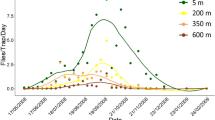
Abstract
Delottococcus aberiae De Lotto (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) is a new invasive citrus pest in Spain. It causes severe fruit distortions and, as a new invasive mealybug, there is a lack of information about its biology. This research aims to examine the seasonal trend of D. aberiae in citrus, using several sampling methods, as a first step to develop an integrated pest management program. Ten citrus orchards from Eastern Spain were periodically sampled during three years using absolute (plant material) and relative (corrugated cardboard band traps and sticky traps) sampling methods. The three sampling methods showed that D. aberiae completes multiple generations per year, two of them being clearly defined and resulting in high populations. D. aberiae peaked between May and June, damaging the developing fruit. Corrugated cardboard band traps were able to detect prepupa and pupa male instars and gravid females, providing a quantitative measurement of D. aberiae density at its first population peak. The use of corrugated cardboard band traps is recommended to monitor population levels and sticky traps to determine male flight periods, representing simple sampling techniques to monitor D. aberiae. These results will improve the sampling protocols and allow for the development of an integrated pest management program.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afifi SA (1968) Morphology and taxonomy of the adult males of the families Pseudococcidae and Eriococcidae: (Homoptera:Coccoidea). Bull Br Mus (Nat Hist) Entomol, Suppl 13. London
Agustí M (2003) Citricultura. Mundi-Prensa, Madrid
Bahder BW, Naidu RA, Daane KM, Millar JG, Walsh DB (2013) Pheromone-based monitoring of Pseudococcus maritimus (Hemiptera:Pseudococcidae) populations in concord grape vineyards. J Econ Entomol 106:482–490. doi:10.1603/ec12138
Bartlett BR, Clancy DW (1972) The comstock mealybug in California and observations on some of its natural enemies. J Econ Entomol 65:1329–1332
Beardsley JW (1960) A preliminary study of the males of some hawaiian mealybugs (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae). Proc Hawaii Entomol Soc 16:199–243
Beltrà A, Soto A (2012) Pseudocóccidos de importancia agrícola y ornamental en España. Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València, Spain
Beltrà A, Soto A, Germain J-F, Matile-Ferrero D, Mazzeo G, Pellizzari G, Russo A, Franco JC, Williams DJ (2010) The Bougainvillea mealybug Phenacoccus peruvianus, a rapid invader from South America to Europe. Entomol Hellenica 19:137–143
Beltrà A, Soto A, Malausa T (2012) Molecular and morphological characterisation of Pseudococcidae surveyed on crops and ornamental plants in Spain. Bull Entomol Res 102:165–172. doi:10.1017/S0007485311000514
Beltrà A, Garcia-Marí F, Soto A (2013a) El cotonet de Les Valls, Delottococcus aberiae, nueva plaga de los cítricos. Levante Agrícola 419:348–352
Beltrà A, Garcia-Marí F, Soto A (2013b) Seasonal phenology, spatial distribution, and sampling plan for the invasive mealybug Phenacoccus peruvianus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). J Econ Entomol 106:1486–1494. doi:10.1603/ec13024
Beltrà A, Tena A, Soto A (2013c) Reproductive strategies and food sources used by Acerophagus n. sp. near coccois, a new successful parasitoid of the invasive mealybug Phenacoccus peruvianus. J Pest Sci 86:253–259. doi:10.1007/s10340-012-0475-5
Beltrà A, Addison P, Avalos JA, Crochard D, Garcia-Mari F, Guerrieri E, Giliomee JH, Malausa T, Navarro-Campos C, Palero F, Soto A (2015) Guiding classical biological control of an invasive mealybug using integrative taxonomy. PLoS ONE 10:e0128685. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0128685
