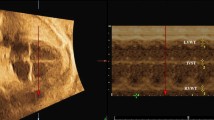
Abstract
Purpose
To assess the accuracy of automated fetal heart rate measurement using two-dimensional tracking (AutoFHR) by comparison with the conventional free-angle M-mode (M-mode) and pulsed-waved Doppler (PWD) methods.
Methods
A multicenter prospective comparative study was conducted. AutoFHR is a novel technique for the automatic calculation of fetal heart rate using a two-dimensional speckle-tracking method. The fetal heart rate (FHR) obtained by AutoFHR was compared with that obtained by the conventional M-mode and PWD. Statistical analysis was performed on the correlation between the FHR measured by AutoFHR and that determined by M-mode and PWD.
Results
Data from 326 singleton pregnancies were analyzed, and all the data and the data from 178 cases were compared with M-mode and PWD, respectively. The intraobserver ICC was 0.96 (95% CI: 0.93–0.98), whereas the interobserver ICC was 0.97 (95% CI: 0.95–0.99). Systematic bias was not observed between M-mode and PWD, based on the Bland–Altman plots. Analyses of the relationships among the FHRs yielded by each method revealed that AutoFHR was strongly associated with M-mode (rs = 0.99, p < 0.001) and PWD (rs = 0.86, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Evaluation of FHR by AutoFHR was proved to be equivalent to evaluation by the conventional M-mode and PWD. AutoFHR can be employed with only B-mode data, making FHR measurement easier and safer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Committee on Practice B-O, the American Institute of Ultrasound in M. Practice bulletin no. 175: ultrasound in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:e241–56.
Reed KL, Sahn DJ, Marx GR, et al. Cardiac Doppler flows during fetal arrhythmias: physiologic consequences. Obstet Gynecol. 1987;70:1–6.
Abramowicz JS, Kossoff G, Marsal K, International society of ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology (ISUOG), et al. Safety statement, 2000 (reconfirmed 2003). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2003;21:100.
Salvesen K, Lees C, Abramowicz J, et al. ISUOG statement on the safe use of Doppler in the 11–13 + 6-week fetal ultrasound examination. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011;37:628.
Murashita K, Kasahara E, Matsushita N, et al. Development of technique to detect fetal heart rate automatically. Medix. 2015;63:35–9 (in Japanese).
Bland JM, Altman DG. Applying the right statistics: analyses of measurement studies. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2003;22:85–93.
Barnett SB, Ter Haar GR, Ziskin MC, et al. International recommendations and guidelines for the safe use of diagnostic ultrasound in medicine. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2000;26:355–66.
Bhide A, Acharya G, Bilardo CM, et al. ISUOG practice guidelines: use of Doppler ultrasonography in obstetrics. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013;41:233–9.
Liao AW, Snijders R, Geerts L, et al. Fetal heart rate in chromosomally abnormal fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2000;16:610–3.
Acknowledgement
This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number: JP16K11114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ryuhei Nagai, Susumu Miyashita, Susumu Murata, Yuichiro Takahashi, Atsushi Tajima, Sumito Nagasaki, and Mayumi Takano declare that they have no conflicts of interest. Masahiko Nakata reports grants from JSPS KAKENHI during the conduct of the study. In addition, Nakata has a patent from the Japan Patent Office licensed to 5386001.
Ethical statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1946 and later versions.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients whose identifying information is included in this article.
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, R., Miyashita, S., Murata, S. et al. Reproducibility of automated fetal heart rate measurement using a novel technique with two-dimensional tracking. J Med Ultrasonics 46, 105–111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-018-0893-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-018-0893-y