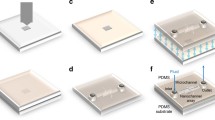
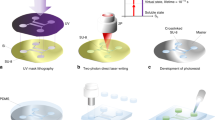
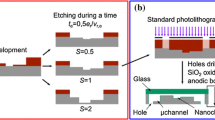
Abstract
Sealed nanofluidic channels with cross-sections as small as 60 nm × 60 nm were created in polymer bilayers using the focused X-rays of a scanning transmission X-ray microscope. These structures were then characterized by near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectromicroscopy, atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The cross-sectional area of the nanochannels could be tuned by adjusting the area patterned in x and y and/or manipulating the bottom layer thickness. The maximum length was found to be limited by the efficiency of excavation of patterned material out of the channel, and the stability of the polymer overlayer which seals the channel. Schemes toward interfacing these nanochannels with conventional microfluidics are discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ade H, Hitchcock AP (2008) NEXAFS microscopy and resonant scattering: composition and orientation probed in real and reciprocal space. Polymer 49:643–675. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2007.10.030
Attwood D (1999) Soft X-rays and extreme ultraviolet radiation: principles and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Attwood D, Halbach K, Kim KJ (1985) Tunable coherent X-rays. Science 228:1265–1272. doi:10.1126/science.228.4705.1265
Coffey T, Urquhart SG, Ade H (2002) Characterization of the effects of soft X-ray irradiation on polymers. J Elec Spec Relat Phenom 122:65–78. doi:10.1016/S0368-2048(01)00342-5
Fouad M, Yavuz M, Cui B (2010) Nanofluidic channels fabricated by e-beam lithography and polymer reflow sealing. J Vac Sci Technol B 28:C6I11–C6I13. doi:10.1116/1.3517620
Gansel JK, Thiel M, Rill MS, Decker M, Bade K, Saile V, Freymann GV, Linden S, Wegener M (2009) Gold helix photonic metamaterial as broadband circular polarizer. Science 325:1513–1515. doi:10.1126/science.1177031
Greeneich JS (1975) Developer characteristics of poly-(methyl methacrylate) electron resist. J Electrochem Soc 122:970–976. doi:10.1149/1.2134380
Henke BL, Gullikson EM, Davis JC (1993) X-ray interactions: photoabsorption, scattering, transmission, and reflection at E = 50–30,000 eV, Z = 1–92. Atom Data Nucl Data Tables 54:181–342. doi:10.1006/adnd.1993.1013
Hitchcock AP (2013) aXis2000 is written in interactive data language (IDL). It is available free for non-commercial use. http://unicorn.mcmaster.ca/aXis2000.html
Howells M, Jacobsen C, Warwick T (2007) Principles and applications of zone plate X-ray microscopes. In: Hawkes PW, Spence JCH (eds) Science of microscopy, vol 2. New York, Springer Science + Business Media, pp 835–926. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-49762-4_13
Ito H, Wilson CG (1983) Chemical amplification in the design of dry developing resist materials. Polym Eng Sci 23:1012–1018. doi:10.1002/pen.760231807
Jacobsen C, Wirick S, Flynn G, Zimba C (2000) Soft X-ray spectroscopy from image sequences with sub-100 nm spatial resolution. J Microscopy 197:173–184. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2818.2000.00640.x
Johnstone RW, Foulds IG, Pallapa MV, Parameswaran AM (2008) Isopropanol/water as a developer for poly(dimethylglutarimide). J Micro/Nanolith MEMS MOEMS 7:043006. doi:10.1117/1.2990738
Kilcoyne ALD, Tyliszczak T, Steele WF, Fakra S, Hitchcock P, Franck K, Anderson E, Harteneck B, Rightor EG, Mitchell GE, Hitchcock AP, Yang L, Warwick T, Ade H (2003) Interferometer-controlled scanning transmission X-ray microscopes at the Advanced Light Source. J Synchrotron Rad 10:125–136. doi:10.1107/S0909049502017739
