Abstract
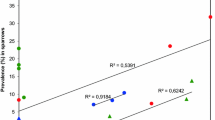
For hunting purposes, several millions of red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa) are released each year in Spain, and these releases have the potential to introduce new parasites and disease into wild populations. We studied the prevalence of Escherichia coli, Campylobacter sp. and Salmonella sp. in the intestinal flora of red-legged partridges from three different husbandry groups: farm-reared, restocked and natural populations. Prevalence of E. coli was significantly higher in farm-reared (45%, p = 0.01) and restocked partridges (60%, p < 0.001) than in wild ones (6%, p > 0.05). The prevalence of Campylobacter sp. (23%, 100 out of 444) did not differ significantly between these three husbandry groups, and Salmonella sp. was only detected in a group of partridge chicks on one of the farms studied (0.9%, 5 out of 544). These results suggest that farm-reared and restocked partridges can act as carriers of these three enteropathogens and highlight a potential risk of transmission to natural populations via the releases of farm-reared partridges. However, future investigations are needed regarding the relation of the isolated bacteria with zoonotic strains and dissemination of antibiotic resistant microorganisms, especially E. coli, and to better evaluate the effect that these three enteropathogens have on partridge health and on the success of restocking with farm-reared birds.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allos BM (2001) Campylobacter jejuni infections: update on emerging issues and trends. Clin Infect Dis 32:1201–1206
Arenas A, Vicente S, Luque I, Gomez-Villamandos JC, Astorga R, Maldonado A, Tarradas C (1999) Outbreak of septicaemic colibacillosis in Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health 46:399–404
Arsenault J, Letellier A, Quessy S, Normand V, Boulianne M (2007) Prevalence and risk factors for Salmonella sp. and Campylobacter sp. caecal colonization in broiler chicken and turkey flocks slaughtered in Quebec, Canada. Prev Vet Med 81:250–264
Atanassova V, Ring C (1999) Prevalence of Campylobacter sp. in poultry and poultry meat in Germany. Int J Food Microbiol 51:187–190
Barnes EM (1972) Avian intestinal flora with particular reference to possible ecological significance of cecal anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr 25:1475–1479
Barnes HJ, Gross WB (1997) Colibacillosis. In: Calnek BW, Barens HJ, Beard CW, MacDougald LR, Saif YM (eds) Diseases of Poultry, 10th ed, 131–141
Beja P, Gordinho L, Reino L, Loureiro F, Santos-Reis M, Borralho R (2009) Predator abundance in relation to small game management in southern Portugal: conservation implications. Eur J Wildl Res 55:227–238
Benskin MHC, Wilson JK, Hartley IR (2009) Bacterial pathogens in wild birds: a review of the frequency and effects of infection. Biol Rev 84:349–373
Bernabeu RL (2000) Evaluación económica de la caza en Castilla-La Mancha. Thesis Dissertation. Castilla-La Mancha University, Spain
Brittingham MC, Temple SA, Duncan RM (1988) A survey of the prevalence of selected bacteria in wild birds. J Wildl Dis 24:299–307
Cramp S, Simmons KEL (1980) Red-legged partridge. In: Handbook of the birds of Europe, Middle East and North Africa: hawks to bustards (ed) Oxford University Press. Oxford pp: 436–469
Craven SE, Stern NJ, Line E, Bailey JS, Cox NA, Fedorka-Cray P (2000) Determination of the incidence of Salmonella spp., Campylobacter jejuni and Clostridium perfringes in wild birds near broiler chicken houses by sampling intestinal droppings. Avian Dis 44:715–720
Creitz JR, Small NN (1967) Escherichia coli septicaemia in pheasants. J Wildl Dis 3:68–69
Cunningham AA (1996) Disease risks of wildlife translocations. Conserv Biol 10:349–353
Damaré JM, Hussong D, Weiner RM, Colwell RR (1979) Aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacteria associated with the gut of Canada geese (Branta canadiensis) and whistling swans (Cygnus colombianus colombianus). Appl Environ Microbiol 38:258–265
