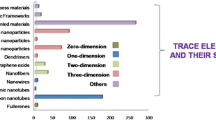
Abstract
The success of any analytical method depends largely on the sample preparation technique which is usually employed for the extraction and pre-concentration of the target analyte from a sample matrix. In this context, solid-phase extraction has been greatly explored by various researchers in many scientific fields including environmental analysis of pollutants, as well as analysis of food and biological samples. One of the solid-phase extraction drawbacks observed over the years is its inability to selectively extract the target analytes from the sample matrix, which could have a consequence of prolonging the analysis times and have negative effect on the analytical data. In this paper, recent trends starting from the work published in 2014–2018 in selective solid-phase extraction are critically reviewed while interesting studies prior to 2014 are mentioned. Solid-phase extraction sorbents that have been revealed in greater extent in literature to offer better selectivity are molecularly imprinted polymers and nano sorbents. Other sorbents reviewed in this work include composite materials which are sometimes designed for improving the adsorption capacity as well as selectivity. Mixed-mode ion-exchange polymers categorized as class selective sorbents have also been reviewed and recent applications are cited. Moreover, a broad discussion on miniaturization, new inventions and future of selective solid-phase extraction utilizing different sorbents in various sample matrices is outlined.
Graphical Abstract



Copied from Ref. [1] with permission from Wiley-VCH

Copied from ref. [2], with permission from Elsevier

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herrero-Latorre C, Barciela-García J, García-Martín S et al (2015) Magnetic solid-phase extraction using carbon nanotubes as sorbents: a review. Anal Chim Acta 892:10–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.07.046
Madikizela LM, Muthwa SF, Chimuka L (2014) Determination of triclosan and ketoprofen in river water and wastewater by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. S Afr J Chem 67:143–150
Madikizela LM, Chimuka L (2017) Simultaneous determination of naproxen, ibuprofen and diclofenac in wastewater using solid-phase extraction with high performance liquid chromatography. Water SA. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v43i2.10
Racamonde I, Rodil R, Quintana JB et al (2014) Determination of benzodiazepines, related pharmaceuticals and metabolites in water by solid-phase extraction and liquid-chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1352:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.064
Turk MF, Senta I, Kniewald G, Mikac N (2018) Determination of organotin compounds (OTC) at low levels in seawater by solid-phase extraction (SPE) and gas chromatography-pulsed flame photometric detection (GC-PFPD). Int J Environ Anal Chem 98:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2018.1426755
Rimayi C, Odusanya D, Weiss JM et al (2018) Contaminants of emerging concern in the Hartbeespoort dam catchment and the uMngeni River estuary 2016 pollution incident, South Africa. Sci Total Environ 627:1008–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.263
Wen Y, Chen L, Li J et al (2014) Recent advances in solid-phase sorbents for sample preparation prior to chromatographic analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 59:26–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.03.011
Rivera-Jaimes JA, Postigo C, Melgoza-Alemán RM et al (2018) Study of pharmaceuticals in surface and wastewater from Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico: occurrence and environmental risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 613–614:1263–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.134
Fontanals N, Marcé RM, Borrull F (2017) Solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry to determine synthetic cathinones in different types of environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1524:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.10.002
Boix C, Ibáñez M, Bagnati R et al (2016) High resolution mass spectrometry to investigate omeprazole and venlafaxine metabolites in wastewater. J Hazard Mater 302:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.059
Wang Z, Zhang X, Jiang S, Guo X (2018) Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the simultaneous enantiomeric analysis of five β-blockers in the environmental samples by chiral liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 180:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.12.034
Poiger T, Buerge IJ, Bächli A et al (2017) Occurrence of the herbicide glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA in surface waters in Switzerland determined with on-line solid phase extraction LC-MS/MS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:1588–1596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7835-2
Goh SXL, Duarah A, Zhang L et al (2016) Online solid phase extraction with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for determination of estrogens and glucocorticoids in water. J Chromatogr A 1465:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.08.040
Ncube S, Lekoto G, Cukrowska E, Chimuka L (2018) Development and optimisation of a novel three-way extraction technique based on a combination of Soxhlet extraction, membrane assisted solvent extraction and a molecularly imprinted polymer using sludge polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Sep Sci 41:918–928. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201701216
