Abstract
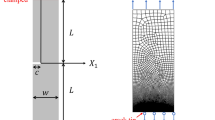
Recent interest in designing soft gels with high fracture toughness has called for simple and robust methods to test fracture behavior. The conventional method of applying tension to a gel sample suffers from a difficulty of sample gripping. In this paper, we study a possible fracture mechanism of soft gels under uni-axial compression. We show that the surfaces of a pre-existing crack, oriented parallel to the loading axis, can buckle at a critical compressive stress. This buckling instability can open the crack surfaces and create highly concentrated stress fields near the crack tip, which can lead to crack growth. We show that the onset of crack buckling can be deduced by a dimensional argument combined with an analysis to determine the critical compression needed to induce surface instabilities of an elastic half space. The critical compression for buckling was verified for a neo-Hookean material model using finite element simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drury, J. L., Mooney, D. J.: Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials 24, 4337–4351 (2003)
Qiu, Y., Park, K.: Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 53, 321–339 (2001)
Chaterji, S., Kwon, I. K., Park, K.: Smart polymeric gels: redefining the limits of biomedical devices. Prog. Polym. Sci. 32, 1083–1122 (2007)
Calvert, P.: Hydrogels for soft machines. Adv. Mater. 21, 743–756 (2009)
Chen, Y. M., Gong, J. P., Osada, Y.: Gel: a potential material as artifical soft tissue. Macromol. Eng. 4, 2689–2717 (2007)
Peretti, G., M., Xu, J., Bonassar, L. J., et al.: Review of injectable cartilage engineering using fibrin gel in mice and swine models. Tissue Eng. 12, 1151–1168 (2006)
Beebe, D. J., Moore, J. S., Bauer, J. M., et al.: Functional hydrogel structures for autonomous flow control inside microfluidic channels. Nature 404, 588–590 (2000)
Dong, L., Jiang, H.: Autonomous microfluidics with stimuliresponsive hydrogels. Soft Matter 3, 1223–1230 (2007)
Li, Y., Tanaka, T.: Phase-transitions of gels. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 22, 243–277 (1992)
Osada, Y., Gong, J. P.: Soft and wet materials: Polymer gels. Adv. Mater. 10, 827–837 (1998)
Gong, J. P., Katsuyama, Y., Kurokawa, T., et al.: Doublenetwork hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Adv. Mater. 15, 1155–1158 (2003)
Kong, H., Wong, E., Mooney, D.: Independent control of rigidity and toughness of polymeric hydrogels. Macromolecules 36, 4582–2588 (2003)
Kushner, A. M., Vossler, J. D., Williams, G. A., et al.: A biomimetic modular polymer with tough and adaptive properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 8766–8768 (2009)
Henderson, K. J., Zhou, T. C., Otim, K. J., et al.: Ionically cross-linked triblock copolymer hydrogels with high strength. Macromolecules 43, 6193–6201 (2010)
Krishnan, V. R., Hui, C. Y., Long, R.: Finite strain crack tip fields in soft incompressible elastic solids. Langmuir 24, 14245–14253 (2008)
Long R., Krishnan, V. R., Hui, C. Y.: Finite strain analysis of crack tip fields in incompressible hyperelastic solids loaded in plane stress. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 59, 672–695 (2011)
Baumberger, T., Caroli, C., Martina, D., Solvent control of crack dynamics in a reversible hydrogel. Nat. Mater. 5, 552–555 (2006)
Seitz, M. E., Martina, D., Baumberger, T., et al.: Fracture and large strain behavior of self-assembled triblock copolymer gels. Soft Matter 5, 447–456 (2009)
Livne, A., Bouchbinder, E., Svetlizky, I., et al.: The near-tip fields of fast cracks, Science. 327, 1359–1363 (2010)
Cai, S., Hu, Y., Zhao, X., et al.: Poroelasticity of a covalently crosslinked alginate hydrogel under compression. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 113514 (2010)
Wu, C. H.: Plane-strain buckling of cracks in incompressible elastic solids. J. Elasticity 10, 163–177 (1980)
Biot, M. A.: Surface instability of rubber in compression. Appl. Sci. Res. A 12, 168–182 (1963)
Usmani, S. A., Beatty, M. F.: On the surface instability of a highly elastic half-space. J. Elasticity 4, 249–263 (1974)
Best, B., Meijers, P., Savkoor, A. R.: The formation of Schallamach waves. Wear 65, 385–396 (1981)
Nowinski, J. L.: Surface instability of a half-space under twodimensional compression. J. Franklin Inst. 288, 367–376 (1969)
Coleman, B. D., Noll, W.: On the thermostatics of continuous media. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 4, 97–128 (1959)
Stephenson, R. A.: The equilibrium field near the tip of crack for finite plane strain of incompressible elastic materials. J. Elasticity 12, 65–99, (1982)
Krishnan, V. R., Hui, C. Y.: Finite strain stress fields near the tip of an interface crack between a soft incompressible elastic material and a rigid substrate. Eur. Phys. J. E 29, 61–72, (2009)
Eshelby, J. D.: The energy momentum tensor in continuum mechanics. Kanninen, M. F. et al., eds. Inelastic Behavior of Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York (1970)
Cottrell, B., Rice, J. R.: Slightly curved or kinked cracks. Int. J. Frac. 16, 155–169 (1980)
Hong, W., Zhao, X., Suo, Z.: Formation of creases on the surfaces of elastomers and gels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 111901 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, R., Hui, CY. Crack buckling in soft gels under compression. Acta Mech Sin 28, 1098–1105 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0130-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0130-7