Abstract
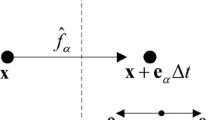
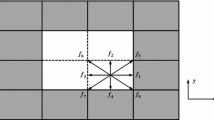
The upper limit of the solid scatters density n s (x), a key parameter for the simulation of flows in porous media with a gray Lattice Boltzmann Method, is studied by an analytical way for the infiltration Poiseuille flow between two infinite parallel plates. Analyses of three different gray Lattice Boltzmann schemes, separately proposed by Gao and Sharma et al., Dardis and McCloskey, and Thorne and Sukop, indicate that the effective domain of Gao and Sharma’s scheme is restricted to \({ n_s < 1/2\sqrt{3} \approx 0.289}\) , Dardis and McCloskey’s scheme is restricted to n s < \({(\sqrt{57}-1)/{28} \approx 0.234}\), and that there is no extra restriction on n s (x) with Thorne and Sukop’s scheme. These results are obtained for the dimensionless relaxation time τ = 1. The above analytical results are verified by our numerical simulations. The use of a gray LBM is further illustrated by simulating the flow at the interface of a porous medium. Simulation results yield velocity profiles which agree very well with Brinkman’s prediction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen S., Doolen G.D.: Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 329–364 (1998)
Rothman D.H.: Cellular-automaton fluids: a model for flow in porous media. Geophysics 53(4), 509–518 (1988)
Guo Z.L., Zhao T.S.: Lattice Boltzmann model for incompressible flows through porous media. Phys. Rev. E 66, 036304 (2002)
Balasubramanian K., Hayot F., Saam W.F.: Darcy’s law from lattice-gas hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. A 36(2), 2248–2253 (1987)
Gao Y., Sharma M.M.: A LGA model for fluid flow in heterogeneous porous media. Transp. Porous Media 17, 1–17 (1994)
Dardis O., McCloskey J.: Lattice Boltzmann scheme with real numbered solid density for the simulation of flow in porous media. Phys. Rev. E 57(4), 4834–4837 (1998)
Thorne, D.T., Sukop, M.C.: Lattice Boltzmann model for the Elder problem. In: Proceedings of the XVth International Conference on Computational Methods in Water Resources, June 13–17, 2004, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, pp. 1549–1557
Qian Y.H., D’Humieres D., Lallemand P.: Lattice BGK models for Navier–Stokes equations. Europhys. Lett. 17(6), 479–484 (1992)
He X., Zou Q., Luo L.S., Dembo M.: Analytic solutions of simple flows and analysis of non-slip boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model. J. Stat. Phys. 87, 115–136 (1997)
Sukop, M.C., Thorne, D.T.: Lattice Boltzmann Modeling, p. 149. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Brinkman H.C.: A calculation of the viscous force exerted by a flowing fluid on a dense swarm of particles. Appl. Sci. Res. 1, 27–34 (1947)
James D.F., Davis A.M.J.: Flow at the interface of a model fibrous porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 426, 47–72 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhu, K. A study of the upper limit of solid scatters density for gray Lattice Boltzmann Method. Acta Mech Sin 24, 515–522 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-008-0167-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-008-0167-9