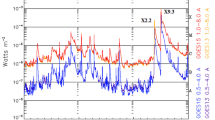
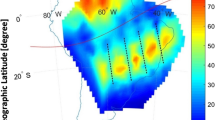
Abstract
A Solar Radio Burst (SRB) is one of the most severe natural hazards affecting the performance of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). Considering the influence of different threat factors, the GNSS developers upgrade the systems to amend the accuracy and noise-proof features of the systems. In particular, GPS gradually replaces “old” satellites (GPS IIA, GPS IIR-A, GPS IIR-B) with new-generation equipment (GPS IIR-M, GPS IIF, GPS III) featured by an increase in the emitted signal power at L2 frequency and by new civilian codes. In this work, based on examples of the extreme SRB of September 24, 2011, and the severe SRB of September 6, 2017, we study how such modernization can improve the GPS system performance during solar flares accompanied by intense SRB. We recorded SRB-related drops in signal strength (S), which were 7.5/0 dB-Hz for the S1C, 10/7 dB-Hz for the S2X, 17/8 dB-Hz for the S2W and 9/7.5 for the S5/S5X in 2011/2017 correspondingly. The drop in the S2W signal strength for the modernized blocks was comparable in amplitude to those of the “old” blocks. However, the modernized IIR-M/IIF blocks were featured by about 5 dB-Hz higher signal strength. This resulted in a double and triple decrease in loss-of-lock density for the IIR-M/IIF satellites in 2011 and 2017, respectively, as compared to IIA/IIR-A during SRBs. Therefore, the increase in the emitted signal power and new civilian codes potentially enhance the stability of the GPS operation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The solar radio spectrographs data are publicly available from the National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC, http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ngdc.html); station ZIM2 data are available from the EUREF Permanent Network Services (ftp://ftp.epncb.oma.be/). We used GNSS data obtained and publicly stored by the Scripps Orbit and Permanent Array Center, UCSD (ftp://garner.ucsd.edu/; http://lox.ucsd.edu/pub/), Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie Data Center (ftp://igs.bkg.bund.de/), Wuhan University (ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/), Crustal Dynamics Data Information System (ftp://cddis.gsfc.nasa.gov/), Korea Astronomy and Space Institute (ftp://nfs.kasi.re.kr/), NOAA's National Geodetic Survey (ftp://www.ngs.noaa.gov/cors), UNAVCO (ftp://data-out.unavco.org/), Système d'Observation du Niveau des Eaux Littorales (SONEL, ftp://ftp.sonel.org/), the EUREF Permanent Network Services (ftp://ftp.epncb.oma.be/), Geoscience Australia (ftp://ftp.ga.gov.au/), the New Zealand GeoNet project (ftp://ftp.geonet.org.nz/), the State GPS network of the Republic of Bulgaria (ftp://195.96.249.3/), Institut Geographique National (ftp://igs.ensg.ign.fr/), Instituto Geográfico Nacional (ftp.geodesia.ign.es), Instituto Tecnológico Agrario de Castilla y León (ftp.itacyl.es), Geodetic Data Archiving Facility (ftp://geodaf.mt.asi.it/), and Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (ftp://geoftp.ibge.gov.br/). Data of Canadian High Arctic Ionospheric Network (http://chain.physics.unb.ca/) and data of SibNet network as a part of Center for Common Use “Angara” (http://ckp-angara.iszf.irk.ru/) are available upon request.
References
Afraimovich EL, Demyanov VV, Kondakova TN (2003) Degradation of GPS performance in geomagnetically disturbed conditions. GPS Solut 7(2):109–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-003-0053-7
Afraimovich EL et al (2013) A review of GPS/GLONASS studies of the ionospheric response to natural and anthropogenic processes and phenomena. J Space Weather Space Clim 3:A27. https://doi.org/10.1051/swsc/2013049
Afraimovich EL, Demyanov VV, Smolkov GY (2009) The total failures of GPS functioning caused by the powerful solar radio burst on December 13, 2006. Earth Planets Space 61:637–641. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352940
Ashjaee J, Lorenz R (1992) Precision GPS surveying after Y-code. In: Proc. ION GPS 1992, Institute of Navigation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, September 16-18, 657-659
Astafyeva E, Yasyukevich Y, Maksikov A, Zhivetiev I (2014) Geomagnetic storms, super-storms, and their impacts on GPS-based navigation systems. Space Weather 12(7):508–525. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014SW001072
Berdermann J, Kriegel M, Banys D, Heymann F, Hoque MN, Wilken V, Borries C, Heßelbarth A, Jakowski N (2018) Ionospheric response to the X9.3 Flare on September 6 2017 and its implication for navigation services over Europe. Space Weather 16:1604–1615. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018SW001933
Bruyninx C, Habrich H, Söhne W, Kenyeres A, Stangl G, Völksen C (2012) Enhancement of the EUREF permanent network services and products. Geodesy Planet Earth IAG Symp Ser 136:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20338-1_4
Carrano CS, Bridgwood CT, Groves KM (2009) Impacts of the December 2006 solar radio bursts on the performance of GPS. Radio Science 44(1):RS0A25. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008RS004071
Cerruti AP, Kintner PM, Gary DE, Lanzerotti LJ, de Paula ER, Vo HB (2006) Observed solar radio burst effects on GPS/Wide area augmentation system carrier-to-noise ratio. Space Weather 4(10):S10006. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006SW000254
Chen Z, Gao Y, Liu Z (2005) Evaluation of solar radio bursts’ effect on GPS receiver signal tracking within international GPS service network. Radio Science 40:RS3012. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004RS003066
Coster A, Komjathy A (2008) Space weather and the global positioning system. Space Weather 6:S06D04. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008SW000400
Demyanov VV, Yasyukevich YUV, Jin S (2013) Effects of solar radio emission and ionospheric irregularities on GPS/GLONASS performance. In: Jin S (ed) Geodetic sciences—observations modeling and applications. Intech, London, pp 177–122. https://doi.org/10.5772/3439
