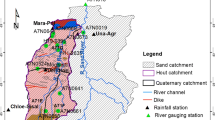
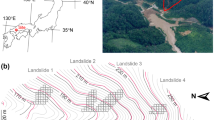
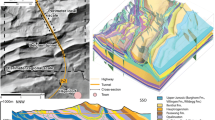
Abstract
This study explores the potential of integrating state-of-the-art physically based hydrogeological modeling into slope stability simulations to identify the hydrogeological triggers of landslides. Hydrogeological models considering detailed morphological, lithological, and climatic factors were elaborated. Groundwater modeling reveals locations with elevated pore water pressures in the subsurface and allows the quantification of temporal dynamics of the pore water pressures. Results of the hydrogeological modeling were subsequently applied as boundary conditions for the slope stability simulations. The numerical models illustrate that the hydrogeological impacts affecting hillslope stability are strongly controlled by local groundwater flow conditions and their conceptualization approach in the hydrogeological model. Groundwater flow itself is heavily influenced by the inherent geological conditions and the dynamics of climatic forcing. Therefore, both detailed investigation of the landslide’s hydrogeology and appropriate conceptualization and scaling of hydrogeological settings in a numerical model are essential to avoid an underestimation of the landslide risk. The study demonstrates the large potential in combining state-of-the-art computational hydrology with slope stability modeling in real-world cases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Āboltiņš O (1995) Gaujas Senleja. In: Kavacs G (ed) Latvijas Daba, 2nd Band. Latvijas Enciklopēdija, Rīga, p 101
Āboltiņš O, Mūrnieks A, Zelčs V (2011) Stop 2: the River Gauja valley and landslides at Sigulda. In: Stinkulis Ģ, Zelčs V (eds) Eighth Baltic stratigraphical conference. Post conference field excursion guidebook. University of Latvia, Rīga, pp 15–20
Anderson AE, Weiler M, Alila Y, Hudson RO (2009) Dye staining and excavation of a lateral preferential flow network. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13:935–944. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-13-935-2009
Aquanty Inc. (2013) HydroGeoSphere: user manual, release 1.0. Waterloo, Ontario
Baligh M, Azzouz A (1975) End effects on stability of cohesive slopes. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering Division 101:1105–1117
Banks EW, Brunner P, Simmons CT (2011) Vegetation controls on variably saturated processes between surface water and groundwater and their impact on the state of connection. Water Resour Res 47(W11517). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR010544.
Brunner P, Simmons CT (2012) HydroGeoSphere: a fully integrated, physically based hydrological model. Ground Water 50:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2011.00882.x
Chen RH, Chameau JL (1983) Three-dimensional limit equilibrium analysis of slopes. Géotechnique. 33:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1983.33.1.31
Cheng Y, Yip C (2007) Three-dimensional asymmetrical sloe stability analysis extension of Bishop’s, Junbu’s, and Morgenstern-Price’s techniques. J Geotech Geoenviron 133(12):1544–1555. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:12(1544)
Doherty J (2015) Calibration and uncertainty analysis for complex environmental models. Watermark Numerical Computing, Brisbane
Formetta G, Rago V, Capparelli G, Rigon R, Muto F, Versace P (2014) Integrated physically based system for modeling landslide susceptibility. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 9:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2014.06.006
Fox GA, Wilson GV (2010) The role of subsurface flow in hillslope and stream bank erosion: a review. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:717–733. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2009.0319
Furuya G, Suemine A, Sassa K, Komatsubara T, Watanabe N, Marui H (2006) Relationship between groundwater flow estimated by soil temperature and slope failures caused by heavy rainfall, Shikoku Island, southwestern Japan. Eng Geol 85:332–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.03.002
Gens A, Hutchinson J, Cavounidis S (1988) Three-dimensional analysis of slides in cohesive soils. Geotechnique 38:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1988.38.1.1
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. (2015) Stability modeling with SLOPE/W: an engineering methodology, June 2015 Edition. Calgary, Alberta
Gerscovich DMS, Vargas EA Jr, de Campos TMP (2006) On the evaluation of unsaturated flow in a natural slope in Rio de Janeiro. Brazil Engineering Geology 88:23–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.07.008
Greco VR (1996) Efficient Monte Carlo technique for locating critical slip surface. J Geotech Eng 122:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1996)122:7(517)
Griffiths DV, Lane PA (1999) Slope stability analysis by finite elements. Géotechnique 49:387–403. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1999.49.3.387
Harp EL, Wells WG, Sarmiento JG (1990) Pore pressure response during failure in soils. Geol Soc Am Bull 102:428–438. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1990)102<0428:PPRDFI>2.3.CO;2
Hovland H (1977) Three-dimensional slope stability analysis method. Journal of Geotechal Engineering Division 103:971–986
Hungr O (1987) An extension of Bishop's simplified method of slope stability analysis to three dimensions. Geotechnique 37:113–117. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1987.37.1.113
Kalatehjari R, Ali N (2013) A review of three-dimensional slope stability analyses based on limit equilibrium method. Electron J Geotech Eng 18:119–134
Kalniņa A (1995) Klimats. In: Kavacs G (ed) Latvijas Daba, 2nd Band. Latvijas Enciklopēdija, Rīga, pp 247–251
Kim J, Lee K, Jeong S, Kim G (2014) GIS-based prediction method of landslide susceptibility using a rainfall infiltration-groundwater flow model. Eng Geol 182:63–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.09.001
Knighton D (1998) Fluvial forms and processes: a new perspective. Arnold, London
Kukemilks K, Saks T (2013) Landslides and gully slope erosion on the banks of the Gauja River between the towns of Sigulda and Ligatne. Estonian Journal of Earth Sciences 62:231–243. https://doi.org/10.3176/earth.2013.17
