Abstract
Purpose
To report the reproducibility profile of optic nerve head parameters obtained by computer software-assisted fundus photoplanimetry.
Methods
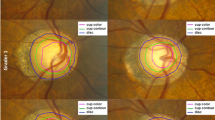
Fundus photographs obtained during a population-based health survey (Sakurae Study) were planimetrically analyzed using newly developed computer software, CDSketch. The parameters assessed included vertical and horizontal cup-to-disc (C/D) ratios, superior and inferior rim-to-disc (R/D) ratios, disc and cup vertical-to-horizontal (V/H) ratios, and disc-macular distance-to-disc diameter (DM/DD) ratio. For intraobserver and interobserver agreement assessments, we calculated the coefficients of variation (CVs) and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) of the mean of three measurements obtained by one observer and a one-time measurement by three observers, respectively.
Results
The intraobserver CVs were between 2.4 % (DM/DD ratio) and 11.0 % (inferior R/D ratio), and the ICCs were between 0.868 (cup V/H ratio) and 0.976 (DM/DD ratio); all intraobserver ICCs had almost perfect agreement (>0.81). The interobserver CVs were between 2.6 % (disc V/H ratio) and 18.0 % (inferior R/D ratio), and the ICCs were between 0.762 (cup V/H ratio) and 0.930 (DM/DD ratio); the interobserver ICCs were categorized as substantial (0.61–0.80) for the inferior R/D and cup V/H ratios and as almost perfect for the other five parameters.
Conclusions
The consistent profiles of the planimetric parameters suggest the suitability of software-assisted photoplanimetry for assessing optic disc characteristics in glaucoma clinical study and practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araie M. Test–retest variability in structural parameters measured with glaucoma imaging devices. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2013;57:1–24.
Kahn HA, Leibowitz H, Ganley JP, Kini M, Colton T, Nickerson R, et al. Randomized controlled clinical trial. National Eye Institute workshop for ophthalmologists. Standardizing diagnostic procedures. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975;79:768–75.
Lichter PR. Variability of expert observers in evaluating the optic disc. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1976;74:532–72.
Iwase A, Suzuki Y, Araie M, Yamamoto T, Abe H, Shirato S, et al. The prevalence of primary open-angle glaucoma in Japanese: the Tajimi Study. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:1641–8.
Sawaguchi S, Sakai H, Iwase A, Yamamoto T, Abe H, Tomita G, et al. Prevalence of primary angle closure and primary angle-closure glaucoma in a southwestern rural population of Japan: the Kumejima Study. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:1134–42.
Kim M, Kim TW, Park KH, Kim JM. Risk factors for primary open-angle glaucoma in South Korea: the Namil study. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012;56:324–9.
Morgan JE, Sheen NJ, North RV, Choong Y, Ansari E. Digital imaging of the optic nerve head: monoscopic and stereoscopic analysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005;89:879–84.
Samarawickrama C, Pai A, Huynh SC, Burlutsky G, Jonas JB, Mitchell P. Measurement of optic nerve head parameters: comparison of optical coherence tomography with digital planimetry. J Glaucoma. 2009;18:571–5.
Saito H, Tsutsumi T, Iwase A, Tomidokoro A, Araie M. Correlation of disc morphology quantified on stereophotographs to results by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II, GD× variable corneal compensation, and visual field tests. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:282–9.
Tsutsumi T, Tomidokoro A, Araie M, Iwase A, Sakai H, Sawaguchi S. Planimetrically determined vertical cup/disc and rim width/disc diameter ratios and related factors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:1332–40.
Tanito M, Sagara T, Takamatsu M, Kiuchi Y, Nakagawa T, Fujita Y, et al. Fundus photoplanimetry of the optic nerve head in the Sakurae Study. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012;116:730–9 (in Japanese).
Miglior S, Albe E, Guareschi M, Rossetti L, Orzalesi N. Intraobserver and interobserver reproducibility in the evaluation of optic disc stereometric parameters by Heidelberg retina tomograph. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:1072–7.