Candish E, Wirth HJ, Gooley AA et al (2015) Characterization of large surface area polymer monoliths and their utility for rapid, selective solid phase extraction for improved sample clean up. J Chromatogr A 1410:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.065
Qin S, Su L, Wang P, Deng S (2015) Mixed templates molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the detection of sulfonamides in fish farming water. J Appl Polym Sci 132:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41491
Pichon V, Rogniaux H, Fischer-Durand N et al (1997) Characteristics of immunosorbents used as a new approach to selective solid-phase extraction in environmental analysis. Chromatographia 45:289–295
Shahtaheri SJ, Kwasowski P, Stevenson D (1998) Highly selective antibody-mediated extraction of isoproturon from complex matrices. Chromatographia 47:453–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02466480
Gilart N, Borrull F, Fontanals N, Marcé RM (2014) Selective materials for solid-phase extraction in environmental analysis. Trends Environ Anal Chem 1:e8–e17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2013.11.002
Płotka-wasylka J, Szczepan N (2016) Modern trends in solid phase extraction: new sorbent media. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 77:23–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.10.010
He C, Long Y, Pan J et al (2007) Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to solid-phase extraction of analytes from real samples. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:133–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbbm.2006.07.005
Olcer YA, Demirkurt M, Demir MM, Eroglu AE (2017) Development of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) as a solid phase extraction (SPE) sorbent for the determination of ibuprofen in water. RSC Adv 7:31441–31447. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra05254e
Caro E, Marcé RM, Cormack PAG et al (2004) A new molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective extraction of naproxen from urine samples by solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr B 813:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.09.019
Madikizela LM, Chimuka L (2016) Determination of ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac in aqueous samples using a multi-template molecularly imprinted polymer as selective adsorbent for solid-phase extraction. J Pharm Biomed Anal 128:210–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.05.037
Özer ET, Osman B, Yazıcı T (2017) Dummy molecularly imprinted microbeads as solid-phase extraction material for selective determination of phthalate esters in water. J Chromatogr A 1500:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.04.013
Du B, Qu T, Chen Z et al (2014) A novel restricted access material combined to molecularly imprinted polymers for selective solid-phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography determination of 2-methoxyestradiol in plasma samples. Talanta 129:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.05.005
Zunngu SS, Madikizela LM, Chimuka L, Mdluli PS (2017) Synthesis and application of a molecularly imprinted polymer in the solid-phase extraction of ketoprofen from wastewater. C R Chim 20:585–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2016.09.006
Khan S, Bhatia T, Trivedi P et al (2016) Selective solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer as a sorbent for the analysis of fenarimol in food samples. Food Chem 199:870–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.12.091
Lian Z, Wang J (2017) Selective isolation of gonyautoxins 1,4 from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum based on molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. Mar Pollut Bull 122:500–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.06.066
Duan YP, Dai CM, Zhang YL, Ling-Chen (2013) Selective trace enrichment of acidic pharmaceuticals in real water and sediment samples based on solid-phase extraction using multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chim Acta 758:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.11.010
Lu W, Wang X, Wu X et al (2017) Multi-template imprinted polymers for simultaneous selective solid-phase extraction of six phenolic compounds in water samples followed by determination using capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1483:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.069
Arabi M, Ghaedi M, Ostovan A, Wang S (2016) Journal of Colloid and Interface Science Synthesis of lab-in-a-pipette-tip extraction using hydrophilic nano-sized dummy molecularly imprinted polymer for purification and analysis of prednisolone. J Colloid Interface Sci 480:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.07.017
Sun X, Wang J, Li Y et al (2014) Highly selective dummy molecularly imprinted polymer as a solid-phase extraction sorbent for five bisphenols in tap and river water. J Chromatogr A 1343:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.03.063
He X, Chen J, Wang J, Tan L (2017) Multipoint recognition of domoic acid from seawater by dummy template molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1500:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.04.023
Ning F, Qiu T, Wang Q et al (2017) Dummy-surface molecularly imprinted polymers on magnetic graphene oxide for rapid and selective quantification of acrylamide in heat-processed (including fried) foods. Food Chem 221:1797–1804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.101
Brigante TAV, Miranda LFC, de Souza ID et al (2017) Pipette tip dummy molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction of Bisphenol A from urine samples and analysis by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 1067:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.09.038
