Abstract
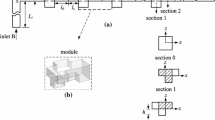
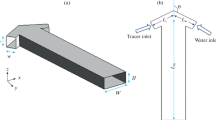
This paper studied a concept of micromixer with a synthetic jet placed at the bottom of a rectangular channel. Due to periodic ejections from and suctions into the channel, the fluids are mixed effectively. To study the effects of the inlet velocity, the jet intensity and frequency, and the jet location on the mixing efficiency, 3-D numerical simulations of the micromixer have been carried out. It has been found that when the jet intensity and the frequency are fixed, the mixing efficiency increases when Re < 50, and decreases when Re > 50 with the best mixing efficiency achieved at Re = 50. When the ratio of the jet velocity magnitude to the inlet velocity is taken as 10 and the jet frequency is 100 Hz, the mixing index reaches the highest value. It has also been found that to get better mixing efficiency, the orifice of the synthetic jet should be asymmetrically located away from the channel’s centerline.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D j :
-
mass diffusion coefficient, m2/s
- D :
-
inlet width of channel, m
- H :
-
cavity height, m
- H c :
-
channel height, m
- L :
-
orifice length, m
- L c :
-
channel length, m
- Mi :
-
mixing index
- P :
-
pressure, Pa
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Sc :
-
Schmitt number
- T :
-
time of period, s
- U :
-
velocity, m/s
- U in :
-
inlet velocity of channel, m/s
- V z :
-
oscillating velocity magnitude, m/s
- W :
-
cavity width, m
- c :
-
concentration
- d :
-
orifice width, m
- f :
-
oscillating frequency, 1/s
- t :
-
time, s
- x :
-
coordinate in x direction, m
- y :
-
coordinate in y direction, m
- ν :
-
viscosity of fluid, m2/s
- δ x :
-
dimensionless x of oscillating wall
- δ y :
-
dimensionless y of oscillating wall
References
Squires T.M., Quake S.T.: Microfluics: Fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Modern Phys. 77, 977–1026 (2005)
Stone H.A., Stroock A.D., Ajdari A.: Engineering flows in small devices: microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 36, 381–411 (2004)
Ottino J.M., Wiggins S.: Introduction: Mixing in microfluidics. Roy. Soc. Lond. Trans. Ser. A 362, 923–935 (2004)
Nguyen N.T., Wu Z.: Micromixers—a review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, R1–R16 (2005)
Wiggins S., Ottino J.M.: Foundations of chaotic mixing. Roy. Soc. Lond. Trans. Ser. A 362, 937–970 (2004)
Bessoth F.G., deMello A.J., Manz A.: Microstructure for efficient continuous flow mixing. Anal. Commun. 36, 213–215 (1999)
Branebjerg, J., et al.: Fast mixing by lamination. In: Proceedings of IEEE MEMS Workshop, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 441–446 (1996)
Voldman J.: An integrated liquid mixer/valve. J. MEMS 9, 295–302 (2000)
Mengaaud V., Josserand J., Girault H.H.: Mixing processes in a zigzag microchannel: finite element simulation and optical study. Anal. Chem. 74, 4279–4286 (2002)
Liu R.H. et al.: Passive mixing in a 3D serpentine microchannel. J. MEMS 9, 190–197 (2000)
Vijayendran R.A. et al.: Evaluation of a 3D micromixer in a surface-based biosensor. Langmuir 19, 1824–1828 (2003)
Strook A.D. et al.: Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295, 647–651 (2002)
EI Moctar A.O., Aubry N., Batton J.: Electrohydrodynamic microfluidic mixer. Lab Chip 3, 273–280 (2003)
Wu, H.Y., Liu, C.H. A novel electrokinetic micromixer. In: Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Solid State Sensors and Actuators, pp. 631–634 (2003)
Qian S., Bau H.H.: A chaotic electroosmotic stirrer. Anal. Chem. 74, 3616–3625 (2002)
Suzuki, H., Ho, C.M. A magnetic force driven chaotic micro-mixer. In: Proc. 15th Int. Conf. on MEMS, pp. 40–43 (2002)
Bottausci F., Mezic I., Meinhart C.D., Cardonne C.: Mixing in the shear superposition micromixer: Three-dimensional analysis. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 362, 1001–1018 (2004)
Zhen Y., Sohei M., Hiroshi G.: Ultrasonic micromixer for microfluidic systems. Sensors Actuat. A 93, 266–272 (2001)
Smith B.L., Glezer A.: The formation and evolution of synthetic jets. Phys. Fluids 10, 2281–2297 (1998)
Li, S.: A numerical study of micro synthetic jet and its application in thermal management. PhD Dissertation, Georgia Institute of Technology (2005)
Mautner T.: Application of the synthetic jet concept to low Reynolds number biosensor microfluidic flows for enhanced mixing: a numerical study using the lattice Boltzmann method. Biosensors Bioelectr. 19, 1409–1419 (2004)
Zhou S., Hou A.P., Jiang Z.L., Ling D.J.: Separation control using synthetic vortex generator jets in axial compressor cascade. Acta Mech. Sin. 22(6), 521–527 (2006)
Papautsky, I., Ammet, T., Frazier A.B. A review of laminar single-phase flow in microchannles. In: Proc. ASME International Mechanical Engineering Systems and Exposition, Nov. 11–16. IMECE, pp. 495–503 (2001)
Hassan I.: Thermal-fluid MEMS devices: a decade of progress and challenges ahead. J. Heat Transfer 128, 1221–1233 (2006)
Gad-el-Hak: The fluid mechanics of microdevices—the freeman scholar lecture. J. Fluids Eng. 121, 5–33 (1999)
Xu B., Ooi K.T. et al.: Evaluation of viscous dissipation in liquid flow in microchannels. J. Micromech. Microeng. 13, 53–57 (2003)
Hsieh S.S., Lin C.Y. et al.: Liquid flow in a micro-channel. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 436–445 (2004)
Engler M., Kockmann N. et al.: Numerical and experimental investigations on liquid mixing in static micromixers. Chem. Eng. J. 101, 315–322 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10372099).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Xie, C., Zhang, X. et al. Numerical simulation on micromixer based on synthetic jet. Acta Mech Sin 24, 629–636 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-008-0183-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-008-0183-9