Abstract
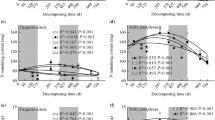
Changes in soil microclimate driven by forest gaps have accelerated mass loss and carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) release from foliar litter in alpine forests ecosystems. Yet, it is unclear whether the same gap effect occurs in twig litter decomposition. A 4-year decomposition experiment was conducted in an alpine forest to explore the litter mass loss and C, N and P release among four gap treatments, including (1) closed canopy, (2) small gap (< 10 m in diameter), (3) middle gap (10–15 m in diameter) and (4) large gap (15–20 m in diameter). Compared to the closed canopy, thicker snow cover within gaps resulted in higher soil temperatures but lower frequency of the freeze–thaw cycles during winter. Moreover, gaps slowed the decay rate and C, N and P release after 4-year decomposition, and a total 31–62% of mass, 42–91% of C, 21–111% of N and all P were lost across gaps in winter. Statistical analysis indicated that gap-caused changes in soil temperature and freeze–thaw cycle had significant effects on C, N and P release of twig litter. This study highlights the importance of winter decomposition and gap-driven process in alpine forest ecosystems in southwestern China.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Callaghan TV, Dorrepaal E, van Logtestijn RSP, Cornelissen JHC (2012) Seasonal climate manipulations have only minor effects on litter decomposition rates and N dynamics but strong effects on litter P dynamics of subarctic bog species. Oecologia 170:809–819
Berg B, McClaugherty C (2014) Plant litter: decomposition, humus formation, carbon sequestration, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Bokhorst S, Bjerke JW, Melillo J, Callaghan TV, Phoenix GK (2010) Impacts of extreme winter warming events on litter decomposition in a sub-Arctic heathland. Soil Biol Biochem 42:611–617
Brokaw NVL (1982) The definition of treefall gap and its effect on measures of forest dynamics. Biotropica 14:158–160
Brussaard LB, Pulleman MM, Ouedraogo E, Mando A, Six J (2007) Soil fauna and soil function in the fabric of the soil food web. Pedobiologia 50:447–462
Buckeridge KM, Cen Y, Layzell DB, Grogan P (2010) Soil biogeochemistry during the early spring in low arctic mesic tundra and the impacts of deepened snow and enhanced nitrogen availability. Biogeochemistry 99:127–141
Campbell JL, Mitchell MJ, Groffman PM, Christenson LM, Hardy JP (2005) Winter in northeastern North America: a critical period for ecological processes. Front Ecol Environ 3:314–322
Chen B, Dong X, Cui L, Tang G (2015) Changes of litter hydrological capacity in low-quality forest in Daxing’ an mountains after ecological reformation. J Northeast For Univ 43:72–77 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Christenson LM, Mitchell MJ, Groffman PM, Lovett GM (2010) Winter climate change implications for decomposition in northeastern forests: comparisons of sugar maple litter with herbivore fecal inputs. Global Change Biol 16:2589–2601
Denslow JS, Ellison AM, Sanford RE (1998) Treefall gap size effects on above- and below-ground processes in a tropical wet forest. J Ecol 86:597–609
Edwards AC, Scalenghe R, Freppaz M (2007) Changes in the seasonal snow cover of alpine regions and its effect on soil processes: a review. Quat Int 162–163:172–181
Elser JJ, Fagan WF, Denno RF, Dobberfuhl DR, Folarin A, Huberty A, Interland S, Kilham SS, McCauley E, Schulz KL, Siemann EH, Sterner RW (2000) Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 408:578–580
Fu C, Yang W, Tan B, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Yang J, Ni X, Wu F (2017) Seasonal dynamics of litterfall in a sub-alpine spruce-fir forest on the eastern Tibetan Plateau: allometric scaling relationships based on one year of observations. Forests 8:314
Gallo AL, Moretto A, López Bernal P, Greslebin A (2019) Characterization and decomposition of Nothofagus pumilio fine woody material. Can J Forest Res 49:715–720
Garrett LG, Kimberley MO, Oliver GR, Pearce SH, Beets PN (2012) Decomposition of coarse woody roots and branches in managed Pinusradiata plantations in New Zealand: a time series approach. For Ecol Manag 269:116–123