Kukemilks K, Wagner J-F, Saks T, Brunner P (2018) Conceptualization of preferential flow for hillslope stability assessment. Hydrogeol J 26:439–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1667-0
Latvian Environment, Geology and Meteorology Centre (2013) Janvāris. Article, available online (accessed 02.01.2017): https://meteo.lv/lapas/laika-apstakli/klimatiska-informacija/latvijas-klimats/menesu-klimatiskaisraksturojums/janvaris/janvaris?id=1160&nid=541
Latvian Environment, Geology and Meteorology Centre (2014) Ekstremāli nokrišņi Siguldā 29. Jūlijā. Article, available online (accessed 05.01.2017): http://meteo.lv/jaunumi/laika-apstakli/ekstremali-nokrisni-sigulda-29-julija?id=768&cid=100
Latvian Environment, Geology and Meteorology Centre (2015) Observations. Data base, available online (accessed 25.01.2017): https://meteo.lv/en/meteorologija-datu-pieejamiba/?nid=697
Lourenço SDN, Sassa K, Fukuoka H (2006) Failure process and hydrologic response of a two layer physical model: implications for rainfall-induced landslides. Geomorphology 73:115–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.06.004
Lu N, Godt JW (2013) Hillslope hydrology and stability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lu N, Şener-Kaya B, Wayllace A, Godt JW (2012) Analysis of rainfall-induced slope instability using a field of local factor of safety. Water Resour Res. 48. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012WR011830
McDonnell JJ (1990) The influence of macropores on debris flow initiation. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 23:325–331. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.QJEG.1990.023.04.06
Metrum SIA (2013) Lidar data, scanned in 2013
Morgenstern NR, Price VE (1965) The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces. Géotechnique. 15:79–93. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1965.15.1.79
Mūrnieks A (2002) Turaidas pils stāv un stāvēs. Latvijas Ģeoloģijas Vēstis 10:2–6
Mūrnieks A, Meirons Z, Lācis A, Levins I (2002) Pārskats par Turaidas pilskalna, tā apkārtnes ģeoloģisko, hidroģeoloģisko un inženierģeoloģisko izpēti. Technical report. Latvian Environment, Geology and Meteorology Centre, Riga
Padilla C, Onda Y, Iida T, Takahashi S, Uchida T (2014) Characterization of the groundwater response to rainfall on a hillslope with fractured bedrock by creep deformation and its implication for the generation of deep-seated landslides on Mt. Wanitsuka, Kyushu Island. Geomorphology 204:444–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.08.024
Pierson TC (1983) Soil pipes and slope stability. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 16:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.QJEG.1983.016.01.01.
Schilling OS, Doherty J, Kinzelbach W, Wang H, Yang PN, Brunner P (2014) Using tree ring data as a proxy for transpiration to reduce predictive uncertainty of a model simulating groundwater–surface water–vegetation interactions. J Hydrol 519:2258–2271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.08.063
Shao W, Bogaard TA, Bakker M, Greco R (2015) Quantification of the influence of preferential flow on slope stability using a numerical modelling approach. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:2197–2212. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-2197-2015
Shao W, Bogaard T, Bakker M (2016) The influence of preferential flow on pressure propagation and landslide triggering of the Rocca Pitigliana landslide. J Hydrol 543B:360–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.10.015
Soms J (2006) Regularities of gully erosion network development and spatial distribution in south-eastern Latvia. Baltica 19:72–79
Sorbino G, Nicotera MV (2013) Unsaturated soil mechanics in rainfall-induced flow landslides. Eng Geol 165:105–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.10.008
Sun G, Zheng H, Jiang W (2012) A global procedure for evaluating stability of three-dimensional slopes. Nat Hazards 61:1083–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-9963-9
The Turaida Museum Reserve (2012) The Historical Centre of Turaida, The Turaida Museum Reserve: a guide. Jurkāne A (ed). Mantojums Publishing House, Rīga, 2012, 160 pp
Uchida T, Kosugi K, Mizuyama T (2001) Effects of pipeflow on hydrological process and its relation to landslide: a review of pipeflow studies in forested headwater catchments. Hydrol Process 15:2151–2174. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.281
van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:892–898
Veinbergs I (1975) Formirovanie Abavsko-Slotsenskoj sistemy dolin stoka talykh lednikovykh vod. In: Danilāns I (ed) Voprosy chetvertichnoj geologii. Zinātne, Rīga, pp 82–102 (in Russian, with English Abstr.)
Xie Y, Cook PG, Brunner P, Irvine DJ, Simmons CT (2014) When can inverted water tables occur beneath streams? Groundwater 52:769–774. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12109
Zelčs V, Markots A (2004) Deglaciation history of Latvija. In: Ehlers J, Gibbard PL (eds) Quaternary glaciations—extent and chronology, part I: Europe. Elsevier B.V, Amsterdam, pp 225–243
Zelčs V, Markots A, Nartišs M, Saks T (2011) Pleistocene glaciations in Latvia. In: Ehlers J et al (eds) Developments in quaternary science. Quaternary glaciations—extent and chronology. A closer look, vol 15. Elsevier B.V, Amsterdam, pp 221–229
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Turaida Museum Reserve and personally Aivars Irbe for providing important modeling data, research assistant Fabien Cochand for the help with the modeling software, and Nelson Parker who provided linguistic corrections of the manuscript. We are grateful to our referees for the constructive reviews which helped to improve the article significantly.
Funding
This work was supported by the Sciex NMS.CH program (grant number: 14.006); and German Academic Exchange Service (grant number: 57129429).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kukemilks, K., Wagner, JF., Saks, T. et al. Physically based hydrogeological and slope stability modeling of the Turaida castle mound. Landslides 15, 2267–2278 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1038-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1038-5