Chang T, Yan X, Liu S, Liu Y (2017) Magnetic dummy template silica sol–gel molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres as magnetic solid-phase extraction material for the selective and sensitive determination of bisphenol A in plastic bottled beverages. Food Anal Methods 10:3980–3990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0969-0
Zhao F, She Y, Zhang C et al (2017) Selective determination of chloramphenicol in milk samples by the solid-phase extraction based on dummy molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Anal Methods 10:2566–2575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0810-9
Zhou Y, Zhou T, Jin H et al (2015) Rapid and selective extraction of multiple macrolide antibiotics in foodstuff samples based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. Talanta 137:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.01.008
Sun H, Li Y, Huang C et al (2015) Solid-phase extraction based on a molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective determination of four benzophenones in tap and river water. J Sep Sci 38:3412–3420. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201500419
Manzoor S, Buffon R, Rossi AV (2015) Talanta Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction of fl uconazole from pharmaceutical formulations. Talanta 134:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.10.057
Yılmaz H, Basan H (2015) Development of a molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction sorbent for the selective extraction of telmisartan from human urine. J Sep Sci 38:1433–1439. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201401349
Dai CM, Zhou XF, Zhang YL et al (2011) Synthesis by precipitation polymerization of molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective extraction of diclofenac from water samples. J Hazard Mater 198:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.027
Sun Z, Schüssler W, Sengl M et al (2008) Selective trace analysis of diclofenac in surface and wastewater samples using solid-phase extraction with a new molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal Chim Acta 620:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.020
Díaz-Álvarez M, Barahona F, Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A (2014) Supported liquid membrane-protected molecularly imprinted beads for micro-solid phase extraction of sulfonamides in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1357:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.038
Díaz-Álvarez M, Martín-Esteban A (2018) Hollow fiber membrane-protected molecularly imprinted microspheres for micro solid-phase extraction and clean-up of thiabendazole in citrus samples. J Chromatogr A 1531:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.11.054
Mhaka B, Cukrowska E, Tse Sum Bui B et al (2009) Selective extraction of triazine herbicides from food samples based on a combination of a liquid membrane and molecularly imprinted polymers. J Chromatogr A 1216:6796–6801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.08.003
Chimuka L, van Pinxteren M, Billing J et al (2011) Selective extraction of triazine herbicides based on a combination of membrane assisted solvent extraction and molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 1218:647–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.12.019
Ncube S, Tavengwa N, Soqaka A et al (2018) Development of a single format membrane assisted solvent extraction-molecularly imprinted polymer technique for extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wastewater followed by gas chromatography mass spectrometry determination. J Chromatogr A 1569:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.07.061
Nemulenzi O, Mhaka B, Cukrowska E et al (2009) Potential of combining of liquid membranes and molecularly imprinted polymers in extraction of 17β-estradiol from aqueous samples. J Sep Sci 32:1941–1948. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800659
Rozaini MNH, Yahaya N, Saad B et al (2017) Rapid ultrasound assisted emulsification micro-solid phase extraction based on molecularly imprinted polymer for HPLC-DAD determination of bisphenol A in aqueous matrices. Talanta 171:242–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.05.006
Sánchez-González J, Tabernero MJ, Bermejo AM et al (2015) Porous membrane-protected molecularly imprinted polymer micro-solid-phase extraction for analysis of urinary cocaine and its metabolites using liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 898:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.10.002
Li X, Wang Y, Sun Q et al (2016) Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction in a syringe filter for determination of triazine herbicides in Radix Paeoniae Alba by ultra-fast liquid chromatography. Talanta 148:539–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.11.027
Wang C, Hu X, Guan P et al (2014) Separation and purification of thymopentin with molecular imprinting membrane by solid phase extraction disks. J Pharm Biomed Anal 102:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.016
Wu YT, Zhang YH, Zhang M et al (2014) Selective and simultaneous determination of trace bisphenol A and tebuconazole in vegetable and juice samples by membrane-based molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and HPLC. Food Chem 164:527–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.071
