Abstract
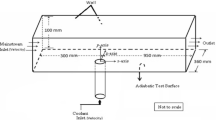
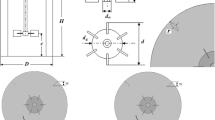
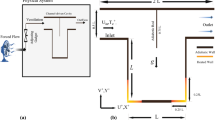
The purpose of this study is to investigate means of controlling the interior ballistic stability of a bulk-loaded propellant gun (BLPG). Experiments on the interaction of twin combustion gas jets and liquid medium in a cylindrical stepped-wall combustion chamber are conducted in detail to obtain time series processes of jet expansion, and a numerical simulation under the same working conditions is also conducted to verify the reliability of the numerical method by comparing numerical results and experimental results. From this, numerical simulations on mutual interference and expansion characteristics of multiple combustion gas jets (four, six, and eight jets) in liquid medium are carried out, and the distribution characteristic of pressure, velocity, temperature, and evolutionary processes of Taylor cavities and streamlines of jet flow field are obtained in detail. The results of numerical simulations show that when different numbers of combustion gas jets expand in liquid medium, there are two different types of vortices in the jet flow field, including corner vortices of liquid phase near the step and backflow vortices of gas phase within Taylor cavities. Because of these two types of vortices, the radial expansion characteristic of the jets is increased, while changing numbers of combustion gas jets can restrain Kelvin–Helmholtz instability to a certain degree in jet expansion processes, which can at last realize the goal of controlling the interior ballistic stability of a BLPG. The optimum method for both suppressing Kelvin–Helmholtz instability and promoting radial expansion of Taylor cavities can be determined by analyzing the change of characteristic parameters in a jet flow field.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M., Barth, E.J.: A compressible fluid power dynamic model of a liquid propellant powered rifle. In: Proceedings of IMECE: international mechanical engineering congress and exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA (2004)
Adams, M., Barth, E.J.: Dynamic modeling and design of a bulk-loaded liquid monopropellant powered rifle. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 130, 1–8 (2008)
Macpherson A. K., Bracuti A. J.: Analysis of gun pres sure instability. In: The 19th international symposium on ballistics. Switzerland, 115–121 (2001)
Knapton, J.D., Stobie, I.C., Cook, D.C.: Multi-point ignition studies in bulk-loaded propellant charges. In: 14th international symposium on ballistics, vol. 1, 193–201 (1993)
Talley, R.L., Owezarezak, J.A.: Interior and exterior testing of bulk-loaded propellant in a 40-mm gun. Veritay report D 48–95-001 (1995)
Rosenberger, T.E., Stobie, I.C., Knapton, J.D.: Test results form a 37-mm segmented-chamber bulk-loaded liquid propellant gun. ARL-TR-871 (1995)
Talley, R.L., Owezarezak, J.A.: Investigation of bulk-loaded liquid propellant gun concepts. AD-A276904 (1997)
DeSpirito, J.: Interior ballistic simulations of the bulk-loaded liquid propellant gun. ARL-TR-2316 (2001)
Morshed, A., Jamal, N., Geoffrey, B., et al.: A computational fluid dynamics model of shrouded supersonic jet impingement on a water surface. ISIJ Int. 52, 1026–1035 (2012)
Nguyen, A., Geoffrey, E.: Computational fluid dynamics modeling of gas jets impinging onto liquid pools. Appl. Math. Model. 30, 1472–1484 (2006)
Ho, Y.H., Gordon, A.I.: A water model study of impinging gas jets on liquid surfaces. Metall. Mater. Trans. 43, 302–315 (2012)
Guo, Q., Shi, H.H., Wang, C.: Study on gas–liquid complex flow induced by submerged supersonic gas jets. J. Eng. Thermophys. 33, 809–812 (2012)
Dai, Z.Q., Wang, B.Y., Qi, L.X.: Experimental study on hydrodynamic behaviors of high-speed gas jets in still water. Acta Mech. Sin. 22, 443–448 (2006)
Xu, X.Q., Deng, J., Ren, A.L.: The research on high-speed gas jet of rocket nozzle underwater. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 17, 204–208 (2005)
Mohammad, A.E., Hassan, B.T., Goodarz, A., et al.: Investigation of fine droplet generation from hot engine oil by impinging gas jets onto liquid surface. J. Aerosol Sci. 65, 49–57 (2013)
Yu, Y.G., Chang, X.X., Zhao, N.: Study of bulk-loaded liquid propellant combustion propulsion processes with stepped-wall combustion chamber. J. Appl. Mech. 78, 051001-1–051001-8 (2011)
Qi, L.T., Yu, Y.G., Peng, Z.G.: A 2-D model of energetic gas jet expansion process in liquid and numerical simulation. Chin. J. Energ. Mater. 16, 131–137 (2008)
Xue, X.C., Yu, Y.G., Zhang, Q.: Study on the effect of distance between the two nozzle holes on interaction of high pressure combustion-gas jets with liquid. Energy Convers. Manag. 85, 675–686 (2014)
Yu, Y.G., Yan, S.H., Zhao, N.: Study on expansion process and interaction of high speed twin combustion-gas jets in liquid. J. Appl. Mech. 77, 051404-1–051404-7 (2010)
Fluent Incorporated: FLUENT User’s guide version 6.3 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 11372139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, X., Yu, Y. & Zhang, Q. Study on the influences of interaction behaviors between multiple combustion-gas jets on expansion characteristics of Taylor cavities. Acta Mech. Sin. 31, 720–731 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-015-0421-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-015-0421-x