Abstract
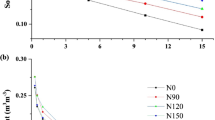
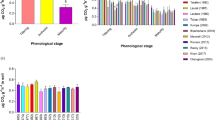
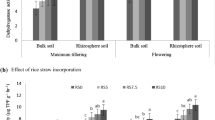
The root is the most sensitive part of the plant. This study examined the effects of wheat straw mulch, nitrogen (N) management and soil fertility on rice root morphology, dry matter accumulation, grain yield and rice quality and explored the correlation between root morphology and rice quality indexes. Wheat straw mulch had an obvious inhibitory effect on rice root morphology, especially on the total root length and total root surface area at 20 days after transplanting in the high- and low-fertility soil. The low-fertility soil treatments had higher levels of inhibition. However, straw mulch significantly promoted root growth, increased dry matter accumulation in the subsequent growth periods and improved the grain yield and rice quality, which mainly reduced the percentage of chalky kernels and the chalkiness degree. Increasing the nitrogen fertilizer percentage applied as a basal or tillering fertilizer reduced the inhibition in the early growth period; for balanced rice root growth, dry matter accumulation, grain yield and rice quality, 30% as basal fertilizer, 30% as tillering fertilizer and 40% as panicle fertilizer were the best N management strategy. Correlation analysis showed that the rice quality was extremely significantly positively correlated (r = 0.30–0.59, P < 0.05) with the root morphology indexes of the brown rice and protein contents and was significantly or extremely negatively correlated (r = − 0.73 to − 0.28, P < 0.05) with the length–width ratio, percentage of chalky kernels, chalkiness degree and amylose content.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ae N, Otani T (1997) The role of cell wall components from groundnut roots in solubilizing sparingly soluble phosphorus in low fertility soils[J]. Plant Soil 196:265–270
Amanullah, Hidayatullah (2016a) Influence of organic and inorganic nitrogen on grain yield and yield components of hybrid rice in northwestern Pakistan. Rice Sci 23:326–333
Amanullah, Hidayatullah (2016b) Dry matter partition and harvest index differ in rice genotypes with variable rates of phosphorus and zinc nutrition. Rice Sci 23:78–87
Amanullah, Khan ST, lqbal A, Fahad. S (2016) Growth and productivity response of hybrid rice to application of animal manures, plant residues and phosphorus. Front Plant Sci 07:1–10
Angers DA, Recous S (1997) Decomposition of wheat straw and rye residues as affected by particle size. Plant Soil 189:197–203
Barraclough PB (1989) Root growth, macro-nutrient uptake dynamics and soil fertility requirements of a high-yielding winter oilseed rape crop. Plant Soil 119:59–70
Chen P, Dong M, Gu J, Hui F, Qiao Z, Yang D, Liu T (2012) Effects of returning wheat residue to field and nitrogen management on grain weight and quality of superior and inferior grains in super rice. Chin J Rice Sci 06:715–722
Crossette B (2010) State of world population 2010: from conflict and crisis to renewal: generations of change. United Nations Population fund
Cui T, Li Z, Wang S (2017) Effects of in-situ straw decomposition on composition of humus and structure of humic acid at different soil depths. J Soil Sediment 17:1–9
Eiland F, Klamer M, Lind AM, Leth M, Th EB (2001) Influence of initial C/N ratio on chemical and microbial composition during long term composting of straw. Microb Ecol 41:272–280
Gao L, Ma L, Zhang W, Wang F, Ma W, Zhang F (2009) Estimation of nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its utilization situation in China. Trans CSAE 07:173–179
Gu J, Chen J, Chen L, Wang Z, Zhang H, Yang J (2015) Grain quality changes and responses to nitrogen fertilizer of japonica rice cultivars released in the Yangtze River Basin from the 1950s to 2000s. Crop J 3:285–297