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Rizos C (2009) The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J Geodesy 83:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s0019000803003
Fortes LPS, Lin T, Lachapelle G (2015) Effects of the 2012–2013 solar maximum on GNSS signals in Brazil. GPS Solut 19:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0389-1
Hofmann-Wellenhof B, Lichtenegger H, Wasle E (2008) GNSS–Global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo & more. Springer, Vienna
Huang W, Ercha A, Shen H, Liu S (2018) Statistical study of GNSS L-band solar radio bursts. GPS Solut 22:114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0780-4
IS-GPS-200J (2018) Global positioning systems directorate. Systems engineering & integration interface specification IS-GPS-200, https://gps.gov/technical/icwg/IS-GPS-200J.pdf
Jakowski N, Stankov SM, Klaehn D (2005) Operational space-weather service for GNSS precise positioning. Ann Geophys 23:3071–3079. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-23-3071-2005
Jayachandran PT, Langley RB, MacDougall JW et al (2009) The Canadian high arctic ionospheric network (CHAIN). Radio Sci 44:RS0A03. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008RS004046
Jin Y, Oksavik K (2018) GPS scintillations and losses of signal lock at high latitudes during the 2015 St. Patrick’s Day storm. J Geophys Res Space Phys 123:7943–7957. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JA025933
Klobuchar JA, Kunches JM, Van Dierendonck AJ (1999) Eye on the ionosphere: potential solar radio burst effects on GPS signal to noise. GPS Solut 3(2):69–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012794
Matsoukas D, Papagiannis M, Aarons J, Klobuchar J (1972) Correlation of solar radio bursts and sudden increases of the total electron content (SITEC) of the ionosphere. J Atmos Terr Phys 34(7):1275–1283. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9169(72)90137-7
Muhammad B, Alberti V, Marassi A, Cianca E, Messerotti M (2015) Performance assessment of GPS receivers during the September 24, 2011 solar radio burst event. J Space Weather Space Clim 5:A32. https://doi.org/10.1051/swsc/2015034
Pestana A (2015) Technical report: reading RINEX 2.11 observation data files. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.4888.4087
Psiaki ML (2001) Block acquisition of weak GPS signals in a software receiver. In: Proc. ION GPS 2001, Salt Lake City, UT, September 11-14, pp 2838-2850
Rodríguez-Bilbao I, Radicella SM, Rodríguez-Caderot G, Herraiz M (2015) Precise point positioning performance in the presence of the 28 October 2003 sudden increase in total electron content. Space Weather 13:698–708. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015SW001201
Sato H, Jakowski N, Berdermann J, Jiricka K, Heßelbarth A, Banyś D, Wilken V (2019) Solar radio burst events on September 6 2017 and its impact on GNSS signal frequencies. Space Weather 17:816–826. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019SW002198
Sreeja V, Aquino M, Jong K (2013) Impact of the September 24 2011 solar radio burst on the performance of GNSS receivers. Space Weather 11:306–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/swe.20057
Sreeja V, Aquino M, Jong K, Visser H (2014) Effect of the September 24 2011 solar radio burst on precise point positioning service. Space Weather 12(3):143–147. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013SW001011
Tsurutani BT, Verkhoglyadova OP, Mannucci AJ, Lakhina GS, Li G, Zank GP (2009) A brief review of ‘“solar flare effects”’ on the ionosphere. Radio Sci 44:RS0A17. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008RS004029
Wan W, Liu L, Yuan H, Ning B, Zhang S (2005) The GPS measured SITEC caused by the very intense solar flare on July 14, 2000. Adv Space Res 36:2465–2469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2004.01.027
Wanninger L (2018) Detection of RINEX-2 files with mixed GPS L2P(Y)/L2C carrier phase observations. Sensors 18(12):4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124507
Yasyukevich Y, Astafyeva E, Padokhin A, Ivanova V, Syrovatskii S, Podlesnyi A (2018) The September 6 2017 X-class solar flares and their impacts on the ionosphere, GNSS, and HF radio wave propagation. Space Weather 16:1013–1027. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018SW001932
Yasyukevich YuV, Vesnin AM, Perevalova NP (2018) SibNet–Siberian global navigation satellite system network: current state. Solar-Terr Phys 4(4):63–72
Zakharov VI, Yasyukevich YuV, Titova MA (2016) Effect of magnetic storms and substorms on GPS slips at high latitudes. Cosmic Res 54(1):20–30. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952516010147
Zhang DH, Xiao Z (2005) Study of ionospheric response to the 4B flare on October 28 2003 using international GPS service network data. J Geophys Res 110:A03307. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JA010738
Zhang SR, Coster AJ, Erickson PJ, Goncharenko LP, Rideout W, Vierinen J (2019) Traveling ionospheric disturbances and ionospheric perturbations associated with solar flares in September 2017. J Geophys Res Space Phys 124:5894–5917. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JA026585
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. I. Zhivetiev for the “tec-suite” software (http://www.gnss-lab.org/) used for RINEX files processing. We acknowledge the organizations providing GNSS data. This work was performed with the support of the Russian Federation President Grant No. MK-3265.2019.5, RFBR and the Government of the Irkutsk Region under project No. 20-45-383010 and the budgetary funding of Basic Research program II.16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasyukevich, Y.V., Yasyukevich, A.S. & Astafyeva, E.I. How modernized and strengthened GPS signals enhance the system performance during solar radio bursts. GPS Solut 25, 46 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01091-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01091-5