Labate L, Galimberti M, Giulietti A, Giulietti D, Gizzi LA, Tomassini P, Di Cocco G (2002) A laser-plasma source for CCD calibration in the soft X-ray range. Nucl Instrum Meth A 495:148–153. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(02)01573-5
Leontowich AFG, Hitchcock AP (2011) Zone plate focused soft X-ray lithography. Appl Phys A 103:1–11. doi:10.1007/s00339-010-6172-4
Leontowich AFG, Hitchcock AP (2012a) Zone plate focused soft X-ray lithography for fabrication of nanofluidic devices. Proc SPIE 8323:83231D. doi:10.1117/12.915803
Leontowich AFG, Hitchcock AP (2012b) Secondary electron deposition mechanism of carbon contamination. J Vac Sci Technol B 30:030601. doi:10.1116/1.3698602
Leontowich AFG, Tyliszczak T, Hitchcock AP (2011) Measurement of the point spread function of a soft X-ray microscope by single pixel exposure of photoresists. Proc SPIE 8077:80770N. doi:10.1117/12.887553
Leontowich AFG, Hitchcock AP, Tyliszczak T, Weigand M, Wang J, Karunakaran C (2012) Accurate dosimetry in scanning transmission X-ray microscopes via the cross-linking threshold dose of poly(methyl methacrylate). J Synchrotron Rad 19:976–987. doi:10.1107/S0909049512034486
Leontowich AFG, Hitchcock AP, Watts B, Raabe J (2013) Sub-25 nm direct write (maskless) x-ray nanolithography. Microelec Eng. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2013.03.006
McDonald JC, Whitesides GM (2002) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc Chem Res 35:491–499. doi:10.1021/ar010110q
Miron C, Simon M, Leclercq N, Hansen DL, Morin P (1998) Site-selective photochemistry of core excited molecules: role of the internal energy. Phys Rev Lett 81:4104–4107. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.4104
Nenner I, Reynaud C, Schmelz HC, Ferrand-Tanaka L, Simon M, Morin P (1996) Site selective fragmentation with soft X-rays: from gaseous polyatomic molecules, free clusters, polymers, adsorbates to biological macromolecules. Z Phys Chem 195:43–63. doi:10.1524/zpch.1996.195.Part_1_2.043
Park S, Huh YS, Craighead HG, Erickson D (2009) A method for nanofluidic device prototyping using elastomeric collapse. PNAS 106:15549–15554. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904004106
Pavkovich JM (1986) Proximity effect correction calculations by the integral equation approximate solution method. J Vac Sci Technol B 4:159–163. doi:10.1116/1.583369
Pawloski AR, Nealey PF, Conley W (2002) Efficiency of photoacid generators in chemically amplified resists for 157 nm lithography. J Photopolymer Sci Tech 15:731–739. doi:10.2494/photopolymer.15.731
Popmintchev T, Chen MC, Popmintchev D, Arpin P, Brown S, Ališauskas S, Andriukaitis G, Balčiunas T, Mücke OD, Pugzlys A, Baltuška A, Shim B, Schrauth SE, Gaeta A, Hernández-García C, Plaja L, Becker A, Jaron-Becker A, Murnane MM, Kapteyn HC (2012) Bright coherent ultrahigh harmonics in the keV X-ray regime from mid-infrared femtosecond lasers. Science 336:1287–1291. doi:10.1126/science.1218497
Schmidt A, Ehrfeld W, Lehr H, Müller L, Reuther F, Schmidt M, Zetterer Th (1996) Aligned double exposure in deep X-ray lithography. Microelec Eng 30:235–238. doi:10.1016/0167-9317(95)00235-9
Seah MP, Dench WA (1979) Quantitative electron spectroscopy of surfaces: a standard data base for electron inelastic mean free paths in solids. Surf Interface Anal 1:2–11. doi:10.1002/sia.740010103
Stavis SM, Edel JB, Samiee KT, Craighead HG (2005) Single molecule studies of quantum dot conjugates in a submicrometer fluidic channel. Lab Chip 5:337–343. doi:10.1039/b416161k
