induced stress. Acta Mech. Sin. 34, 187–198 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-017-0704-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-017-0704-5