Abstract
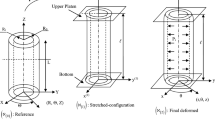
Under isothermal quasi-static stretching the phase transition of a superelastic NiTi tube involves the formation (during loading) and vanishing (in unloading) of a high strain (martensite) domain. The two events are accompanied by a rapid stress drop/rise due to the formation/vanishing of domain fronts. From a thermodynamic point of view, both are instability phenomena that occur once the system reaches its critical state. This paper investigates the stability of a shrinking cylindrical domain in a tube configuration during unloading. The energetics and thermodynamic driving force of the cylindrical domain are quantified by using an elastic inclusion model. It is demonstrated that the two domain fronts exhibit strong interaction when they come close to each other, which brings a peak in the total energy and a sign change in the thermodynamic driving force. It is proved that such domain front interaction plays an important role in controlling the stability of the domain and in the occurrence of stress jumps during domain vanishing. It is also shown that the process is governed by two nondimensional length scales (the normalized tube length and normalized wall-thickness) and that the length scale dependence of the critical domain length and stress jump for the domain vanishing can be quantified by the elastic inclusion model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otsuka, K., Wayman, C.M.: Shape Memory Materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Yoneyama, T., Miyazaki, S.: Shape Memory Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge (2009)
Siddons, D.J., Moon, J.R.: Tensile and compression performance of superelastic NiTi tubing. Mater. Sci. Tech. 17, 1073–1078 (2001)
Li, Z. Q., Sun, Q. P.: The initiation and growth of macroscopic martensite band in nano-grained NiTi microtube under tension. Int. J. Plast. 18, 1481–1498 (2002)
Sun, Q. P., Li, Z. Q.: Phase transformation in superelastic NiTi polycrystalline micro-tubes under tension and torsion-from localization to homogeneous deformation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 3797–3809 (2002)
McNaney, J. M., Imbeni, V., Jung, Y., et al.: An experimental study of the superelastic effect in a shape-memory Nitinol alloy under biaxial loading. Mech. Mater. 35, 969–986 (2003)
Matsui, R., Tobushi, H., Furuichi, Y., et al.: Tensile deformation and rotating-bending fatigue properties of a high elastic thin wire, a superelastic thin wire, and a superelastic thin tube of NiTi alloys. J. Engng. Mater. Tech. 126, 384–391 (2004)
Ng, K. L., Sun, Q. P.: Stress-induced phase transformation and detwinning in NiTi polycrystalline shape memory alloy tubes. Mech. Mater. 38, 41–56 (2006)
Feng P., Sun, Q. P.: In situ profilometry for non-uniform strain field measurement of NiTi shape memory alloy microtubing under complex stress states. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 179–186 (2007)
Feng, P., Sun, Q. P.: Experimental investigation on macroscopic domain formation and evolution in polycrystalline NiTi microtubing under mechanical force. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 54, 1568–1603 (2006)
Favier, D., Louche, H., Schlosser, P., et al.: Homogeneous and heterogeneous deformation mechanisms in an austenitic polycrystalline Ti-50.8 at.% Ni thin tube under tension-investigation via temperature and strain fields measurements. Acta Mater. 55, 5310–5322 (2007)
Grabe, C., Bruhns, O. T.: On the viscous and strain rate dependent behavior of polycrystalline NiTi. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45, 1876–1895 (2008a)
Grabe, C., Bruhns, O. T.: Tension/torsion tests of pseudoelastic, polycrystalline NiTi shape memory alloys under temperature control. Mater. Sci. Engng.: A 481–482, 109–113 (2008b)
Grabe, C., Bruhns, O. T.: Path dependence and multiaxial behavior of a polycrystalline NiTi alloy within the pseudoelastic and pseudoplastic temperature regimes. Int. J. Plast. 25, 513–545 (2009)
He, Y. J., Sun, Q. P.: Effects of structural and material length scales on stress-induced martensite macro-domain patterns in tube configurations. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46, 3045–3060 (2009)
He, Y. J., Sun, Q. P.: Scaling relationship on macroscopic helical domains in NiTi tubes. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46, 4242–4251 (2009)
Zhou, R. H.: Macroscopic domain pattern selectrion in shape memory alloys: effects of length and time scales. [Ph.D. Thesis]. The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Hongkong China (2011)
Leo, P. H., Shield, T. W., Bruno, O. P.: Transient heat transfer effects on the pseudoelastic behavior of shape-memory wires. Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 2477–2485 (1993)
Bruno, O. P., Leo, P. H., Reitich, F.: Free boundary conditions at austenite-martensite interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 746–749 (1995)