Dho-Moulin M, Fairbrother JM (1999) Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Vet Res 30:22–316
Dipineto L, Gargiulo A, Bossa LMD, Rinaldi L, Borreli L, Menna LF, Fioretti A (2008) Prevalence of thermotolerant Campylobacter in pheasants (Phaisanus colchicus). Avian Pathol 37:507–508
Dipineto L, Gargiulo A, Bossa LMD, Rinaldi L, Borreli L, Santaniello A, Menna LF, Fioretti A (2009) Prevalence of thermotolerant Campylobacter in partridges (Perdix perdix). Lett Appl Microbiol 49:351–353
Draycott RAH, Woodburn MIA, Ling DE, Sage RB (2006) The effect of an indirect antihelmintic treatment on parasites and breeding success of free-living pheasants (Phaisanus colchicus). J Helmintol 80:409–415
Duarte J, Vargas JM (2004) Field interbreeding of released farm-reared partridges (Alectoris rufa) with wild ones. Game Wildl Sci 21:55–61
Duarte J, Farfán MA, Vargas JM (2010) New data on mortality, home range and dispersal of red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa) released in a mountain range. Eur J Wildl Res. doi:10.1007/s10344-010-0467-9
Durairaj V, Dustan FC (2007) E. coli an opportunist that causes enteritis. Avian Advice 9:3
El-Ghareeb WR, Smulders FJM, Morshdy AMA, Winkelmayer R, Paulsen P (2009) Microbiological condition and shelf life of meat from hunted game birds. Eur J Wildl Res 55:317–323
Fiennes RN (1959) Report of the society’s pathologist for the year 1957. Proc Zool Soc Lond 132:129–146
Foster G, Ross HM, Pennycott TW, Hopkins GF, McLaren IM (1998) Isolation of Escherichia coli 186:K61 producing cyto-lethal distending toxin from wild-birds of the finch family. Lett Appl Microbiol 26:395–398
Garrido JL (2002) Capturas de perdiz roja (Economía inducida por la caza de perdiz) In: Aportaciones a la gestión sostenible de la caza, tomo I. FEDENCA. Madrid, 141–147
Gibbens JC, Pascoe SJS, Evans SJ, Davies RH, Sayers AR (2001) A trial of biosecurity as a means to control Campylobacter infection of broiler chickens. Prev Vet Med 48:85–99
Gibbs PS, Kasa R, Newbrey JL, Petermann SR, Wooley RE, Vinson HM, Reed W (2007) Identification, antimicrobial resistance profiles and virulence of members from the Family Enterobacteriaceae from the feces of Yellow Headed Blackbirds (Xantocephalus xantocephalus) in North Dakota. Avian Dis 51:649–655
Gill CO (2007) Microbiological conditions of meats from large game animals and birds. Meat Sci 77:149–160
Glünder G (1981) Occurrence of Enterobacteriaceae in feces of granivorous passeriform birds. Avian Dis 25:195–198
Glünder G (2002) Influence of diet on the occurrence of some bacteria in the intestinal flora of wild and pet birds. Dtsch Tierärztl Wschr 109:266–270
Goodchild WM, Tucker JF (1968) Salmonellae in British wild birds and their transfer to domestic fowl. Br Vet J 124:95–101
Gortázar C, Villafuerte R, Martín M (2000) Success of traditional restocking of red-legged partridge for hunting purposes in areas of low density of northeast Spain, Aragón. Z Jadwiss 46:23–30
Gross WB (1984) Effect of a range of social stress severity on Escherichia coli challenge infection. Am J Vet Res 45:2074–2076
Hanssen I (1979) A comparison of the microbiological conditions in the small intestine and caeca of wild and captive willow grouse (Lagopus lagopus lagopus). Acta Vet Scand 20:365–371
Heryford AG, Seys SA (2004) Outbreak of occupational Campylobacteriosis associated with pheasant farm. J Agric Saf Health 10:127–132
Heuvelink AE, Zwartkruis JTM, Van Heerwaarden C, Arends B, Stortelder V, de Boer E (2008) Pathogenic bacteria and parasites in wildlife and surface water. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd 133:330–335
Hudson PJ, Dobson AP, Newborn D (1992) Do parasites make prey vulnerable to predation? Red grouse and parasites. J Anim Ecol 61:681–692
ISO 6579 (2002) Microbiology of food an animal feeding stuffs. Horizontal method for the detection of Salmonella sp.
