Abstract
Objective
To find structural differences between brain metastases of lung and breast cancer, computing their heterogeneity parameters by means of both 2D and 3D texture analysis (TA).
Materials and methods
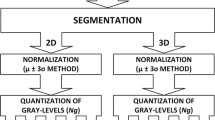
Patients with 58 brain metastases from breast (26) and lung cancer (32) were examined by MR imaging. Brain lesions were manually delineated by 2D ROIs on the slices of contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (CET1) images, and local binary patterns (LBP) maps were created from each region. Histogram-based (minimum, maximum, mean, standard deviation, and variance), and co-occurrence matrix-based (contrast, correlation, energy, entropy, and homogeneity) 2D, weighted average of the 2D slices, and true 3D TA were obtained on the CET1 images and LBP maps.
Results
For LBP maps and 2D TA contrast, correlation, energy, and homogeneity were identified as statistically different heterogeneity parameters (SDHPs) between lung and breast metastasis. The weighted 3D TA identified entropy as an additional SDHP. Only two texture indexes (TI) were significantly different with true 3D TA: entropy and energy. All these TIs discriminated between the two tumor types significantly by ROC analysis. For the CET1 images there was no SDHP at all by 3D TA.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that the used textural analysis methods may help with discriminating between brain metastases of different primary tumors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nayak L, Quant Lee E, Wen PY (2012) Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 14(1):48–54
Brastianos HC, Cahill DP, Brastianos PK (2015) Systemic therapy of brain metastases. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 15:518
Lee EK, Lee EJ, Kim MS, Kim MS, Park H-J, Park NH, Park S, Lee YS (2012) Intracranial metastases: spectrum of MR imaging findings. Acta Radiol 53(10):1173–1185
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC (2014) Robbins and cotran pathologic basis of disease, 9th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia
Bekaert L, Emery E, Levallet G, Lechapt-Zalcman E (2017) Histopathologic diagnosis of brain metastases: current trends in management and future considerations. Brain Tumor Pathol 34(1):8–19
Fink KR, Fink JR (2013) Imaging of brain metastases. Surg Neurol Int 4(Suppl 4):S209–S219
Balériaux D, Colosimo C, Ruscalleda J et al (2002) Diagnostic neuroradiology magnetic resonance imaging of metastatic disease to the brain with gadobenate dimeglumine. Neuroradiol 44(3):191–203
Yuh WTC, Fisher DJ, Runge VM, Atlas SW, Harms SE, Maravilla KR, Mayr NA, Mollman JE, Price AC (1994) Phase III multicenter trial of high-dose gadoteridol in MR evaluation of brain metastases. Am J Neuroradiol 15(6):1037–1051
Marusyk A, Polyak K (2010) Tumor heterogeneity: causes and consequences. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805(1):105–117
Marusyk A, Almendro V, Polyak K (2012) Intra-tumour heterogeneity: a looking glass for cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 12(5):323–334
Lerski RA, Smith MJ, Morley P, Barnett E, Mills PR, Watkinson G, MacSween RNM (1981) Discriminant analysis of ultrasonic texture data in diffuse alcoholic liver disease: 1 fatty liver and cirrhosis. Ultrason Imaging 3(2):164–172
Haralick RM (1979) Statistical and structural approach to textures. Proc IEEE 67(5):786–804
Ng TSC, Bading JR, Park R, Sohi H, Procissi D, Colcher D, Conti PS, Cherry SR, Raubitschek AA, Jacobs RE (2012) Quantitative, simultaneous PET/MRI for intratumoral imaging with an MRI-compatible PET scanner. J Nucl Med 53(7):1102–1109
Asselin M-C, O’connor JPB, Boellaard R, Thacker NA, Jackson A (2012) Quantifying heterogeneity in human tumours using MRI and PET. Eur J Cancer 48(4):447–455
Larroza A, Moratal D, Paredes-Sánchez A, Soria-Olivas E, Chust ML, Arribas LA, Arana E (2015) Support vector machine classification of brain metastasis and radiation necrosis based on texture analysis in MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 42(5):1362–1368
Oppedal K, Eftestøl T, Engan K, Beyer MK, Aarsland D (2015) Classifying dementia using local binary patterns from different regions in magnetic resonance images. Int J Biomed Imag. doi:10.1155/2015/572567
Nanni L, Lumini A, Brahnam S (2010) Local binary patterns variants as texture descriptors for medical image analysis. Artif Intell Med 49(2):117–125
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):971–987
Guo ZH, Zhang L, Zhang D (2010) Rotation invariant texture classification using LBP variance (LBPV) with global matching. Pattern Recognit 43(3):706–719
Mouthuy N, Cosnard G, Abarca-Quinones J, Michoux N (2012) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate high-grade gliomas and brain metastases. J Neuroradiol 39(5):301–307
