Abstract
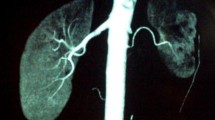
The case of a 16-year-old male patient with left renal artery stenosis due to fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) and an atrophic kidney due to a right multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) who presented with refractory hypertension is reported. On continuous Doppler imaging, the peak systolic velocity (PSV) at the stenotic site of the left renal artery was 404 cm/s. The FMD formed a “string-of-beads” appearance on computed tomographic angiography (CTA) and renal artery angiography. Percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty (PTRA) with a balloon catheter was performed, after which the left renal artery returned to near normal, and his blood pressure decreased to within the normal range. In this case, the main cause of refractory hypertension was considered to have been renal artery stenosis due to left FMD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slovut DP, Olin JW. Fibromuscular dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1862–71.
Plouin PF, Perdu J, La Batide-Alanore A, et al. Fibromuscular dysplasia. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:28.
Narchi H. Risk of hypertension with multicystic kidney disease: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child. 2005;90:921–4.
Gottsäter A, Lindblad B. Optimal management of renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:583–95.
Rountas C, Vlychou M, Vassiou K, et al. Imaging modalities for renal artery stenosis in suspected renovascular hypertension: prospective intraindividual comparison of color Doppler US, CT angiography, GD-enhanced MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. Ren Fail. 2007;29:295–302.
Pickering T. Peripheral and renal vein renin testing. In: Novick A, Scoble J, Hamilton G, editors. Renal vascular disease. London: WB Saunders; 1996. p. 185–93.
Prasad A, Zafar N, Mahmud E. Assessment of renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia: angiography, intravascular ultrasound (with virtual histology), and pressure wire measurements. Catheter Cardiovasc Intervent. 2009;74:260–4.
Bruyne BD, Manoharan G, Pijls NHJ, et al. Assessment of renal artery stenosis severity by pressure gradient measurements. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:1851–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statements
Additional informed consent was obtained from the patient and his parents for whom identifying information is included in this article.
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, S., Takizawa, Y., Nakano, S. et al. A refractory hypertensive patient with fibromuscular dysplasia and multicystic dysplastic kidney. J Med Ultrasonics 45, 657–660 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-018-0884-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-018-0884-z