Ju H, Liu X, Zhang F (2003) Soil nitrogen mineralization and its prediction in winter wheat-summer maize rotation system. Chin J Appl Ecol 12:221–2245
Kanal A (1995) Effect of incorporation depth and soil climate on straw decomposition rate in a loamy Podzoluvisol. Biol Fertil Soils 20:190–196
Lemaire G (2013) Crop, responses to nitrogen. Springer, New York
Leuschner C, Hertel D, Schmid I, Koch O, Muhs A, Lscher DH (2004) Stand fine root biomass and fine root morphology in old-growth beech forests as a function of precipitation and soil fertility. Plant Soil 258:43–56
Li Y, Li X (1998) Advances in studies on genetic and environmental factors influencing rice grain quality. Chin J Rice Sci 12:13–15
Li M, Tan X (1996) Studies on the relationship between the characteristics of nutrition uptake of rice roots and the dry matter production, grain yield and grain quality. Acta Agric Univ Jiangxiensis 18:376–382
Li Y, Cao H, Chu Y, Deng J, Zhu R, Zhu C, Jiang X, Bai R (2010) Effects of wheat straw returning and nitrogen application model on rice yield and soil nitrogen supply. Soils 42:569–573
Li X, Sun Y, Chen H, Zheng H, Yang Z, Jia X, Liu S, Hu R, Ma J (2011a) Effects of nitrogen application strategy and cultivation model on the performances of canopy apparent photosynthesis of Indica hybrid rice eryou 498 during filling stage. Acta Agronom Sin 09:1650–1659
Li X, Sun Y, Chen H, Zheng H, Yang Z, Jia X, Liu S, Hu R, Ma J (2011b) Effects of nitrogen regulation on dry matter accumulation and grain yield of rice under different cultivation models and two kinds of ecological conditions. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 17:773–781
Liang Y, Zhou J, Nan W, Duan D, Zhang H (2016) Progress in rice root system research. Chin Bull Bot 51:98–106
Liu J (2016) Promote structural reform of food supply side with ‘Three Forces’. China Grain Econ 09:22–24
Liu S, Chen W, Nie X, Zhang H, Dai Q, Huo Z, Xu K (2007) Effect of embedding depth on decomposition course of crop residues in rice-wheat system. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 13:1049–1053
Liu H, Zhao Y, Wang X, Feng Y, Yang W (2008) Discussion of evaluation methods on soil fertility. J Yangtze River Sci Res Inst 25:62–66
Liu L, Chang E, Fan M, Wang Z, Yang J (2011) Effects of potassium and calcium on root exudates and grain quality during grain filling. Acta Agronom Sin 37:661–669
Luo D, Bai J, Xie D (2002) Research on evaluation norm and method of soil fertility. Soil Environ Sci 11:202–205
NBQTC (1999) National Bureau of Quality and Technology Control. The National Standard for Rice Quality Evaluation GB/T15682-2008. People’s Republic of China
Norton GJ, Shafaei M, Travis AJ, Deacon CM, Danku J, Pond D, Cochrane N, Lockhart K, Salt D, Zhang H, Dodd IC, Hossain M, Islam MR, Price AH (2017) Impact of alternate wetting and drying on rice physiology, grain production, and grain quality. Field Crop Res 205:1–13
Pan X, Wang R, Fu R (1996) Advance in the study on the growth-physiology in rice of root system (Oryza sativa). Chin Bull Bot 13:14–21
Pan S, Zhai J, Cao C, Cai M, Wang R, Huang S, Li J (2010) Effects of nitrogen management practices on nutrition uptake and grain qualities of rice. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 16:522–527
Peng Y, Ma J, Jiang M, Yan F, Sun Y, Yang Z (2013) Effects of slow/controlled release fertilizers on root morphological and physiological characteristics of rice. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 19:1048–1057
Said-Pullicino D, Cucu MA, Sodano M, Birk JJ, Glaser B, Celi L (2014) Nitrogen immobilization in paddy soils as affected by redox conditions and rice straw incorporation. Geoderma 228–229:44–53
Sun J, Zhang X, Jia S (2013) The effect of soil physical and chemical properties on soil microbial community in Agro-ecosystem. Soil Crop 02:138–144
Tao X, Wang X, Huang X, Min S, Cheng S (2004) Effects of soil moisture content on physiological activity of rice root system during filling stage. Sci Agric Sin 37:1616–1620
