Abstract
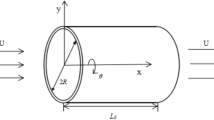
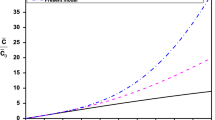
A dynamic Timoshenko beam model is established based on the new nonlocal strain gradient theory and slip boundary theory to study the wave propagation behaviors of fluid-filled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) at nanoscale. The nanoscale effects caused by the CNTs and the inner fluid are simulated by the nonlocal strain gradient effect and the slip boundary effect, respectively. The governing equations of motion are derived and resolved to investigate the wave characteristics in detail. The numerical solution shows that the strain gradient effect leads to the stiffness enhancement of CNTs when the nonlocal stress effect causes the decrease in stiffness. The dynamic properties of CNTs are affected by the coupling of these two scale effects. The flow velocity of fluid inside the CNT is increased due to the slip boundary effect, resulting in the promotion of wave propagation in the dynamic system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iijima S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature. 1991;354(6348):56–8.
Treacy MMJ, Ebbesen TW, Gibson JM. Exceptionally high Young’s modulus observed for individual carbon nanotubes. Nature. 1996;381(6584):678–80.
Wong EW, Sheehan PE, Lieber CM. Nanobeam mechanics elasticity, strength and toughness of nanorods and nanotubes. Science. 1997;277(5334):1971–5.
Ball P. Roll up for the revolution. Nature. 2001;414(6860):142–4.
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, de Heer WA. Carbon nanotubes-the route toward applications. Science. 2002;297(5582):787–92.
Hauquier F, Pastorin G, Hapiot P, et al. Carbon nanotube-functionalized silicon surfaces with efficient redox communication. Chem Commun. 2006;43(43):4536–8.
Liew KM, Wong CH, Tan MJ. Buckling properties of carbon nanotube bundles. Appl Phys Lett. 2005;87(4):041901–3.
Kitipornchai S, He XQ, Liew KM. Buckling analysis of triple-walled carbon nanotubes embedded in an elastic matrix. J Appl Phys. 2005;97(11):114318–24.
Yan Y, He XQ, Zhang LX, et al. Flow-induced instability of double-walled carbon nanotubes based on an elastic shell model. J Appl Phys. 2007;102(4):044307.
Yan Y, He XQ, Zhang LX, et al. Dynamic behavior of triple-walled carbon nanotubes conveying fluid. J Sound Vib. 2009;319(3–5):1003–18.
Yan Y, Wang WQ, Zhang LX. Dynamical behaviors of fluid-conveyed multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl Math Model. 2009;33(3):1430–40.
Yoon J, Ru CQ, Mioduchowski A. Vibration and instability of carbon nanotubes conveying fluid. Compos Sci Technol. 2005;65(9):1326–36.
Yoon J, Ru CQ, Mioduchowski A. Flow-induced flutter instability of cantilever carbon nanotubes. Int J Solids Struct. 2006;43(11–12):3337–49.
Eringen AC. Nonlocal continuum field theories. New York: Springer; 2002.
Bahaadini R, Hosseini M. Effects of nonlocal elasticity and slip condition on vibration and stability analysis of viscoelastic cantilever carbon nanotubes conveying fluid. Comput Mater Sci. 2016;114:151–9.
Zhen YX, Fang B. Nonlinear vibration of fluid-conveying single-walled carbon nanotubes under harmonic excitation. Int J Non Linear Mech. 2015;76:48–55.
Deng QT, Yang ZC. Vibration of fluid-filled multi-walled carbon nanotubes seen via nonlocal elasticity theory. Acta Mech Solida Sin. 2014;27(6):568–78.
Filiz S, Aydogdu M. Wave propagation analysis of embedded (coupled) functionally graded nanotubes conveying fluid. Compos Struct. 2015;132:1260–73.
Toupin RA. Elastic materials with couple-stresses. Arch Ration Mech Anal. 1962;11(1):385–414.
Lim CW, Zhang G, Reddy JN. A higher-order nonlocal elasticity and strain gradient theory and its applications in wave propagation. J Mech Phys Solids. 2015;78:298–313.
Li L, Hu YJ. Buckling analysis of size-dependent nonlinear beams based on a nonlocal strain gradient theory. Int J Eng Sci. 2015;97:84–94.
Li L, Hu YJ, Ling L. Flexural wave propagation in small-scaled functionally graded beams via a nonlocal strain gradient theory. Compos Struct. 2015;133:1079–92.
Li L, Hu YJ, Ling L. Wave propagation in viscoelastic single-walled carbon nanotubes with surface effect under magneticfield based on nonlocal strain gradient theory. Phys E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct. 2016;75:118–24.
Paidoussis MP. Fluid-structure interactions slender structures and axial flow. San Diego: Academic Press; 1998.
Aifantis EC. Strain gradient interpretation of size effect. Int J Fract. 1999;95(1–4):299–314.
Aifantis EC. Gradient deformation models at nano, micro, and macro scales. J Eng Mater Technol. 1999;121(2):189–202.
Mindlin RD. Micro-structure in linear elasticity. Arch Ration Mech Anal. 1964;16(1):51–78.
Mindlin RD. Second gradient of strain and surface-tension in linear elasticity. Int J Solids Struct. 1965;1(4):417–38.
Hagedorn P, Dasgupta A. Vibration and waves in continuous mechanical system. London: Wiley; 2007.
Hu L, Zheng LV, Qi L. Flexural wave propagation in fluid-conveying carbon nanotubes with system uncertainties. Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2017;21(8):140.
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11462010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Wang, J. & Yu, Y. Wave Propagation in Fluid-Filled Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Based on the Nonlocal Strain Gradient Theory. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 31, 484–492 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-018-0035-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-018-0035-5