Abstract
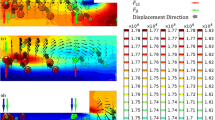
Combined with acoustic separation and hydraulic separation technology, a microfluidic chip, which can achieve multi-level particle separation, is proposed in this work. The chip uses the sheath flow on both sides to align the mixed particles in the set area (near the side of the channel) of the separation channel. And then, the mixed particles successively pass through the acoustic surface wave and hydraulic action area, which are generated by modulating interdigital transducers and adjusting the flow ratio, respectively, and finally realize multiple particle separation under the acoustic radiation and hydraulic force. The corresponding separation experiments were carried out using polystyrene (PS) microparticles with diameters of 1 µm, 5 µm, and 10 µm, respectively. Moreover, we explored the influence of the peak-to-peak voltage (Vpp) and flow ratio on the PS microparticles separation effect, and the separation effect is optimal at the flowrate in the main channel is 4 mm/s, Vpp = 25 V, A1 = 0.2, A2 = 0.5. Under these conditions, the separation purity of 1 µm, 5 µm, and 10 µm PS microparticles are 95.60%, 91.67%, 93.75%, respectively, and their separation rates are 96.67%, 89.19%, and 96.77%, respectively. The combined multi-level separation chip has the advantages of simple structure, high separation accuracy, high separation efficiency, and the ability to sort multiple particles, which can be applied to chemical analysis, cell sorting, biomedicine.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai Y, Sanders CK, Marrone BL (2013) Separation of Escherichia coli bacteria from peripheral blood mononuclear cells using standing surface acoustic waves. Anal Chem 85:9126–9134
Chang CB, Huang WX, Lee KH, Sung HJ (2014) Optical separation of ellipsoidal particles in a uniform flow. Phys Fluids 26:062001
Chono K, Shimizu N, Matsui Y, Kondoh J, Shiokawa S (2004) Development of novel atomization system based on SAW streaming. Jpn J Appl Phys 43:2987–2991
Collins DJ, Alan T, Neild A (2014) Particle separation using virtual deterministic lateral displacement (vDLD). Lab Chip 14:1595–1603
Collins DJ, Morahan B, Garcia-Bustos J, Doerig C, Plebanski M, Neild A (2015) Two-dimensional single-cell patterning with one cell per well driven by surface acoustic waves. Nat Commun 6:8686
Destgeer G, Lee KH, Jung JH, Alazzam A, Sung HJ (2013) Continuous separation of particles in a PDMS microfluidic channel via travelling surface acoustic waves (TSAW). Lab Chip 13:4210–4216
Destgeer G, Ha BH, Jung JH, Sung HJ (2014) Submicron separation of microspheres via travelling surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 14:4665–4672
Destgeer G, Ha BH, Park J, Jung JH, Alazzam A, Sung HJ (2015) Microchannel anechoic corner for size-selective separation and medium exchange via traveling surface acoustic waves. Anal Chem 87:4627–4632
Destgeer G, Alazzam A, Sung HJ (2016) High frequency travelling surface acoustic waves for microparticle separation. J Mech Sci Technol 30:3945–3952
Devendran C, Gunasekara NR, Collins DJ, Neild A (2016) Batch process particle separation using surface acoustic waves (SAW): integration of travelling and standing SAW. RSC Adv 6:5856–5864
Dincer C, Kling A, Chatelle C, Armbrecht L, Kieninger J, Weber W, Urban GA (2016) Designed miniaturization of microfluidic biosensor platforms using the stop-flow technique. Analyst 141:6073–6079
Ding X, Wang L, Huang TJ (2012) High-efficiency blood cell separation using standing surface acoustic waves. In: Proceedings of the 16th international conference on miniaturized systems for chemistry and life sciences. MicroTAS, pp 539–541
Ding XY, Peng ZL, Lin SCS, Geri M, Li SX, Li P, Chen YC, Dao M, Suresh S, Huang TJ (2014) Cell separation using tilted-angle standing surface acoustic waves. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:12992–12997
Duffy DC, Mcdonald JC, Schueller OJ, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70:4974–4984
Fouet M, Mader MA, Iraïn S, Yanha Z, Naillon A, Cargou S, Gue AM, Joseph P (2016) Filter-less submicron hydrodynamic size sorting. Lab Chip 16:720–733
Guldiken R, Jo MC, Gallant ND, Demirci U, Zhe J (2012) Sheathless size-based acoustic particle separation. Sensors 12:905–922