Gliksman D, Haenel S, Osem Y, Yakir D, Zangy E, Preisler Y, Grünzweig JM (2018) Litter decomposition in Mediterranean pine forests is enhanced by reduced canopy cover. Plant Soil 422:317–329
González G, Lodge DJ, Richardson BA, Richardson MJ (2014) A canopy trimming experiment in Puerto Rico: the response of litter decomposition and nutrient release to canopy opening and debris deposition in a subtropical wet forest. For Ecol Manag 332:32–46
Groffman PM, Hardy JP, Fisk MC, Fahey TJ, Driscoll CT (2009) Climate variation and soil carbon and nitrogen cycling processes in a northern hardwood forest. Ecosystems 12:927–943
He W, Wu F, Yang W, Zhang D, Xu Z, Tan B, Zhao Y, Justine MF (2016) Gap locations influence the release of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in two shrub foliar litter in an alpine fir forest. Sci Rep 6:22014
IUSS Working Group (2014) World reference base for soil resources: international soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. World soil resources reports
Kneeshaw DD, Bergeron Y (1998) Canopy gap characteristics and tree replacement in the southeastern boreal forest. Ecology 79:783–794
Konestabo HS, Michelsen A, Holmstrup M (2007) Responses of springtail and mite populations to prolonged periods of soil freeze–thaw cycles in a sub-arctic ecosystem. Appl Soil Ecol 36:136–146
Ladwig LM, Ratajczak ZR, Ocheltree TW, Hafich KA, Churchill AC, Frey SJK, Fuss CB, Kazanski CE, Muñoz JD, Petrie MD, Reinmann AB, Smith JG (2016) Beyond arctic and alpine: the influence of winter climate on temperate ecosystems. Ecology 97:372–383
Li X, Zhu J, Lange H, Han S (2012) A modified ingrowth core method for measuring fine root production, mortality and decomposition in forests. Tree Physiol 33:18–25
Lin N, Bartsch N, Heinrichs S, Vor T (2015) Long-term effects of canopy opening and liming on leaf litter production, and on leaf litter and fine-root decomposition in a European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forest. For Ecol Manag 338:183–190
Liu Y, Zhang J, Yang W, Wu F, Xu Z, Tan B, Zhang L, He X, Guo L (2018) Canopy gaps accelerate soil organic carbon retention by soil microbial biomass in the organic horizon in a subalpine fir forest. Appl Soil Ecol 125:169–176
Lu R (1999) Soil and agro-chemical analytical methods. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing, pp 146–195 (in Chinese)
Moore TR, Trofymow JA, Prescott CE, Fyles J, Titus BD (2006) Patterns of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in decomposing foliar litter in Canadian forests. Ecosystems 9:46–62
Moore TR, Trofymow JA, Prescott CE, Titus BD, CIDET Working Group (2011) Nature and nurture in the dynamics of C, N and P during litter decomposition in Canadian forests. Plant Soil 339:163–175
Ni X, Yang W, Li H, Xu L, He J, Tan B, Wu F (2014) The responses of early foliar litter humification to reduced snow cover during winter in an alpine forest. Can J Soil Sci 94:453–461
Ni X, Berg B, Yang W, Li H, Liao S, Tan B, Yue K, Xu Z, Zhang L, Wu F (2018a) Formation of forest gaps accelerates C, N and P release from foliar litter during 4 years of decomposition in an alpine forest. Biogeochemistry 139:321–335
Ni X, Yang W, Liao S, Li H, Tan B, Yue K, Xu Z, Zhang L, Wu F (2018b) Rapid release of labile components limits the accumulation of humic substances in decomposing litter in an alpine forest. Ecosphere 9:e02434
Olajuyigbe SO, Tobin B, Gardiner P, Nieuwenhuis M (2011) Stocks and decay dynamics of above-and belowground coarse woody debris in managed Sitka spruce forests in Ireland. For Ecol Manag 262:1109–1118
Olson JS (1963) Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44:322–331
Prescott CE (1997) Effects of clearcutting and alternative silvicultural systems on rates of decomposition and nitrogen mineralization in a coastal montane coniferous forest. For Ecol Manag 95:253–260
Prescott CE, Blevins LL, Staley CL (2000) Effects of clearcutting on decomposition rates of litter and forest floor in forests of British Columbia. Can J For Res 30:1751–1757
Prescott CE, Hope GD, Blevins LL (2003) Effect of gap size on litter decomposition and soil nitrate concentrations in a high-elevation spruce-fir forest. Can J For Res 33:2210–2220