Itai N, Tanito M, Chihara E. Comparison of optic disc topography measured by retinal thickness analyzer with measurement by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2003;47:214–20.
Correnti AJ, Wollstein G, Price LL, Schuman JS. Comparison of optic nerve head assessment with a digital stereoscopic camera (discam), scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, and stereophotography. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:1499–505.
Arthur SN, Aldridge AJ, De Leon-Ortega J, McGwin G, Xie A, Girkin CA. Agreement in assessing cup-to-disc ratio measurement among stereoscopic optic nerve head photographs, HRT II, and stratus OCT. J Glaucoma. 2006;15:183–9.
DeLeon Ortega JE, Sakata LM, Kakati B, McGwin G Jr, Monheit BE, Arthur SN, et al. Effect of glaucomatous damage on repeatability of confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope, scanning laser polarimetry, and optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:1156–63.
Abe H, Shirakashi M, Tsutsumi T, Araie M, Tomidokoro A, Iwase A, et al. Laser scanning tomography of optic discs of the normal Japanese population in a population-based setting. Ophthalmology. 2009;116:223–30.
Seymenoglu G, Baser E, Ozturk B. Comparison of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography and Heidelberg Retina Tomograph III optic nerve head parameters in glaucoma. Ophthalmologica. 2012;. doi:10.1159/000341574.
Yang B, Ye C, Yu M, Liu S, Lam DS, Leung CK. Optic disc imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: variability and agreement study with Heidelberg retinal tomograph. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:1852–7.
Shin HY, Park HY, Jung KI, Park CK. Glaucoma diagnosis optic disc analysis comparing Cirrus spectral domain optical coherence tomography and Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2013;57:41–6.
Goto T, Tanito M, Itai N, Chihara E. Scanning laser polarimetry measurement with variable corneal compensation compared with fixed corneal compensation. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2004;48:507–9.
Mwanza JC, Chang RT, Budenz DL, Durbin MK, Gendy MG, Shi W, et al. Reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic nerve head parameters measured with Cirrus HD-OCT in glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:5724–30.
Kim JH, Kim NR, Kim H, Lee ES, Seong GJ, Kim CY. Effect of signal strength on reproducibility of circumpapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurement and its classification by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2011;55:220–7.
Arnalich-Montiel F, Munoz-Negrete FJ, Rebolleda G, Sales-Sanz M, Cabarga C. Cup-to-disc ratio: agreement between slit-lamp indirect ophthalmoscopic estimation and stratus optical coherence tomography measurement. Eye. 2007;21:1041–9.
Manassakorn A, Aupapong S. Retinal nerve fiber layer defect patterns in primary angle-closure and open-angle glaucoma: a comparison using optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2011;55:28–34.
Yoo YC, Park KH. Influence of angular width and peripapillary position of localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects on their detection by time-domain optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2011;55:115–22.
The Japan Glaucoma Society Guidelines for Glaucoma (3rd edn). Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012;116:3–46 (in Japanese).
Gloster J, Parry DG. Use of photographs for measuring cupping in the optic disc. Br J Ophthalmol. 1974;58:850–62.
Foster PJ, Buhrmann R, Quigley HA, Johnson GJ. The definition and classification of glaucoma in prevalence surveys. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002;86:238–42.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–74.
Tielsch JM, Katz J, Quigley HA, Miller NR, Sommer A. Intraobserver and interobserver agreement in measurement of optic disc characteristics. Ophthalmology. 1988;95:350–6.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported and conducted in part by the research project “The preventive study of critical diseases in the elderly through the application of the cohort framework” at the Center for Community-Based Health Research and Education (COHRE), Shimane University, Shimane Japan. The authors are grateful to Ms. Ryoko Takahashi for her technical assistance in digitization of the fundus films.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tanito, M., Sagara, T., Takamatsu, M. et al. Intraobserver and interobserver agreement of computer software-assisted optic nerve head photoplanimetry. Jpn J Ophthalmol 58, 56–61 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-013-0280-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-013-0280-6