Ben-Dov Y (1994) A systematic catalogue of the mealybugs of the world (Insecta: Homoptera: Coccoidea: Pseudococcidae and Putoidae), with data on geographical distribution, host plants, biology and economic importance. Intercept Limited, AndoverUK
Blumberg D, Ben-Dov Y, Mendel Z (1999) The citrulus mealybug, Pseudococcus cryptus Hempel, and its natural enemies in Israel: history and present situation. Entomologica 33:141–152
Browning TO (1959) The long-tailed mealybug, Pseudocuccus aonidum (L.), in South Australia. J Agric Res 10:322–339
De Lotto G (1961) New Pseudococcidae (Homoptera: Coccoidea) from Africa. Bull Br Mus (Nat Hist) Entomol 10:211–238
De Villiers M, Pringle KL (2007) Seasonal occurrence of vine pests in commercially treated vineyards in the Hex River Valley in the Western Cape Province, South Africa. Afr Entomol 15:241–260
DeBach P (1949) Population studies of the long-tailed mealybug and its natural enemies on citrus trees in Southern California. Ecology 30:14–25
Franco J (1994) Citrus phenology as a basis to study the population dynamics of the citrus mealybug complex in Portugal. In: Tribulato E, Gentile A, Reforgiato G (eds) Proceedings of the international society of citriculture, vol 3, pp 929–930
Franco JC, Silva EB, Carvalho JP (2000) Cochonilhas-algodão (Hemiptera, Pseudococcidae) associadas aos citrinos em Portugal. ISA Press, Lisboa
Franco JC, Suma P, Silva EB, Blumberg D, Mendel Z (2004) Management strategies of mealybug pests of citrus in mediterranean countries. Phytoparasitica 32:507–522
Franco JC, Zada A, Mendel Z (2009) Novel approaches for the management of mealybug pests. In: Ishaaya I, Horowitz AR (eds) Biorational control of arthropod pests: application and resistance managements. Springer, Netherlands, pp 233–278. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-2316-2_10
Furness G (1976) The dispersal, age-structure and natural enemies of the long-tailed mealybug, Pseudocccus longispinus (Targioni-Tozzetti), in relation to sampling and control. Aust J Zool 24:237–247
García-Morales M, Denno BD, Miller DR, Miller GL, Ben-Dov Y, Hardy NB (2016) ScaleNet: a literature-based model of scale insect biology and systematics. Database (Oxford) 2016:1–5. doi:10.1093/database/bav118
Geiger CA, Daane KM (2001) Seasonal movement and distribution of the grape mealybug (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae): developing a sampling program for San Joaquin Valley vineyards. J Econ Entomol 94:291–301. doi:10.1603/0022-0493-94.1.291
Gonzalez D (1971) Sampling as a basis for pest management strategies. In: Komarek EV (ed) Proceedings of the tall timbers conference on ecological animal control by habitat management, vol 2, pp 83–101
Goolsby J, Kirk A, Meyerdirk DE (2002) Seasonal phenology and natural enemies of Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) in Australia. Fla Entomol 85:494–498
Grimes E, Cone W (1985) Life history, sex attraction, mating and natural enemies of the grape mealybug, Pseudococcus maritimus (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 78:554–558
Grout TG, Richards GI (1991) Value of pheromone traps for predicting infectations of red scale Aonidiella aurantii (Maskell) (Hom., Diaspididae), limited by natural enemy activity and insecticides used to control citrus thrips, Scirtothrips aurantii Faure (Thys., Thripidae). J Appl Entomol 111:20–27
Gullan PJ, Martin J (2009) Sternorrhyncha (jumping plant-lice, whiteflies, aphids, and scale insects). In: Vincent H, Resh RTC (eds) Encyclopedia of insects. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 957–967
Hall DG, Roda A, Lapointe SL, Hibbard K (2008) Phenology of Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) in Florida based on attraction of adult males to pheromone traps. Fla Entomol 91:305–310
Hardy NB, Gullan PJ, Hodgson CJ (2008) A subfamily-level classification of mealybugs (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) based on integrated molecular and morphological data. Syst Entomol 33:51–71