Ritter E, Bjørnlund L (2005) Nitrogen availability and nematode populations in soil and litter after gap formation in a seminatural beech-dominated forest. Appl Soil Ecol 28:175–189
Ritter E, Dalsgaard L, Einhorn KS (2005) Light, temperature and soil moisture regimes following gap formation in a semi-natural beech-dominated forest in Denmark. For Ecol Manag 206:15–33
Sariyildiz T (2008) Effects of gap-size classes on long-term litter decomposition rates of beech, oak and chestnut species at high elevations in Northeast Turkey. Ecosystems 11:841–853
Scharenbroch BC, Bockheim JG (2008) Gaps and soil C dynamics in old growth northern hardwood–hemlock forests. Ecosystems 11:426–441
Schliemann SA, Bockheim JG (2011) Methods for studying treefall gaps: a review. For Ecol Manag 261:1143–1151
Shorohova E, Kapitsa E (2016) The decomposition rate of non-stem components of coarse woody debris (CWD) in European boreal forests mainly depends on site moisture and tree species. Eur J Forest Res 135:593–606
Tan B, Wu F, Yang W, Liu L, Yu S (2010) Characteristics of soil animal community in the subalpine/alpine forests of western Sichuan during onset of freezing. Acta Ecol Sin 30:93–99
Tan B, Wu F, Yang W, He X (2014) Snow removal alters soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in a Tibetan alpine forest. Appl Soil Ecol 76:34–41
Vesterdal L (1999) Influence of soil type on mass loss and nutrient release from decomposing foliage litter of beech and Norway spruce. Can J For Res 29:95–105
Wu F, Yang W, Zhang J, Deng R (2010) Litter decomposition in two subalpine forests during the freeze–thaw season. Acta Oecol 36:135–140
Wu Q, Wu F, Yang W, Tan B, Yang Y, Ni X, He J (2013) Characteristics of gaps and disturbance regimes of the alpine fir forest in western Sichuan. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 19:922–928 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu F, Peng C, Zhu J, Zhang J, Tan B, Yang W (2014) Impacts of freezing and thawing dynamics on foliar litter carbon release in alpine/subalpine forests along an altitudinal gradient in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Biogeosciences 11:6471–6481
You C, Wu F, Yang W, Xu Z, Tan B, Zhang L, Yue K, Ni X, Li H, Chang C, Fu C (2018) Does foliar nutrient resorption regulate the coupled relationship between nitrogen and phosphorus in plant leaves in response to nitrogen deposition? Sci Total Environ 645:733–742
Yue K, Peng Y, Fornara DA, Van Meerbeek K, Vesterdal L, Yang W, Peng C, Tan B, Zhou W, Xu Z, Ni X, Zhang L, Wu F, Svenning JC (2019) Responses of nitrogen concentrations and pools to multiple environmental change drivers: a meta-analysis across terrestrial ecosystems. Global Ecol Biogeogr 28:690–724
Zhang Q, Liang Y (1995) Effects of gap size on nutrient release from plant litter decomposition in a natural forest ecosystem. Can J For Res 25:1627–1638
Zhang Q, Zak JC (1995) Effects of gap size on litter decomposition and microbial activity in a subtropical forest. Ecology 76:2196–2204
Zhang Q, Zak JC (1998) Potential physiological activities of fungi and bacteria in relation to plant litter decomposition along a gap size gradient in a natural subtropical forest. Microb Ecol 35:172–179
Zhu J, Yang W, He X (2013) Temporal dynamics of abiotic and biotic factors on leaf litter of three plant species in relation to decomposition rate along a subalpine elevation gradient. PLoS ONE 8:e62073
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Dr. Wei He and Dr. Qiqian Wu for their helpful suggestions on the statistical analysis. We also thank the long-term experimental platform—Research Station of Alpine Forest Ecosystems. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870602, 31700542 31570601 and 31500509). Bo Tan and Chengming You acknowledge the China Scholarship Council for supporting a visiting scholar program grant (201806915014) and Ph.D. program grant (201806910030), respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Agustín Merino.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, B., Zhang, J., Yang, W. et al. Forest gaps retard carbon and nutrient release from twig litter in alpine forest ecosystems. Eur J Forest Res 139, 53–65 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-019-01229-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-019-01229-8