Ito K, Kubona Y, Kaneko K, Totake Y, Ogawa M (1988) Ocurrence of Campylobacter jejuni in free-living wild birds from Japan. J Wildl Dis 24(3):467–470
Kapperud G, Rosef O (1983) Avian wildlife reservoir of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni, Yersinia sp. and Salmonella sp. in Norway. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:375–380
La Ragione RM, Cooley WA, Parmar DDG, Ainsworth HL (2004) Attaching and effacing Escherichia coli O103: K+:H- in red-legged partridges. Vet Rec 155:397–398
Leitner G, Heller ED (1992) Colonization of Escherichia coli in young turkeys and chickens. Avian Dis 36:211–220
Lucientes J (1998) Las principales patologías de la perdiz roja silvestre. La perdiz roja, I curso, FEDENCA/Grupo Editorial V, Madrid, Spain
Luechtefeld NAW, Blaser MJ, Reller LB, Wang WLL (1980) Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp jejuni from migratory waterfowl. J Clin Microbiol 12:406–408
Lutful Kabir SM (2010) Avian Colibacillosis and Salmonellosis: a closer look at epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, control and public health concerns. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7:89–114
Madsen H (1941) The occurrence of helminths and coccidian in partridges and pheasants in Denmark. J Parasitol 27:29–34
Martínez J, Viñuela J, Villafuerte R (2002) Socioeconomic and cultural aspectos of gamebird hunting. REGHAB project, European Commisision, Brussels, Belgium
Matsusaki SA, Katayama K, Hagok H, Yamagota K, Tanaka T, Yamami T, Uchida W (1986) Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli among wild and domestic animals in Yamagochi prefecture. Microbiol Inmununology 30:1317–1322
Meriggi A, Brangi A, Cuccus P, Della Stella RM (2002) High mortality rate in a re-introduced grey partridge population in central Italy. Ital J Zool 69:19–24
Millán J (2009) Diseases of the red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa L.): a review. Wildl Biol Pract 5:70–88
Millán J, Gortázar C, Buenestado FJ, Rodriguez P, Tortosa FS, Villafuerte R (2003) Effects of a fiber rich diet on physiology and survival of farm-reared red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa). Comp Biochem Physiol 134:85–91
Millán J, Gortázar C, Martin-Mateo MP, Villafuerte R (2004) Comparative survey of the ectoparasite fauna of wild and farm-reared red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa) with an ecological study in wild birds populations. Parasitol Res 93:605–611
Naldo JL, Silvanose CD, Samour JH, Bailey TA (1998) Developmental intestinal aerobic microflora in the kori bustard (Ardeotis kori). Avian Pathol 27:359–365
Newell DG, Fearnley C (2003) Sources of Campylobacter colonization in broiler chickens. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4343–4351
Paulsen P, Nagy J, Popelka P, Ledecky V, Marcincak S, Pipova M, Smulders FJM, Hofbauer P, Lazar P, Dicakova Z (2008) Influence of storage conditions and shotshell wounding on the higyenic condition of hunted, uneviscerated pheasant (Phaisanus colchicus). Poult Sci 87:191–195
Pierson FW, Barta VD (1996) Exposure to multiple infectious agents and the development of colibacillosis in turkeys. J Appl Poult Res 5:347–357
Putaala A, Hissa R (1995) Effects of hand-rearing on physiology and anatomy in the gray partridge. Wildl Biol 1:27–31
Ramos R, Cerdá-Cuéllar M, Ramírez F, Jover L, Ruiz X (2010) Influence of refuse sites on the prevalence of Campylobacter sp and Salmonella serovars in seagulls. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3052–3056
Robino P, Tomassone L, Tramuta C, Rodo M, Giammarino M, Vaschetti G, Nebbia P (2010) Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli and enteric Helicobacter in domestic and free living birds in North-Western Italy. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd 152:425–431
Shini S, Huff GR, Shini A, Kaiser P (2010) Understanding stress-induced inmunosuppression: Exploration of cytokine and chemokine gene profiles in chicken peripheral leukocytes. Poult Sci 89:841–851