Fontanals N, Cormack PAG, Marce RM, Borrull F (2010) Mixed-mode ion-exchange polymeric sorbents: dual-phase materials that improve selectivity and capacity. Trends Anal Chem 29:765–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2010.03.015
Zhang P, Bui A, Rose G, Allinson G (2014) Mixed-mode solid-phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to determine phenoxy acid, sulfonylurea, triazine and other selected herbicides at nanogram per litre levels in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1325:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.12.021
Salas D, Borrull F, Marcé RM, Fontanals N (2016) Study of the retention of benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles and benzenesulfonamides in mixed-mode solid-phase extraction in environmental samples. J Chromatogr A 1444:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.03.053
Gilart N, Cormack PAG, Marcé RM et al (2014) Selective determination of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in wastewaters using a novel strong cation-exchange solid-phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1325:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.12.012
Li Y, Yang J, Huang C et al (2015) Dendrimer-functionalized mesoporous silica as a reversed-phase / anion-exchange mixed-mode sorbent for solid phase extraction of acid drugs in human urine. J Chromatogr A 1392:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.003
Chambers EE, Woodcock MJ, Wheaton JP et al (2014) Systematic development of an UPLC– MS/MS method for the determination of tricyclic antidepressants in human urine. J Pharm Biomed Anal 88:660–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2013.09.001
Zhao X, Ma F, Li P et al (2015) Simultaneous determination of isoflavones and resveratrols for adulteration detection of soybean and peanut oils by mixed-mode SPE LC–MS/MS. Food Chem 176:465–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.12.082
How ZT, Busetti F, Linge KL et al (2014) Analysis of free amino acids in natural waters by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1370:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.10.040
Nahar LK, Cordero RE, Nutt D et al (2016) Validated method for the quantification of baclofen in human plasma using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 40:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkv125
Park Y, Choe S, Lee H et al (2015) Advanced analytical method of nereistoxin using mixed-mode cationic exchange solid-phase extraction and GC/MS. For Sci Int 252:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.04.010
Regueiro J, Wenzl T (2015) Determination of bisphenols in beverages by mixed-mode solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1422:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.10.046
Casado J, Rodríguez I, Ramil M, Cela R (2014) Selective determination of antimycotic drugs in environmental water samples by mixed-mode solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1339:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.02.087
Tang X, Gu Y, Nie J et al (2014) Quantification of amino acids in rat urine by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/ electrospray tandem mass spectrometry: application to radiation injury rat model. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 37:951–973. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2013.765451
Janusch F, Scherz G, Mohring SAI et al (2014) Comparison of different solid-phase extraction materials for the determination of fluoroquinolones in chicken plasma by LC–MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 951–952:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.01.024
Yang X, Zhang Z, Li J et al (2014) Novel molecularly imprinted polymers with carbon nanotube as matrix for selective solid-phase extraction of emodin from kiwi fruit root. Food Chem 145:687–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.114
Bagheri H, Molaei K, Asgharinezhad AA et al (2016) Magnetic molecularly imprinted composite for the selective solid-phase extraction of p-aminosalicylic acid followed by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Sep Sci 39:4166–4174. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201600865
Dai X, Wang D, Li H et al (2017) Hollow porous ionic liquids composite polymers based solid phase extraction coupled online with high performance liquid chromatography for selective analysis of hydrophilic hydroxybenzoic acids from complex samples. J Chromatogr A 1484:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.01.022
Liu X, Feng J, Li Y (2018) Preparation of carbon-functionalized magnetic graphene/mesoporous silica composites for selective extraction of miglitol and voglibose in rat plasma. Talanta 182:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.01.079
Li W, Zhang H xia, Shi Y ping (2017) Selective determination of aromatic amino acids by magnetic hydroxylated MWCNTs and MOFs based composite. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 1059:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.05.025
Shu H, Ge YH, Xu XY et al (2018) Hybrid-type carbon microcoil-chitosan composite for selective extraction of aristolochic acid I from Aristolochiaceae medicinal plants. J Chromatogr A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.05.037
Háková M, Raabová H, Havlíková LC et al (2018) Testing of nylon 6 nanofibers with different surface densities as sorbents for solid phase extraction and their selectivity comparison with commercial sorbent. Talanta 181:326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.01.043
