Abstract
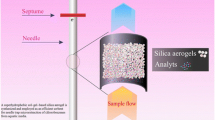
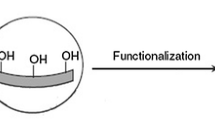
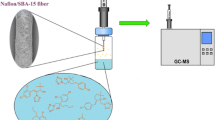
In this work, a modified nanoporous silica aerogel was used as a new sorbent for headspace needle trap extraction of chlorobenzenes from aqueous samples. The needle trap extraction is derived from solid-phase microextraction and the sorbent is inside the needle. The thermal stability and functional groups of the sorbent were studied by TG/DTA and FT-IR, respectively. The modified silica aerogels, characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy, showed a three-dimensional network containing a homogeneous pore structure with pore sizes of a few tens of nm and a sponge-like microstructure. The developed method was applied to the trace level extraction of some chlorobenzene compounds from aqueous samples. The influential parameters on the extraction efficiency, including the extraction temperature, ionic strength and extraction time were investigated and optimized. Under optimized conditions, the detection and quantification limits were in the range of 0.4–0.8 and 1–3 ng L−1, respectively. The relative standard deviation values for water spiked with chlorobenzenes at 100 ng L−1 under optimum conditions were 3–7%. The dynamic linear range of the method in the range of 3–3000 ng L−1 was investigated. Finally, the current method for the analysis of real water samples containing spiked chlorobenzenes was applied and the relative recovery values were found to be in the range of 96–101%.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yonglai Z, Shu W, Fujian L, Yunchen D, Sen L, Yanyan J (2009) Nano Today 4:135–142
Dorcheh AS, Abbasi MH (2008) J Mater Process Technol 199:10–26
Hwang S, Kim TY, Hyun SH (2008) J Colloid Interface Sci 2:5–15
Rao AP (2007) J Mater Sci 42:8418–8425
Rao AP, Rao AV, Pajonk GM (2007) Appl Surf Sci 253:6032–6040
Kim GS, Hyun SH (2003) J Noncryst Solids 320:125–132
Bhagat SD (2007) Solid State Sci 9:628–635
Shi F, Wang L, Liu J (2006) Mater Lett 58:2369–2373
Lee CJ, Kim GS, Hyun SH (2002) J Mater Sci 37:2237–2241
Shewale PM, Rao AV, Rao AP (2008) Appl Surf Sci 254:6902–6907
US EPA (1980) Ambient water quality criteria for chlorinated benzenes; EPA 440-/5-80/028; Department of Commerce National Technical Information Service, Alexandria, VA
European Commission (2008) Europa-environment, water quality in the EU, The EU water framework directive-integrated river basin management for Europe priority substances. http://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/water-framework/priority_substances.htm. Accessed May 2008
Koziel JA, Odziemkowski M, Pawliszyn J (2001) Anal Chem 73:47–54
Wang A, Fang F, Pawliszyn J (1072) J Chromatogr A 2005:127–135
Musshoff F, Lachenmeier DW, Kroener L, Madea B (2003) Forensic Sci Int 133:32–37
Kubinec R, Berezkin VG, Gorova R, Addova G, Mracnova H, Sojak L (2004) J. Chromatogr B 800:295–301
Eom Y, Tugulea AM, Pawliszyn J (2008) J Chromatogr A 3:1196–1197
Eom IY, Niri VH, Pawliszyn J (2008) J Chromatogr A 10:1196–1197
Koester CJ, Clement RE (1993) Crit Rev Anal Chem 24:263–316
Kolb B, Ettre LS (1997) Static head-space gas chromatography. Wiley, New York, pp 13–20
Bagheri H, Aghakhani A (2011) Anal Methods 3:1284–1289
He Y, Wang Y, Lee HK (2000) J Chromatogr A 847:149–154
Noche GG, Laespada MEF, Pavón JLP, Cordero BMS, Lorenzo M (2013) Anal Bioanal Chem 405:6739–6748
Moodley KG, Chetty DK, Ramphal SR, Gericke G (2013) Water SA 39:23–30
Acknowledgement
The Research Council and Graduates School of Islamic Azad University Central Tehran Branch are acknowledged for supporting the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roostaie, A., Mohammadiazar, S., Bargozin, H. et al. A Modified Nanoporous Silica Aerogel as a New Sorbent for Needle Trap Extraction of Chlorobenzenes from Water Samples. Chromatographia 81, 649–655 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3456-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3456-2