Hung LH, Wang HL, Yang RJ (2016) A portable sample concentrator on paper-based microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 20:80
Isiksacan Z, Erel O, Elbuken C (2016) A portable microfluidic system for rapid measurement of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Lab Chip 16:4682–4690
Jo MC, Guldiken R (2012) Active density-based separation using standing surface acoustic waves. Sens Actuators A Phys 187:22–28
Li SX, Ding XY, Mao ZM, Chen YC, Nama N, Guo F, Li P, Wang L, Cameron CE, Huang TJ (2015) Standing surface acoustic wave (SSAW)-based cell washing. Lab Chip 15:331–338
Li SX, Ma F, Bachman H, Cameron CE, Zeng XQ, Huang TJ (2017) Acoustofluidic bacteria separation. J Micromech Microeng 27:015031
Ma ZC, Collins DJ, Guo JH, Ai Y (2016) Mechanical properties based particle separation via traveling surface acoustic wave. Anal Chem 88:11844–11851
Ma ZC, Collins DJ, Ai Y (2017) Single-actuator bandpass microparticle filtration via traveling surface acoustic waves. Colloid Interface Sci Commun 16:6–9
Mashaghi S, Abbaspourrad A, Weitz DA, van Oijen AM (2016) Droplet microfluidics: a tool for biology, chemistry and nanotechnology. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 82:118–125
McGrath J, Jimenez M, Bridle H (2014) Deterministic lateral displacement for particle separation: a review. Lab Chip 14:4139–4158
Nam J, Lim H, Kim C, Kang JY, Shin S (2012) Density-dependent separation of encapsulated cells in a microfluidic channel by using a standing surface acoustic wave. Biomicrofluidics 6:024120
Naseer SM, Manbachi A, Samandari M, Walch P, Gao Y, Zhang YS, Davoudi F, Wang W, Abrinia K, Cooper JM (2017) Surface acoustic waves induced micropatterning of cells in gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biofabrication 9:015020
Ng JW, Collins DJ, Devendran C, Ai Y, Neild A (2016) Flow-rate-insensitive deterministic particle sorting using a combination of travelling and standing surface acoustic waves. Microfluid Nanofluid 20:151
Nivedita N, Garg N, Lee AP, Papautsky I (2017) A high throughput microfluidic platform for size-selective enrichment of cell populations in tissue and blood samples. Analyst 142:2558–2569
Pamme N (2007) Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7:1644–1659
Sehgal P, Kirby BJ (2017) Separation of 300 and 100 nm particles in Fabry–Perot acoustofluidic resonators. Anal Chem 89:12192–12200
Skowronek V, Rambach RW, Franke T (2015) Surface acoustic wave controlled integrated band-pass filter. Microfluid Nanofluid 19:335–341
Soliman AM, Eldosoky MA, Taha TE (2017) The separation of blood components using standing surface acoustic waves (SSAWs) microfluidic devices: analysis and simulation. Bioengineering 4:4020028
Song PY, Hu R, Tng DJH, Yong KT (2014) Moving towards individualized medicine with microfluidics technology. Rsc Adv 4:11499–11511
Sun MR, Agarwal P, Zhao ST, Zhao Y, Lu XB, He XM (2016) Continuous on-chip cell separation based on conductivity-induced dielectrophoresis with 3D self-assembled ionic liquid electrodes. Anal Chem 88:8264–8271
Theberge AB, Courtois F, Schaerli Y, Fischlechner M, Abell C, Hollfelder F, Huck WTS (2010) Microdroplets in microfluidics: an evolving platform for discoveries in chemistry and biology. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:5846–5868
Wang SD, Sung KJ, Lin XXNN, Burns MA (2017) Bead mediated separation of microparticles in droplets. PLoS One 12:e0173479
Wu J, Yan QF, Xuan SH, Gong XL (2017) Size-selective separation of magnetic nanospheres in a microfluidic channel. Microfluid Nanofluid 21:47
Xu WC, Hou ZN, Liu ZH, Wu ZG (2016) Viscosity-difference-induced asymmetric selective focusing for large stroke particle separation. Microfluid Nanofluid 20:128
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the Jilin Province Natural Science Foundation Projects (No. 20170101136JC), the National Natural Science Foundation Projects (Nos. 51375207; 51875234), and the Jilin Provincial Department of Education Project (JJKH20190140KJ) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., He, F., Li, X. et al. Multi-level separation of particles using acoustic radiation force and hydraulic force in a microfluidic chip. Microfluid Nanofluid 23, 23 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2189-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2189-y