Abstract
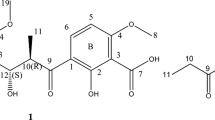
Since the discovery of the first antibiotic, natural products have played an important role in chemistry, biology and medicine. To explore the potential of bioactive compounds from microbes isolated from the southeast of Tibet, China, a crude extract library was constructed and screened against Staphylococcus aureus. The strain Nocardiopsis sp. LS150010 was scaled up and subjected to further chemical studies, resulting in the identification of N-salicyloyl-2-aminopropan-1,3-diol (2) and its rare aziridine derivative, madurastatin B3 (1). Their structures were determined by detailed analysis of 1D, 2D NMR and HRMS data. Compounds 1 and 2 displayed significant inhibitory activity against S. aureus and methicillin resistant S. aureus, with MIC values of 6.25 µg/mL. Compound 1 also showed potent inhibitory activity against Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli, as well as activity in a Mycobacterium tuberculosis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin infected THP-1 cell model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beutler JA (2009) Natural products as a foundation for drug discovery. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 46:9.11.1–9.11.21. doi:10.1002/0471141755.ph0911s46
Changsen C, Franzblau SG, Palittapongarnpim P (2003) Improved green fluorescent protein reporter gene-based microplate screening for antituberculosis compounds by utilizing an acetamidase promoter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47(12):3682–3687. doi:10.1128/AAC.47.12.3682-3687.2003
Cowley SC, Av-Gay Y (2001) Monitoring promoter activity and protein localization in Mycobacterium spp. using green fluorescent protein. Gene 264(2):225–231. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00336-5
David B, Wolfender JL, Dias A (2015) The pharmaceutical industry and natural products: historical status and new trends. Phytochem Rev 14(2):299–315. doi:10.1007/s11101-014-9367-z
Genilloud O (2014) The re-emerging role of microbial natural products in antibiotic discovery. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 106(1):173–188. doi:10.1007/s10482-014-0204-6
Harada K, Tomita K, Fujii K, Masuda K, Mikami Y, Yazawa K, Komaki H (2004) Isolation and structural characterization of siderophores, madurastatins, produced by a pathogenic Actinomadura madurae. J Antibiot 57(2):125–135. doi:10.1007/s10295-016-1788-9
Hossain MS, Hossain MA, Rahman MM, Mondol MAM, Bhuiyan MSA, Gray AI, Flores ME, Rashid MA (2004) Amides from the fungus Streptomyces hygroscopicus and their antimicrobial activity. Phytochemistry 65(14):2147–2151. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.06.010
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application toproliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63. doi:10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2016) Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod 79(3):629–661. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b01055
Prata-Sena M, Ramos AA, Buttachon S, Castro-Carvalho B, Marques P, Dethoup T, Kijjoa A, Rocha E (2016) Cytotoxic activity of secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungus Neosartorya siamensis in human cancer cells. Phytother Res 30(11):1862–1871. doi:10.1002/ptr.5696
Shen B (2015) A new golden age of natural products drug discovery. Cell 163(6):1297–1300. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.031
Song F, Liu X, Guo H, Ren B, Chen C, Piggott AM, Yu K, Gao H, Wang Q, Liu M, Liu X, Dai H, Zhang L, Capon RJ (2012) Brevianamides with antitubercular potential from a marine-derived isolate of Aspergillus versicolor. Org Lett 14(18):4770–4773. doi:10.1021/ol302051x
Song F, Ren B, Chen C, Yu K, Yu K, Liu X, Zhang Y, Yang N, He H, Liu X, Dai H, Zhang L (2014) Three new sterigmatocystin analogues from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor MF359. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(8):3753–3758. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5409-5
Wang Q, Song F, Xiao X, Huang P, Li L, Monte A, Abdel-Mageed WM, Wang J, Guo H, He W, Xie F, Dai H, Liu M, Chen C, Xu H, Liu M, Piggott AM, Liu X, Capon RJ, Zhang L (2013) Abyssomicins from the South China Sea deep-sea sediment Verrucosispora sp.: natural thioether michael addition adducts as antitubercular prodrugs. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(4):1231–1234. doi:10.1002/anie.201208801
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the Special Training Program for the Professional and Technical Personnel of Tibet Minority Nationality, the Natural Science Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Tibet (2015ZR-14-29), the Natural Science Foundation of China (31430002, 31320103911, 31260005, 31400090, 81302678 and 31125002), and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (2011ZX09102-011-11, 2013ZX10005004-005), China Ocean Mineral Resources R & D Association (Grant No. DY125-15-T-07), and the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program (FP7/2007-2013) under Grant Agreement No. 312184. LZ is an awardee for the National Distinguished Young Scholar Program in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article is dedicated to Dr. Arnold L. Demain on his 90th birthday for his excellent contribution as a leading advocator and mentor in the field of industrial microbiology. As the pioneer in research on the elucidation and regulation of the biosynthetic pathways of penicillins and cephalosporins, he is also characterized by his research on microbial production of immunosuppressive anti-tumor and anti-fungal drugs.
X. Zhang and H. He contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., He, H., Ma, R. et al. Madurastatin B3, a rare aziridine derivative from actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. LS150010 with potent anti-tuberculosis activity. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44, 589–594 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1908-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1908-1