Wade LJ, Amarante ST, Olea A, Harnpichitvitaya D, Naklang K, Wihardjaka A, Sengar SS, Mazid MA, Singh G, McLaren CG (1999) Nutrient requirements in rainfed lowland rice. Field Crop Res 64:91–107
Wang Q, Huang J, He F, Cui K, Zeng J, Nie L, Peng S (2012) Head rice yield of “super” hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu grown under different nitrogen rates. Field Crop Res 134:71–79
Wang J, Wang D, Zhang G, Wang Y, Wang C, Teng Y, Christie P (2014a) Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching losses from intensively managed paddy fields with straw retention. Agric Water Manag 141:66–73
Wang Y, Chang SX, Fang S, Tian Y (2014b) Contrasting decomposition rates and nutrient release patterns in mixed vs singular species litter in agroforestry systems. J Soil Sediment 14:1071–1081
Xu G, Tan G, Wang Z, Liu L, Yang J (2009) Effects of wheat-residue application and site-specific nitrogen management on grain yield and quality and nitrogen use efficiency in direct-seeding rice. Sci Agric Sin 42:2736–2746
Xu G, Lv Q, Lu D, Wang H, Chen M (2016) Effect of wetting and drying alternative irrigation coupling with nitrogen application on root characteristic and grain-sink activity. Acta Agronom Sin 42:1495–1505
Yang J (2011) Relationships of rice root morphology and physiology with the formation of grain yield and quality and the nutrient absorption and utilization. Sci Agric Sin 44:36–46
Yang J, Chang E, Zhang W, Wang Z, Liu Z (2006) Relationship between root chemical signals and grain quality of rice. Sci Agric Sin 39:38–47
Yuan L, Zhang Z, Cao X, Zhu S, Zhang X, Wu L (2014) Responses of rice production, milled rice quality and soil properties to various nitrogen inputs and rice straw incorporation under continuous plastic film mulching cultivation. Field Crop Res 155:164–171
Zeng H, Gan L, Kinoshita T, Zhang R, Zhu Y, Shen Q, Xu G (2012) Stimulation of phosphorus uptake by ammonium nutrition involves plasma membrane H + ATPase in rice roots. Plant Soil 357:205–214
Zhang S, Wu W, Li Z, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhao J, Fang W (2008) The effect of different proportion of nitrogen application on yield and quality of double cropping late rice. Soil Fertil Sci 26:28–31
Zhao S, Li K, Zhou W, Qiu S, Huang S, He P (2016a) Changes in soil microbial community, enzyme activities and organic matter fractions under long-term straw return in north-central China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 216:82–88
Zhao Z, Sha Z, Liu Y, Wu S, Zhang H, Li C, Zhao Q, Cao L (2016b) Modeling the impacts of alternative fertilization methods on nitrogen loading in rice production in Shanghai. Sci Total Environ 566–567:1595–1603
Zhao J, Ni T, Xun W, Huang X, Huang Q, Ran W, Shen B, Zhang R, Shen Q (2017) Influence of straw incorporation with and without straw decomposer on soil bacterial community structure and function in a rice-wheat cropping system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:1–13
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the National Science and Technology Project of Food Production of China (2013BAD07B13), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0300506), Scientific Research Fund of Sichuan Provincial Education Department (16ZA0044), the Funding of Academic and Technical Leaders Cultivation of Sichuan Province and the Rice Breeding Project in Sichuan Province of China (2016NYZ0051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, F., Sun, Y., Xu, H. et al. Effects of wheat straw mulch application and nitrogen management on rice root growth, dry matter accumulation and rice quality in soils of different fertility. Paddy Water Environ 16, 507–518 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-018-0643-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-018-0643-1