Hattingh V, Cilliers C, Bedford E (1998) Citrus mealybugs. In: Bedford E, Van den Berg M, De Villiers E (eds) Citrus pests in the Republic of South Africa. ARC-ITSC, South Africa, pp 112–120
Haviland DR, Beede RH, Daane KM (2012) Seasonal phenology of Ferrisia gilli (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) in commercial pistachios. J Econ Entomol 105:1681–1687. doi:10.1603/ec12070
Hulme PE, Bacher S, Kenis M, Klotz S, Kühn I, Minchin D, Nentwig W, Olenin S, Panov V, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Roques A, Sol D, Solarz W, Vilà M (2008) Grasping at the routes of biological invasions: a framework for integrating pathways into policy. J Appl Ecol 45:403–414. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01442.x
Islam KS, Copland MJW (1997) Host preference and progeny sex ratio in a solitary koinobiont mealybug endoparasitoid, Anagyrus pseudococci (Girault), in response to its host stage. Biocontrol Sci Technol 7:449–456. doi:10.1080/09583159730857
Jervis MA, Copland MJW, Harvey JA (2005) The lyfe-cycle. In: Jervis MA (ed) Insect as natural enemies: a practical perspective. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 73–165
Kenis M, Auger-Rozenberg MA, Roques A, Timms L, Péré C, Cock MJW, Settele J, Augustin S, Lopez-Vaamonde C (2009) Ecological effects of invasive alien insects. In: Langor DW, Sweeney J (eds) Ecological impacts of non-native invertebrates and fungi on terrestrial ecosystems. Springer, Netherlands, pp 21–45. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9680-8_3
Kozár F (1989) Microhabitat specialization and similarity of scale-insect assemblages on different fruit trees and in different countries. Ecol Entomol 14:175–180
Lacirignola C, D’Onghia AM (2009) The Mediterranean citriculture: productions and perspectives. In: D’Onghia AM, Djelouah K, Roistacher CN (eds) Citrus tristeza virus and Toxoptera citricidus: a serious threat to the Mediterranean citrus industry. Options Méditerranéennes: Série B. Etudes et Recherches, vol 65. CIHEAM, Bari, pp 13–17
Longo S, Mazzeo G, Russo A (1995) Biological observations on some scale insects (Homoptera: Coccoidea) in Sicily. Isr J Entomol 29:219–222
Mansour R, Grissa-Lebdi K, Suma P, Mazzeo G, Russo A (2017) Key scale insects (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) of high economic importance in a Mediterranean area: host plants, bio-ecological characteristics, natural enemies and pest management strategies—a review. Plant Prot Sci 53:1–14. doi:10.17221/53/2016-pps
Martínez-Ferrer MT, García-Marí F, Ripollés JL (2003) Population dynamics of Planococcus citri (Risso) (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) in citrus groves in Spain. IOBC-WPRS Bull 26:149–161
Martínez-Ferrer MT, Ripollés JL, Garcia-Marí F (2006) Enumerative and binomial sampling plans for citrus mealybug (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) in citrus groves. J Econ Entomol 99:993–1001. doi:10.1603/0022-0493-99.3.993
Mazzeo G, Russo A, Suma P (1999) Phenacoccus solani ferris (Homoptera: Coccoidea) on ornamental plants in Italy. Boll Zool agr Bachic 31:31–35
Mazzeo G, Longo S, Pellizzari G, Porcelli F, Suma P, Russo A (2014) Exotic scale insects (Coccoidea) on ornamental plants in Italy: a never-ending story. Acta Zool Bulg 6:55–61
McKenzie HL (1967) Mealybugs of California, with taxonomy, biology, and control of North American species (Homoptera: Coccoidea: Pseudococcidae). Cambridge University Press, Berkeley
Mendel Z, Watson GW, Protasov A, Spodek M (2016) First record of the papaya mealybug, Paracoccus marginatus Williams & Granara de Willink (Hemiptera: Coccomorpha: Pseudococcidae), in the Western Palaearctic. EPPO Bull 46:580–582. doi:10.1111/epp.12321