Chernov MF, Hayashi M, Izawa M, Ono Y, Hori T (2006) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of metastatic brain tumors: variations of metabolic profile. Int J Clin Oncol 11(5):375–384
Orlhac F, Soussan M, Chouahnia K, Martinod E, Buvat I (2015) 18F-FDG PET-derived textural indices reflect tissue-specific uptake pattern in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145063
Mahmoud-Ghoneim D, Alkaabi MK, De Certaines JD, Goettsche F-M (2008) The impact of image dynamic range on texture classification of brain white matter. BMC Med Imaging 8:18
Fetit AE, Novak J, Peet AC, Arvanitis TN (2015) Three-dimensional textural features of conventional MRI improve diagnostic classification of childhood brain tumours. NMR Biomed 28(9):1174–1184
Depeursinge A, Foncubierta-Rodriguez A, Van De Ville D, Müller H (2014) Three-dimensional solid texture analysis in biomedical imaging: review and opportunities. Med Image Anal 18(1):176–196
Suoranta S, Holli-Helenius K, Koskenkorva P, Niskanen E, Könönen M, Äikiä M, Eskola H, Kälviäinen R, Vanninen R (2013) 3D Texture analysis reveals imperceptible MRI textural alterations in the thalamus and putamen in progressive myoclonic epilepsy type 1, EPM1. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069905
Allin Christe S, Vasantha Kumari B, Kandaswamy A (2012) Experimental study for 3D statistical property based intracranial brain tumor classification. J Sci Ind Res 71(1):36–44
Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO (2007) Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(2):375–385
Li Z, Mao Y, Li H, Yu G, Wan H, Li B (2016) Differentiating brain metastases from different pathological types of lung cancers using texture analysis of T1 postcontrast MR. Magn Reson Med 76(5):1410–1419
Ben Sassi O, Sellami L, Ben Slima M, Chtourou K, Ben Hamida A (2013) Improved spatial gray level dependence matrices for texture analysis. Int J Comput Sci Inf Technol 4(6):209
Carl P, Daniel L (2008) Matlab function—cooc3d.m, available at https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/19058-cooc3d
Ganeshan B, Miles KA, Young RC, Chatwin CR (2007) Hepatic entropy and uniformity: additional parameters that can potentially increase the effectiveness of contrast enhancement during abdominal CT. Clin Radiol 62(8):761–768
Wibmer A, Hricak H, Gondo T, Matsumoto K, Veeraraghavan H, Fehr D, Zheng J, Goldman D, Moskowitz C, Fine SW, Reuter VE, Eastham J, Sala E, Vargas HA (2015) Haralick texture analysis of prostate MRI: utility for differentiating non-cancerous prostate from prostate cancer and differentiating prostate cancers with different Gleason scores. Eur Radiol 25(10):2840–2850
Molina D, Pérez-Beteta J, Martínez-González A, Martino J, Velásquez C, Arana E, Pérez-García VM (2016) Influence of gray level and space discretization on brain tumor heterogeneity measures obtained from magnetic resonance images. Comput Biol Med 78:49–57
Yang D, Rao G, Martinez J, Veeraraghavan A, Rao A (2015) Evaluation of tumor-derived MRI-texture features for discrimination of molecular subtypes and prediction of 12-month survival status in glioblastoma. Med Phys 42(11):6725–6735
Sikio M, Holli-Helenius KK, Ryymin P, Dastida P, Eskola H, Harrison L (2015) The effect of region of interest size on textural parameters: 9th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis (2015) IEEE, pp:149–153
Brooks FJ, Grigsby PW (2014) The effect of small tumor volumes on studies of intratumoral heterogeneity of tracer uptake. J Nucl Med 55(1):37–42
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (MINECO) and FEDER funds under Grant BFU2015-64380-C2-2-R, by the “Richter Gedeon Talentum Alapítvány” and by the Campus Hungary Mobility Program. Andrés Larroza was funded by the Spanish Ministerio de Educación, Cultura y Deporte (MECD) under Grant FPU12/01140. The authors also thank to the continuous help of Dr. Joaquin Gavila from Fundación IVO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Protocol/project development: David Moratal, Estanislao Arana, Monika Béresová. Data collection or management: David Moratal, Estanislao Arana, László Balkay. Andrés Larroza, Monika Béresová. Data analysis: David Moratal, Estanislao Arana, Balkay László, József Varga, Monika Béresová.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All exams came from individuals who gave informed consent at admission for research and follow-up, in accordance with Institutional Board Review (IBR) approval.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Béresová, M., Larroza, A., Arana, E. et al. 2D and 3D texture analysis to differentiate brain metastases on MR images: proceed with caution. Magn Reson Mater Phy 31, 285–294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0653-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0653-9