Hao Y, Gao R, Shi L et al (2015) Water-compatible magnetic imprinted nanoparticles served as solid-phase extraction sorbents for selective determination of trace 17beta-estradiol in environmental water samples by liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1396:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.083
Hu C, Deng J, Zhao Y et al (2014) A novel core-shell magnetic nano-sorbent with surface molecularly imprinted polymer coating for the selective solid phase extraction of dimetridazole. Food Chem 158:366–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.143
Zeng Q, Liu YM, Jia YW et al (2017) PEGylation of magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for enhanced selectivity of dispersive solid phase extraction. Mater Sci Eng C 71:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.09.082
Mukdasai S, Butwong N, Thomas C et al (2016) A sensitive and selective spectrophotometric method for 2-chlorophenol based on solid phase extraction with mixed hemimicelle magnetic nanoparticles. Arab J Chem 9:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.023
Devasurendra AM, Palagama DSW, Rohanifar A et al (2018) Solid-phase extraction, quantification, and selective determination of microcystins in water with a gold-polypyrrole nanocomposite sorbent material. J Chromatogr A. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHROMA.2018.04.027
Chen J, Cao S, Zhu M et al (2018) Fabrication of a high selectivity magnetic solid phase extraction adsorbent based on β-cyclodextrin and application for recognition of plant growth regulators. J Chromatogr A 1547:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.03.004
Chen LQ, Wang H, Xu Z et al (2018) High-throughput and selective solid-phase extraction of urinary catecholamines by crown ether-modified resin composite fiber. J Chromatogr A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.05.041
Gan H, Xu H (2018) A novel aptamer-based online magnetic solid phase extraction method for the selective determination of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in human urine. Anal Chim Acta 1008:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.12.032
Huang C, Li Y, Yang J et al (2017) Preparation of a reversed-phase/anion-exchange mixed-mode spherical sorbent by Pickering emulsion polymerization for highly selective solid-phase extraction of acidic pharmaceuticals from wastewater. J Chromatogr A 1521:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.09.021
He HB, Dong C, Li B et al (2014) Fabrication of enrofloxacin imprinted organic-inorganic hybrid mesoporous sorbent from nanomagnetic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes for the selective extraction of fluoroquinolones in milk samples. J Chromatogr A 1361:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.07.089
Tan D, Jin J, Li F et al (2017) Phenyltrichlorosilane-functionalized magnesium oxide microspheres: preparation, characterization and application for the selective extraction of dioxin-like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils with matrix solid-phase dispersion. Anal Chim Acta 956:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.12.040
Zhang Y, Yu M, Zhang C et al (2014) Highly selective and ultra fast solid-phase extraction of N-glycoproteome by oxime click chemistry using aminooxy-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Anal Chem 86:7920–7924. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5018666
Santos da Silva RC, Mano V, Pereira AC et al (2016) Development of pipette tip-based on molecularly imprinted polymer micro-solid phase extraction for selective enantioselective determination of (–)-(2S,4R) and (+)-(2R,4S) ketoconazole in human urine samples prior to HPLC-DAD. Anal Methods 8:4075–4085. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY00392C
Teixeira RA, Flores DHÂ, da Silva RCS et al (2018) Pipette-tip solid-phase extraction using poly(1-vinylimidazole-co-trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate) as a new molecularly imprinted polymer in the determination of avermectins and milbemycins in fruit juice and water samples. Food Chem 262:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.076
Yang C, Lv T, Yan H et al (2015) Glyoxal-urea-formaldehyde molecularly imprinted resin as pipette tip solid-phase extraction adsorbent for selective screening of organochlorine pesticides in spinach. J Agric Food Chem 63:9650–9656. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02762
da Silva ATM, de Oliveira HL, Silva CF et al (2017) Efficient molecularly imprinted polymer as a pipette-tip solid-phase sorbent for determination of carvedilol enantiomers in human urine. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 1061–1062:399–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.07.056
de Oliveira HL, da Silva Anacleto S, da Silva ATM et al (2016) Molecularly imprinted pipette-tip solid phase extraction for selective determination of fluoroquinolones in human urine using HPLC-DAD. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 1033–1034:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.08.008
Yuan Y, Liang S, Yan H et al (2015) Ionic liquid-molecularly imprinted polymers for pipettetip solid-phase extraction of (Z)-3-(chloromethylene)-6-flourothiochroman-4-one in urine. J Chromatogr A 1408:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.028
Zhou SN, Lai EPC, Miller JD (2004) Analysis of wheat extracts for ochratoxin A by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and pulsed elution. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1903–1906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-003-2409-9
Masque N, Marce RM, Borrull F et al (2000) Synthesis and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer for selective online solid-phase extraction of 4-nitrophenol from environmental water. Anal Chem 72:4404–4408. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0000628