Meyerdirk DE, Newell IM (1979) Seasonal development and flight activity of Pseudocccus comstocki in California. Ann Entomol Soc Am 72:492–494
Meyerdirk DE, Newell IM, Warkentin RW (1981) Biological control of comstock mealybug. J Econ Entomol 74:79–84
Meyerdirk DE, Warkentin R, Attavien B, Gersabeck E, Fracis A, Adams M, Francis G (2001) Biological control of pink hibiscus mealybug project manual. United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Washington
Millar JG, Daane KM, McElfresh JS, Moreira JA, Malakar-Kuenen R, Guillén M, Bentley WJ (2002) Development and optimization of methods for using sex pheromone for monitoring the mealybug Planococcus ficus (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) in California vineyards. J Econ Entomol 95:706–771
Miller DR, Giliomee JH (2011) Systematic revision of the mealybug genus Delottococcus Cox & Ben-Dov (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). Afr Entomol 19:614–640
Miller DR, Miller GL, Watson GW (2002) Invasive species of mealybugs (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) and their threat to U.S. agriculture. Proc Entomol Soc Wash 104:825–836
Moreno DS, Reed DK, Shaw JG, Newell IM (1972) Sex lure survey trap for comstock mealybug. Citograph 58(43):68
Moreno DS, Fargerlund J, Ewart WH (1984) Citrus mealybug (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae): behavior of males in response to sex pheromone in laboratory and field. Ann Entomol Soc Am 77:32–38
Mudavanhu P (2009) An investigation into the integrated pest management of the obscure mealybug, Pseudococcus viburni (Signoret) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), in pome fruit orchards in the Western Cape Province, South Africa. Dissertation, University of Stellenbosch
Mudavanhu P, Addison P, Pringle Ken L (2011) Monitoring and action threshold determination for the obscure mealybug Pseudococcus viburni (Signoret) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) using pheromone-baited traps. Crop Prot 30:919–924. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2011.02.034
Panis A (1986) Biological features of Pseudococcus affinis (Mask.) (Homoptera, Pseudococcidae) as guidelines of its control in water-sprinkled citrus orchards. In: Cavalloro R, Di Martino E (eds) Integrated pest control in citrus groves. Proceedings of the expert’s meetings, pp 59–65
Pellizzari G (2005) Cocciniglie nuove o poco note potenzialmente dannose per l’Italia: Fiorinia pinicola Maskell, Pseudococcus comstocki (Kuwana), Peliococcus turanicus (Kiritshenko). Inf Fitopatol 55:20–25
Pellizzari G, Germain J-F (2010) Scales (Hemiptera, Superfamily Coccoidea), Chapter 9.3. BioRisk 4:475–510. doi:10.3897/biorisk.4.45
Pellizzari G, Porcelli F (2014) Alien scale insects (Hemiptera Coccoidea) in European and Mediterranean countries: the fate of new and old introductions. Phytoparasitica 42:713–721. doi:10.1007/s12600-014-0414-5
Pimentel D, McNair S, Janecka J, Wightman J, Simmonds C, O’Connell C, Wong E, Russel L, Zern J, Aquino T, Tsomondo T (2001) Economic and environmental threats of alien plant, animal, and microbe invasions. Agric Ecosyst Environ 84:1–20
Roltsch WJ, Meyerdirk DE, Warkentin R, Andress ER, Carrera K (2006) Classical biological control of the pink hibiscus mealybug, Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Green), in southern California. Biol Control 37:155–166. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2006.01.006
Roques A, Rabitsch W, Rasplus J-Y, Lopez-Vaamonde C, Nentwig W, Kenis M (2009) Alien terrestrial invertebrates of Europe. In: DAISIE (ed) Handbook of alien species in Europe, vol 3. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 63–79. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-8280-1
Rotundo G, Tremblay E (1975) Sull’attrattività delle femmine vergini di due specie di Pseudococcidi (Homoptera Coccoidea) per un Imenottero parassita (Hymenoptera Chalcidoidea). Boll Lab Entomol Agr Portici 32:172–179