Shield, T.W., Leo, P. H., Grebner, W. C. C.: Quasi-static extension of shape memory wires under constant load. Acta Mater. 45, 67–74 (1997)
Shaw, J. A., Kyriakides, S.: Thermomechanical aspects of NiTi. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 43, 1243–1281 (1995)
Shaw, J. A., Kyriakides, S.: On the nucleation and propagation of phase transformation fronts in a NiTi alloy. Acta Mater. 45, 683–700 (1997)
Tobushi, H., Shimeno, Y., Hachisuka, T., et al.: Influence of strain rate on superelastic properties of TiNi shape memory alloy. Mech. Mater. 30, 141–150 (1998)
Iadicola, M. A., Shaw, J. A.: Rate and thermal sensitivities of unstable transformation behavior in a shape memory alloy. Int. J. Plast. 20, 577–605 (2004)
Vitiello, A., Giorleo, G., Morace, R. E.: Analysis of thermomechanical behaviour of Nitinol wires with high strain rates. Smart Mater. Struct. 14, 215–221 (2005)
Pieczyska, E. A., Gadaj, S. P., Nowacki, W. K., et al.: Phasetransformation fronts evolution for stress- and strain-controlled tension tests in TiNi shape memory alloy. Exp. Mech. 46, 531–542 (2006)
He, Y. J., Sun, Q. P.: Rate-dependent domain spacing in a stretched NiTi strip. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47, 2775–2783 (2010)
Zhang, X. H., Feng, P., He, Y. J., et al.: Experimental study on rate dependence of macroscopic domain and stress hysteresis in NiTi shape memory alloy strips. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 52, 1660–1670 (2010)
Sun, Q. P., Zhong, Z.: An inclusion theory for the propagation of martensite band in NiTi shape memory alloy wires under tension. Int. J. Plast. 16, 1169–1187 (2000)
Zhong, Z., Sun, Q. P., Tong, P.: On the elastic axisymmetric deformation of a rod containing a single cylindrical inclusion. Int. J. Solids Struct. 37, 5934–5955 (2000)
Yu, X. B., Sun, Q. P., Zhong, Z.: Effect of elastic matrix constraint on the tensile deformation of NiTi superelastic fiber. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 2659–2683 (2004)
Mura, T.: Micromechanics of Defects in Solids, (2nd edn). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht Netherlands Boston (1987)
Landau, L. D., Lifshitz, E.M.: Theory of Elasticity. Pergamon, Oxford (1986)
Cook, R. D., Young, W. C.: Advanced Mechanics of Materials, (2nd edn). Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1999).
Eshelby, J. D.: The force on an elastic singularity. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A 224, 87–112 (1951)
Eshelby, J. D.: Energy relations and the energy-momentum tensor in continuum mechanics. In: Kanninen MF, Adler WF, Rosefield AR, Jaffe RI (eds) Inelastic Behavior of Solids. McGraw-Hill. New York, 77–114 (1970)
Eshelby, J. D.: The elastic energy-momentum tensor. J. Elast. 5, 321–335 (1975)
Knowles, J. K.: On the dissipation associated with equilibrium shocks in finite elasticity. J. Elast. 9, 131–158 (1979)
Abeyaratne, R., Knowles, J. K.: On the driving traction acting on a surface of discontinuity in a continuum. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 40, 345–360 (1990)
Maugin, G. A.: Material Inhomogeneities in Elasticity, (1st edn). Chapman and Hall, London New York (1993)
Fried, E., Gurtin, M.E.: Coherent solid-state phase transitions with atomic diffusion: a thermomechanical treatment. J. Stat. Phys. 95, 1361–1427 (1999)
Gurtin, M.E.: Configurational Forces as Basic Concept of Continuum Physics. Springer, New York (2000)
Mueller, R., Kolling, S., Gross, D.: On configurational forces in context of the finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 53, 1557–1574 (2002)
Gross, D., Kolling, S., Mueller, R., et al.: Configurational forces and their application in solid mechanics. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 22, 669–692 (2003)
Dong, L., Sun, Q. P.: On equilibrium domains in superelastic NiTi tubes — helix versus cylinder. Int. J. Solids Struct. 49, 1063–1076 (2012)
Rice, J. R.: Inelastic constitutive relations for solids: an internal-variable theory and its application to metal plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 19, 433–455 (1971)
Cahn, J.W., Hilliard, J. E.: Free energy of a nonuniform system I. Interfacial free energy. J. Chem. Phys. 28, 258–267 (1958)
Cahn, J. W.: On spinodal decomposition. Acta Metal. 9, 795–801 (1961)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The project was supported by the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (GRF619511) and from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11128204).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Sun, QP. On stability of elastic domain during isothermal solid-solid phase transformation in a tube configuration. Acta Mech Sin 28, 683–694 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0110-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0110-y