Abstract
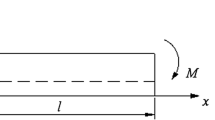
A thermomechanical model of a shape memory alloy beam bending under tip force loading is implemented in finite element codes. The constitutive model is a one dimensional model which is based on free energy and motivated by statistical thermodynamics. The particular focus of this paper is on the aspects of finite element modeling and simulation of the inhomogeneous beam bending problem. This paper extends previous work which is based on the small deformation Euler-Bernoulli beam theory and by treating an SMA beam as consisting of multi-layers in a two-dimensional model. The flux terms are involved in the heat transfer equation. The simulations can represent both shape memory effect and super-elastic behavior. Different thermal boundary condition effect and load rate effect can also be captured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krulevitch, P., Lee, A.P., Ramsey, P.B. et al.: Thin film shape memory alloy microactuators. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 5(4), 270–282 (1996)
Kohl, M., Krevet, B., Just, B.: SMA microgripper system. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 97–98, 646–652 (2002)
Xu, D., Wang, L., Ding G. et al.: Characteristics and fabrication of NiTi/Si diaphragm micropump. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 93(1), 87–92 (2002)
Ishida, A., Sato, M., Yoshikawa W. et al.: Bimorph-type microactuator using TiNi shape-memory thin film. Material Science Forum 394–395, 487–490 (2001)
Kohl, M., Brugger, D., Ohtsuka D. et al.: A novel actuation mechanism on the basis of ferromagnetic SMA thin films. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 114(2–3), 445–450 (2004)
Namazu T., Tashiro Y., Inoue S.: Ti-Ni shape memory alloy film-actuated microstructures for a MEMS probe card. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering. 17(1), 154–162 (2007)
Tanaka K., NagaKi S.: A thermomechanical description of materials with internalvariables in the process of phase transition. Archive of Applied Mechanics 51(5), 287–299 (1982)
Liang, C., Rogers, C.A.: One-dimensional thermomechanical constitutive relations for shape memory materials. Journal of IntelligentMaterial System and Structures 1(2), 207–234 (1990)
Ahluwalia, R., Lookman, T., Saxena, A. et al.: Landau theory for shape memory polycrystals. Acta Materialia 52(1), 209–218 (2004)
Elliott, R.S., Shaw, J.A., Triantafyllidis, N.: Stability of crystalline solids-II: application to temperature-induced martensitic phase transformations in a bi-atomic crystal. Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids 54(1), 193–232 (2006)
Huang, X., Ackland, G.J., Rabe, K.M.: Crystal structures and shape-memory behaviour of NiTi. Nature Materials 2(5), 307–311 (2003)
Ivshin, Y., Pence, T.J.: A thermomechanical model for a one variant shape memory material. Journal of Intelligent Materials System and Structures 5(4), 455–473 (1994)
Amalraj, J.J., Bhattacharyya, A., Faulkner, M.G.: Finiteelement modeling of phase transformation in shape memory alloy wires with variable material properties. Smart Mater. Struct. 9(5), 622–631 (2000)
Meier, H., Oelschlaeger, L.: Numerical thermomechanical modeling of shape memory alloy wires. Materials Science and Engineering A 378(1–2), 484–489 (2004)
Tsoi, K.A., Schrooten, J., Stalmans, R.: Part I. Thermomechanical characteristics of shape memory alloys. Materials Science and Engineering A 368(1–2), 286–298 (2004)
Müller, C., Bruhns, O.T.: A thermodynamic finite-strain model for pseudoelastic shape memory alloys. International Journal of Plasticity 22(9), 1658–1682 (2006)
Azadi, B., Rajapakse, R.K.N.D., Maijer, D.M.: Onedimensional thermomechanical model for dynamic pseudoelastic response of shape memory alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 15(4), 996–1008 (2006)
Zhu, S., Zhang, Y.: A thermomechanical constitutive model for superelastic SMA wire with strain-rate dependence. Smart Mater. Struct. 16(5), 1696–1707 (2007)
Shaw, J.A.: A thermomechanical model for a 1D shape memory alloy wire with propagating instabilities. International Journal of Solids and Structures 39(5), 1275–1305 (2002)
Iadicola, M.A., Shaw, J.A.: Rate and thermal sensitivities of unstable transformation behavior in a shape memory alloy. International Journal of Plasticity 20(4–5), 577–605 (2004)
Chang, B.C., Shaw, J.A., Iadicola, M.A.: Thermodynamics of shape memory alloy wire: modeling, experiments, and application. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 18(1–2), 83–118 (2006)
Shaw, J.A., Churchill, C.B.: A reduced-order thermomechanical model and analytical solution for uniaxial shape memory alloy wire actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(6), 065001–065022 (2009)
Achenbach, M., Müller, I.: Simulation of material behavior of alloys with shape memory. Arch Mech. 37(6), 573–585 (1985)
Achenbach, M.: A model for an alloy with shape memory. International Journal of Plasticity 5(4), 371–395 (1989)
Seelecke, S., Müller, I.: Shape memory alloy actuators in smart structures-modeling and simulation. Appl. Mech. Rev. 57(1), 23–46 (2004)
Thiebaud, F., Collet, M., Foltete, E. et al.: Implementation of a multi-axial pseudoelastic model to predict the dynamic behavior of shape memory alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 16(4), 935–947 (2007)
Rahman, M.A., Kowser, M.A.: Nonlinear analysis of cantilever shape memory alloy beams of variable cross section. Smart Mater. Struct. 16(2), 531–540 (2007)
Yang, S., Seelecke, S., Li, Q.: Finite element analysis of SMA beam bending using COMSOL. Proc. of SPIE 7289, (2009) doi: 10.1117/12.816714
Auricchio, F., Sacco, E.: A temperature-dependent beam for shape memory alloys: constitutive modelling, finite element implemenation and numerical simulations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics Engineering 174(1–2), 171–190 (1999)
Auricchio, F., Sacco, E.: Thermo-mechanical modeling of a superelastic shape-memory wire under cyclic stretching-bending loadings. International Journal of Solid and Structures 38(34–35), 6123–6145 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, SB., Xu, M. Finite element analysis of 2D SMA beam bending. Acta Mech Sin 27, 738–748 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-011-0496-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-011-0496-y