Lai EPC, Wu SG (2003) Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction for rapid screening of cephalexin in human plasma and serum. Anal Chim Acta 481:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00087-4
Zhong Q, Hu Y, Hu Y, Li G (2012) Dynamic liquid-liquid-solid microextraction based on molecularly imprinted polymer filaments on-line coupling to high performance liquid chromatography for direct analysis of estrogens in complex samples. J Chromatogr A 1241:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.04.017
Caro E, Marcø RM, Cormack PAG (2006) Direct determination of ciprofloxacin by mass spectrometry after a two-step solid-phase extraction using a molecularly imprinted polymer. J Sep Sci 29:1230–1236. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200500439
Gilart N, Marcé RM, Fontanals N, Borrull F (2013) A rapid determination of acidic pharmaceuticals in environmental waters by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled to tandem mass spectrometry without chromatography. Talanta 110:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.02.039
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Dai C et al (2013) Sorption of carbamazepine from water by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on chitosan-Fe3O4. Carbohydr Polym 97:809–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.072
Krupadam RJ, Khan MS, Wate SR (2010) Removal of probable human carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from contaminated water using molecularly imprinted polymer. Water Res 44:681–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.09.044
Ncube S, Kunene P, Tavengwa NT et al (2017) Synthesis and characterization of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the isolation of the 16 US-EPA priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in solution. J Environ Manag 199:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.041
Dai CM, Zhang J, Zhang YL et al (2012) Selective removal of acidic pharmaceuticals from contaminated lake water using multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymer. Chem Eng J 211–212:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.090
Dai CM, Geissen SU, Zhang YL et al (2011) Selective removal of diclofenac from contaminated water using molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres. Environ Pollut 159:1660–1666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.041
Cao J, Zhou S, Kong W et al (2013) Molecularly imprinted polymer-based solid phase clean-up for analysis of ochratoxin A in ginger and LC–MS/MS confirmation. Food Control 33:337–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.03.023
Krupadam RJ, Patel GP, Balasubramanian R (2012) Removal of cyanotoxins from surface water resources using reusable molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1841–1851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0703-1
Andrade-Eiroa A, Canle M, Leroy-Cancellieri V, Cerdà V (2016) Solid-phase extraction of organic compounds: a critical review. part ii. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 80:655–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.08.014
Gałuszka A, Migaszewski Z, Namieśnik J (2013) The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 50:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2013.04.010
Armenta S, De Guardia M, Abad-fuentes A et al (2016) Highly selective solid-phase extraction sorbents for chloramphenicol determination in food and urine by ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9995-9
Martinez-Sena T, Armenta S, Guardia M, de la Esteve-Turrillas FA (2016) Determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water and urine using selective molecular imprinted polymer extraction and liquid chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 131:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.08.006
Zorita S, Boyd B, Jönsson S et al (2008) Selective determination of acidic pharmaceuticals in wastewater using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. Anal Chim Acta 626:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.07.051
Madikizela LM, Tavengwa NT, Chimuka L (2017) Applications of molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics from environmental waters and biological samples. J Pharm Biomed Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.04.010
Płotka-Wasylka J (2018) A new tool for the evaluation of the analytical procedure: Green Analytical Procedure Index. Talanta 181:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.01.013
Gałuszka A, Migaszewski ZM, Konieczka P, Namieśnik J (2012) Analytical eco-scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 37:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.03.013
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Research Foundation of South Africa (Grant number: 114415) awarded to Dr. Lawrence Madikizela and the University of South Africa Postdoctoral Fellowship (Grant number: 409000) awarded to Dr. Somandla Ncube.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Recent Trends in Solid-Phase Extraction for Environmental, Food and Biological Sample Preparation with guest editors Anna Laura Capriotti, Giorgia La Barbera, and Susy Piovesana.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madikizela, L.M., Ncube, S. & Chimuka, L. Recent Developments in Selective Materials for Solid Phase Extraction. Chromatographia 82, 1171–1189 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3644-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3644-8