Stephens CP, On SLW, Gibson JA (1998) An outbreak of infectious hepatitis in commercially reared ostriches associated with Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni. Vet Microbiol 61:183–190
Tompkins DM, Greenman JV, Hudson PJ (2001) Differential impact of shared nematode parasite on two gamebird hosts: implications for apparent competition. Parasitology 122:187–193
Tompkins DM, Parish DMB, Hudson PJ (2002) Parasite-mediated competition among red-legged partridges and other lowland gamebirds. J Wildl Manage 66:445–450
Vázquez B, Esperón F, Neves E, López J, Ballesteros C, Muñoz MJ (2010) Screening for several potential pathogens in feral pigeons (Columba livia) in Madrid. Acta Vet Scand 52:6
Viggers KL, Lindenmayer DB, Spratt DM (1993) The importance of disease in reintroduction programmes. Wildl Res 20:687–698
Villanúa D, Acevedo P, Höfle U, Rodriguez O, Gortázar C (2006) Changes in parasite transmission stage excretion after pheasant release. J Helmintol 80:313–318
Villanúa D, Casas F, Viñuela J, Gortázar C, Garcia de la Morena E, Morales M (2007a) First occurence of Eucoleus contortus in a Little Bustard (Tetrax tetrax). Negative effect of red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa) releases on steppe bird conservation? Ibis 195:405–406
Villanúa D, Perez-Rodriguez L, Rodriguez O, Viñuela J, Gortázar C (2007b) How effective is pre-release nematode control in farm-reared red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa)? J Helmintol 81:101–103
Villanúa D, Perez-Rodriguez L, Casas F, Alzaga V, Acevedo P, Viñuela J, Gortázar C (2008) Sanitary risks of red-legged partridge releases: introduction of parasites. E J Wild Res 54:199–204
Vláhovic KMB, Bata I, Pavalak M, Pavicic Z, Popovic M, Nejedli S, Dovc A (2004) Campylobacter, Salmonella and Chlamydia in free-living birds in Croatia. E J Wild Res 50:127–132
Volkheimer A, Wuthe HH (1986) Campylobacter jejuni/coli in partridges (Perdix perdix L.) and pheasants (Phaisanus colchicus L.). Berl Münch Tierärztl Wochenschr 99:374
Waldeström J, Broman T, Carlsson I, Hasselquist D, Achterberg RP, Wagenaar JA, Olsen B (2002) Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter lari and Campylobacter coli in different ecological guilds and taxa of migrating birds. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5911–5917
Waldeström J, Axelsson-Olsson D, Olsen B, Hasselquist D, Griekspoor P (2010) Campylobacter jejuni colonization in wild birds: results from an infection experiment. PLoS ONE 5(2):e9082
Wallace JS, Stanley KN, Jones K (1998) The colonization of turkeys by termophilic Campylobacters. J Appl Microbiol 85:224–230
Yogasundram K, Shane SM, Harrington KS (1989) Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni in selected domestic and wild birds in Lousiana. Avian Dis 33:664–667
Acknowledgements
The authors thank E. Perez, L. Perez-Rodriguez, F. Mougeot, J.T García, M. Calero Riestra and C. Alonso for their assistance in the field and D. Vidal and S. Sánchez-Prieto for the technical assistance. This study was funded by Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha (JCCM, Spain; project reference: PAC08-0296-7771) and is also a contribution to project Ag2008-02504GAN funded by the Spanish Ministry for Science and Innovation. Capture of partridges from natural populations was carried out under projects PII1I09-0271-5037, PAI06-0112 and PAII1C09-0227-0104. Sandra Diaz-Sanchez holds a PhD research grant funded by Junta de Comunidades de Castilla–La Mancha (JCCM) (AG07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Gortázar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-Sánchez, S., Moriones, A.M., Casas, F. et al. Prevalence of Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp. and Campylobacter sp. in the intestinal flora of farm-reared, restocked and wild red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa): is restocking using farm-reared birds a risk?. Eur J Wildl Res 58, 99–105 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-011-0547-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-011-0547-5