Abstract
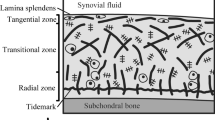
It is well known that subtle changes in structure and tissue composition of articular cartilage can lead to its degeneration. The present paper puts forward a modified layered inhomogeneous triphasic model with four parameters based on the inhomogeneous triphasic model proposed by Narmoneva et al. Incorporating a piecewise fitting optimization criterion, the new model was used to obtain the uniaxial modulus Ha, and predict swelling pattern for the articular cartilage based on ultrasound-measured swelling strain data. The results show that the new method can be used to provide more accurate estimation on the uniaxial modulus than the inhomogeneous triphasic model with three parameters and the homogeneous mode, and predict effectively the swelling strains of highly nonuniform distribution of degenerated articular cartilages. This study can provide supplementary information for exploring mechanical and material properties of the cartilage, and thus be helpful for the diagnosis of osteoarthritis-related diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mow V.C., Ratcliffe A., Poole A.R.: Cartilage and diarthrodial joints as paradigms for hierarchical materials and structures. Biomaterials 13, 67–97 (1992)
Mow V.C., Gu W.Y., Chen F.H.: Structure and function of articular cartilage and meniscus. In: Mow, V.C., Huiskes, R. (eds) Basic Orthopaedic Biomechanics and Mechano-biology, 3rd edn, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia (2005)
Wang, Q.: Ultrasonic characterization of transient and inhomogeneous swelling behavior and progressive degeneration of articular cartilage. [Phd Thesis], Hongkong Polytechnic University, Hongkong, China (2007)
Mow V.C., Guo X.E.: Mechano-electrochemical properties of articular cartilage: their inhomogeneities and anisotropies. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 4, 175–209 (2002)
Brandt K., Doherty M., Lohmander S.: Osteoarthritis Cartilage. Oxford University Press, London (1998)
Kempson G.E.: The Joints and Synovial Fluid, vol. II, pp. 177–238. Academic Press, New York (1980)
Mow V.C., Zhu W., Ratcliffe A.: Basic othopaedic biomechanics: structure and function of articular cartilage and meniscus. In: Mow, V.C., Hayes, W.C. (eds) Basic Orthopaedic Biomechanics, pp. 143–198. Raven Press, New York (1991)
Maroudas A.: Balance between swelling pressure and collagen tension in normal and degenerate cartilage. Nature 260, 808–809 (1976)
Lai W.M., Hou J.S., Mow V.C.: A triphasic theory for the swelling and deformation behaviors of articular cartilage. J. Biomech. Eng. 113, 245–258 (1991)
Maroudas A.: Transport of solutes through cartilage—permeability to large molecules. J. Anat. 122, 335–347 (1976)
Narmoneva D.A., Wang J.Y., Setton L.A.: Nonuniform swelling-induced residual strains in articular cartilage. J. Biomech. 32, 401–408 (1999)
Mow V.C., Kuer S.C., Lai W.M., Armstrong C.G.: Biphasic creep and stress relaxation of articular cartilage in compression: theory and experiments. J. Biomech. Eng. 102, 73–84 (1980)
Mak A.F.: The apparent viscoelastic behavior of articular cartilage—the contributions from the intrinsic matrix viscoelasticity and interstitial fluid flows. J. Biomech. Eng. 108, 123–130 (1986)
Narmoneva, D.A.: Material property determination for normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage using triphasic mechano-chemical theoretical model of osmotic loading. [Phd Thesis], Duke University, Durham, North Carolina (2000)
Chen W.Y., Zhang Q.Y., Wei X.C., Wang X.H., Li X.N.: Viscoelastic properties of chondrocytes isolated from normal and osteoarthritic rabbit knee cartilage. Chin. J. Theo. Appl. Mech. 39, 517–521 (2007)
Zheng Y.P., Mak A.F.T., Lau K.P., Qin L.: An ultrasonic measurement for in vitro depth-dependent equilibrium strains of articular cartilage in compression. Phys. Med. Biol. 47, 3165–3180 (2002)
Zheng Y.P., Niu H.J., Wang Q., Mak A.F.T.: Extraction of mechanical properties of articular cartilage from osmotic swelling behavior monitored using high frequency ultrasound. J. Biomech. Eng. 129, 413–422 (2007)
Niu H.J., Wang Q., Zheng Y.P., Pu F.: Computation of uniaxial modulus of the normal and degenerated articular cartilage using inhomogeneous triphasic model. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Int. Conf. Life Syst. Model. Simul. 4689, 104–110 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10772018, 30872720).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, H., Wang, Q., Zheng, Y. et al. A new method for computing the uniaxial modulus of articular cartilages using modified inhomogeneous triphasic model. Acta Mech Sin 26, 121–126 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0287-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0287-x