Abstract
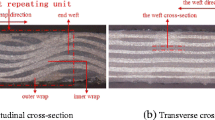
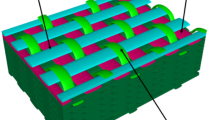
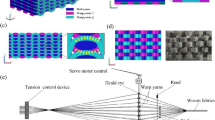
A micromechanical model for elastic behavior analysis of angle-interlock woven ceramic composites is proposed in this paper. This model takes into account the actual fabric structure by considering the fiber undulation and continuity in space, the cavities between adjacent yarns and the actual cross-section geometry of the yarn. Based on the laminate theory, the elastic properties of 3D angle-interlock woven ceramic composites are predicted. Different numbers of interlaced wefts have almost the same elastic moduli. The thickness of ceramic matrix has little effect on elastic moduli. When the undulation ratio increases longitudinal modulus decreases and the other Young’s moduli increase. Good agreement between theoretical predictions and experimental results demonstrates the feasibility of the proposed model in analyzing the elastic properties of 3D angle-interlock woven ceramic composites. The results of this paper verify the fact that the method of analyzing polyester matrix composites is suitable for woven ceramic composites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishikawa, T. and Chou, T.W., Stiffness and strength behaviour of woven fabric composites, J. Mater. Sci., Vol.17, 1982, 3211–3220.
Chou, T.W. and Ishikawa, T., Textile Structural Composites, Elsevier Science Publishers, 1989, 209–264.
Naik., N.K. and Shembekar, P.S., Elastic behavior of woven fabric composites: I-Lamina analysis, J. Compos. Mater., Vol.26, 1992, 2196–2225.
Naik., N.K. and Ganesh, V.K., An analytical method for plain weave fabric composites, Compos., Vol.26, 1995, 281–289.
Whitcomb, J.D., Composite Materials: Fatigue and Fracture, ASTM STP 1100 (O’Brien, T.K. ed.), Vol.3, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1991, 417–438.
Raju, I.S., Craft, W.J. and Avva, V.S., Advances in Structural Testing, Analysis and Design, ICSTAD Proceedings, Vol.1, New Delphi: Tata-McGraw Hill, 1990, 3–10.
Yi, H.L. and Ding, X., A model to predict elastic properties of 3D woven composites, Acta Mechanica Sinica, Vol.35, No.5, 2003, 569–577 (in Chinese).
Ding, X. and Yi, H.L., Proc. of the 6th Asian Textile Conference (CD Version), 2001, No.103.
Wang, B. and Jiao, G.Q., et al., Flexure property analysis of three-dimensional braided composite, Acta Mechanica Solid Sinica, Vol.25, No.1, 2004, 75–79 (in Chinese).
Aubard, X., Lamon, J. and Allix, O., Model of the nonlinear mechanical behavior of 2D SiC-SiC chemical vapor infiltration composites, J. Am. Ceram. Soc, Vol.77, 1994, 2118–2126.
Ismar, H., Schröter, F. and Streicher, F., Modeling and numerical simulation of the mechanical behavior of woven SiC/SiC regarding a three-dimensional unit cell, Comput. Mater. Sci., Vol.19, 2000, 320–328.
Sun, H.Y. and Wu, C.C., Experimental research on mechanical properties of composite materials with textile structure, Journal of Experimental Mechanics, Vol.12, No.3, 1997, 335–341 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.90405015)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y., Jiao, G., Wang, B. et al. Elastic behavior analysis of 3D angle-interlock woven ceramic composites. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 19, 152–159 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-006-0618-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-006-0618-4