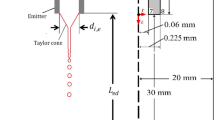
Abstract
Electrospinning experiments are performed by using a set of experimental apparatus, a stroboscopic system is adopted for capturing instantaneous images of the conejet configuration. The cone and the jet of aqueous solutions of polyethylene oxide (PEO) are formed from an orifice of a capillary tube under the electric field. The viscoelastic constitutive relationship of the PEO solution is measured and discussed. The phenomena owing to the jet instability are described, five flow modes and corresponding structures are obtained with variations of the fluid flow rate Q, the electric potential U and the distance h from the orifice of the capillary tube to the collector. The flow modes of the cone-jet configuration involves the steady bending mode, the rotating bending mode, the swinging rotating mode, the blurring bending mode and the branching mode. Regimes in the Q-U plane of the flow modes are also obtained. These results may provide the fundamentals to predict the operating conditions expected in practical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang, Z. M., Zhang, Y. Z., Kotakic, M., et al.: A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Composites Science and Technology 63, 2223–2253 (2003)
Reneker, D. H., Yarin, A. L., Zussman, E., et al.: Electrospinning of nanofibers from polymer solutions and melts. Adv. Appl. Mech. 41, 43–195 (2007)
Reneker, D. H., Yarin, A. L.: Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 49, 2387–2425 (2008)
Graham, K., Ouyang, M., Raether, T., et al.: Polymeric nanofibers in air filtration applications. In: Proc. the Fifteenth Annual Technical Conference Expo of the American Filtration Separations Society, Galveston, Texas, 2002, April 9–12.
Zhang, H. B., Jayasinghe, S. N., Edirisinghe, M. J.: Electrically forced microthreading of highly viscous dielectric liquids. Journal of Electrostatics 64, 355–360 (2006)
Theron, A., Zussman, E., Yarin, A. L.: Electrostatic fieldassisted alignment of electrospun nanofibres. Nanotechnology 12, 384–390 (2001)
Kong, C. S., Lee, T. H., Lee, S. H., et al.: Nano-web formation by the electrospinning at various electricfields. J Mater Sci. 42, 8106–8112 (2007)
Yarin, A. L., Kataphinan, W., Reneker, D. H.: Branching in electrospinning of nanofibers. Journal of Applied Physics 98, 064501 (2005)
Chronakis, I. S., Grapenson, S., Jakob, A.: Conductive polypyrrole nanofibers via electrospinning: Electrical and morphological properties. Polymer 47, 1597–1603 (2006)
Fong, H., Chun, I., Reneker, D. H.: Beaded nanofibers formed during electro-spinning. Polymer 40, 4585–4592 (1999)
Zuo, W. W., Zhu, M. F., Yang, W., et al.: Experimental study on relationship between jet instability and formation of beaded fibers during electrospinning. Poly. Eng. Sci. 45, 704–709 (2005)
Taylor, G.: Electrically driven jets. proceedings of the royal society of london. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences 313, 453–475 (1969)
Baumgarten, P. K.: Electrostatic spinning of acrylic mi crofibers. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 36, 71–79 (1971)
Reneker, D. H., Yarin, A. L., Fong, H., et al.: Bending instability of electrically charged jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. Journal of Applied Physics 87, 4531–4547 (2000)
Yarin, A. L., Koombhongse, S., Reneker, D. H.: Bending instability in electrospinning of nanofibers. Journal of Applied Physics 89, 3018–3026 (2001)
Yarin, A. L., Koombhongse, S., Reneker, D. H.: Taylor cone and jetting from liquid droplets in electrospinning of nanofibers. Journal of Applied Physics 90, 4836–4846 (2001)
Riboux, G., Marin, A. G., Loscertales, I. G., et al.: Whipping instability characterization of an electrified visco-capillary jet. J. Fluid Mech. 671, 226–253 (2011)
Li, F., Ganan-Calvo, A. M., Lopez-Herrera, J.: Absoluteconvective instability transition of low permittivity, low conductivity charged viscous liquid jets under axial electric fields. Phys. Fluids 23, 094108 (2011)
Bird, R., Armstrong, R., Hassager, O.: Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids, vol. 1: Fluid Mechanics. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1987.
Friedrich, C.: Relaxation and retardation functions of the maxwell model with fractional derivatives. Rheologica Acta 30, 151–158 (1991)
Schiessel, H., Metzler, R., Blumen, A., et al.: Generalized viscoelastic models: Their fractional equations with solutions. Journal of Physics a-Mathematical and General 28, 6567–6584 (1995)
Khan, M., Hayat, T., Asghar, S.: Exact solution for mhd flow of a generalized oldroyd-b fluid with modified darcy’s law. International Journal of Engineering Science 44, 333–339 (2006)
Khan, M., Ali, S. H., Qi, H.: On accelerated flows of a viscoelastic fluid with the fractional Burgers’ model. Nonlinear Analysis-Real World Applications 10, 2286–2296 (2009)
Shin, Y.M., Hohman, M.M., Brenner, M. P., et al.: Experimental characterization of electrospinning: the electrically force jet and instabilities. Polymer 42, 9955–9967 (2001)
Hohman, M. M., Shin, Y. M., Rutledge, G., et al.: Electrospinning and electrically forced jets. I. Stability theory. Phys. Fluids 13, 2201–2220 (2001)
Carroll, C. P., Joo, Y. L.: Electrospinning of viscoelastic Boger fluids: Modeling and experiments. Phys. Fluids 18, 053102 (2006)
Huebner, A. L.: Disintegration of charged liquid jets. J. Fluid Mech. 38, 679–688 (1969)
Carroll, C. P., Joo, Y. L.: Axisymmetric instabilities of electrically driven viscoelastic jets. J. Non-Newt. Fluid Mech. 153, 130–148 (2008)
Carroll, C. P., Joo, Y. L.: Axisymmetric instabilities in electrospinning of highly conducting, viscoelastic polymer solutions. Phys. Fluids 21, 103101 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Project (11002139) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (20100470854).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Si, T., Li, GB., Chen, XX. et al. Experimental investigation on flow modes of electrospinning. Acta Mech Sin 28, 644–652 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0101-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-012-0101-z