Urquhart SG, Ade H (2002) Trends in the carbonyl core (C 1s, O 1s) → π*C=O transition in the near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectra of organic molecules. J Phys Chem B 106:8531–8538. doi:10.1021/jp0255379
Wang J, Stöver HDH, Hitchcock AP, Tyliszczak T (2007a) Chemically selective soft X-ray patterning of polymers. J Synchrotron Rad 14:181–190. doi:10.1107/S0909049506053829
Wang J, Stöver HDH, Hitchcock AP (2007b) Chemically selective soft X-ray direct-write patterning of multilayer polymer films. J Phys Chem C 111:16330–16338. doi:10.1021/jp072570s
Wang J, Morin C, Li L, Hitchcock AP, Scholl A, Doran A (2009a) Radiation damage in soft X-ray microscopy. J Elec Spec Relat Phenom 170:25–36. doi:10.1016/j.elspec.2008.01.002
Wang J, Botton GA, West MM, Hitchcock AP (2009b) Quantitative evaluation of radiation damage to polyethylene terephthalate by soft X-rays and high-energy electrons. J Phys Chem B 113:1869–1876. doi:10.1021/jp808289e
Warwick T, Ade H, Kilcoyne D, Kritscher M, Tylisczcak T, Fakra S, Hitchcock A, Hitchcock P, Padmore H (2002) A new bend-magnet beamline for scanning transmission x-ray microscopy at the Advanced Light Source. J Synchrotron Rad 9:254–257. doi:10.1107/S0909049502005502
Winston D, Cord BM, Ming B, Bell DC, DiNatale WF, Stern LA, Vladar AE, Postek MT, Mondol MK, Yang JKW, Berggren KK (2009) Scanning-helium-ion-beam lithography with hydrogen silsesquioxane resist. J Vac Sci Technol B 27:2702–2706. doi:10.1116/1.3250204
Yang JKW, Cord B, Duan H, Berggren KK, Klingfus J, Nam S, Kim K, Rooks MJ (2009) Understanding of hydrogen silsesquioxane electron resist for sub-5-nm-half-pitch lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B 27:2622–2627. doi:10.1116/1.3253652
Yasin S, Hasko DG, Ahmed H (2001) Fabrication of <5 nm width lines in poly(methylmethacrylate) resist using a water:isopropyl alcohol developer and ultrasonically-assisted development. Appl Phys Lett 78:2760–2762. doi:10.1063/1.1369615
Zhang X, Jacobsen C, Lindaas S, Williams S (1995) Exposure strategies for polymethyl methacrylate from in situ X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy. J Vac Sci Technol B 13:1477–1483. doi:10.1116/1.588175
Zhou W, Kuebler SM, Braun KL, Yu T, Cammack JK, Ober CK, Perry JW, Marder SR (2002) An efficient two-photon-generated photoacid applied to positive-tone 3D microfabrication. Science 296:1106–1109. doi:10.1126/science.296.5570.1106
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Canada Foundation for Innovation and the Canada Research Chair program. We thank Dongqing Li and Jose Moran-Mirabal for useful discussion on interfacing microfluidics with nanofluidics, Yujie Zhu for performing initial interfacing experiments, and Ash Parameswaran for providing the poly(dimethylglutarimide). We also thank David Kilcoyne and Tolek Tyliszczak for their support of the STXM facilities. The experiments were performed at beamline 5.3.2.2 of the ALS, LBNL. The ALS is supported by the Director, Office of Energy Research, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Materials Sciences Division of the USA Department of Energy, under Contract No. DE-AC03-76SF00098. A.F.G.L. acknowledges support from an ALS doctoral fellowship in residence.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leontowich, A.F.G., Hitchcock, A.P. Fabrication of sealed nanofluidic channels using site-selective direct write (maskless) X-ray lithography. Microfluid Nanofluid 15, 509–518 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1170-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1170-4