Samways MJ (1988) Comparative monitoring of red scale Aonidiella aurantii (Mask.) (Hom., Diaspididae) and its Aphytis spp. (Hym., Aphelinidae) parasitoids. J Appl Entomol 105:483–489
Santorini A (1977) Etude de quelques caractères biologiques de Planococcus citri (Risso) en Grèce (Homoptera, Coccoidea, Pseudococcidae). Fruits 32:611–612
Serrano MS, Lapointe SL, Meyerdirk DE (2001) Attraction of males by virgin females of the mealybug Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). Popul Ecol 30:339–345
Soto A, Martínez-Blay V, Beltrà A, Pérez-Rodríguez J, Tena A (2016a) Delottococcus aberiae (De Lotto) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), comportamiento de la plaga en parcelas de cítricos valencianos. Phytoma 277:49–53
Soto A, Martínez-Blay V, Benito M, Beltrà A (2016b) Delottococcus aberiae (De Lotto) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae): viabilidad de su control biológico. Phytoma 284:85–87
Suckling DM (2000) Issues afecting the use of pheromones and other semiochemicals in orchards. Crop Prot 19:677–683
Suma P, Mazzeo G, La Pergola A, Nucifora S, Russo A (2015) Establishment of the pineapple mealybug Dysmicoccus brevipes (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) in Italy. EPPO Bull 45:218–220. doi:10.1111/epp.12206
Sun J, Clarke SR, DeBarr GL, Berisford CW (2002) Yellow sticky traps for monitoring males and two parasitoids of Oracella acuta (Lobdell) (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae). J Entomol Sci 37:177–181
Tena A, García-Marí F (2011) Current situation of citrus pests and diseases in the Mediterranean basin. IOBC/WPRS Bull 62:365–378
Tena A, Catalán J, Bru P, Urbaneja A (2014) Delottococcus aberiae, nueva plaga de cítricos. Agricultura 978:746–748
Tena A, García-Bellón J, Urbaneja A (2017) Native and naturalized mealybug parasitoids fail to control the new citrus mealybug pest Delottococcus aberiae. J Pest Sci 90:659–667. doi:10.1007/s10340-016-0819-7
Tremblay E, Tranfaglia A, Rotundo G, Iaccarino F (1977) Osservazioni comparate su alcune specie di Pseudococcidi (Homoptera: Coccoidea). Boll Lab Entomol Agr Portici 34:113–135
Walton VM, Daane KM, Pringle KL (2004) Monitoring Planococcus ficus in South African vineyards with sex pheromone-baited traps. Crop Prot 23:1089–1096. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2004.03.016
Waterworth RA, Redak RA, Millar JG (2011) Pheromone-baited traps for assessment of seasonal activity and population densities of mealybug species (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) in nurseries producing ornamental plants. J Econ Entomol 104:555–565. doi:10.1603/ec10317
Way MJ, van Emden HF (2000) Integrated pest management in practice—pathways towards successful application. Crop Prot 19:81–103
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the owners of the orchards for allowing us to use their plantations and P. Bru (IVIA) and J. Catalán (IVIA) for their help in sampling. This research was supported by two predoctoral grants (FPU to V. Martínez-Blay and Val I + d to J. Pérez-Rodríguez from the Spanish Ministry of Education, Culture and Sport and Generalitat Valenciana, respectively), the European Grants FP7-IAPP #324475 ‘Colbics’ and FP7-IRSES #612566 ‘Biomodic,’ and a national project provided by INIA (Project No. RTA2014-00067). The authors thank Debra Westall (UPV) for revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by A.R. Horowitz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Blay, V., Pérez-Rodríguez, J., Tena, A. et al. Density and phenology of the invasive mealybug Delottococcus aberiae on citrus: implications for integrated pest management. J Pest Sci 91, 625–637 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0928-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0928-y