Abstract
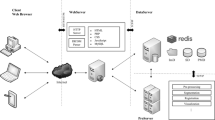
Radiomics has been shown to have considerable potential and value in quantifying the tumor phenotype and predicting the treatment response. In most scenarios, the commercial and open-source software programs are available for quantitative analysis in medical images to streamline radiomics research. However, at this stage, most of these programs are local applications and require users to have experience in programming and software engineering, which clinicians usually do not have. Therefore, in this article, a web-based tool was proposed to flexibly support radiomics research workflow tasks. Radiomics in RayPlus requires zero installation, is easy to maintain, and accessible anywhere via any PC or MAC with an Internet connection. The system provides functions including multimodality image import and viewing, ROI definition, feature extraction, and data sharing. As a web application, it appears an effective way to multi-institution and multi-department collaborative radiomics research and moreover, its transparency, flexibility, and portability can greatly accelerate the pace of clinical data analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fass L: Imaging and cancer: A review. Molecular Oncology 2(2):115–152, 2008
Kurland BF, Gerstner ER, Mountz JM, Schwartz LH, Ryan CW, Graham MM, Buatti JM, Fennessy FM, Eikman EA, Kumar V, Forster KM, Wahl RL, Lieberman FS: Promise and pitfalls of quantitative imaging in oncology clinical trials. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 30(9):1301–1312, 2012
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). European Journal of Cancer 45(2):228–247, 2009
Levy MA, Rubin DL: Current and future trends in imaging informatics for oncology. Cancer Journal (Sudbury, Mass.) 17(4):203, 2011
Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout RGPM, Granton P, Zegers CML, Gillies R, Boellard R, Dekker A, Aerts HJWL: Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. European Journal of Cancer 48(4):441–446, 2012
Hugo JWLA, Emmanuel RV, Ralph L et al.: Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nature Communications. 5:4006, 2014
Yanqi H, Changhong L, He L et al.: Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 34(18):2157–2164, 2016
Hui L, Yitan Z, Elizabeth SB et al.: MR imaging radiomics signatures for predicting the risk of breast cancer recurrence as given by research versions of MammaPrint, Oncotype DX, and PAM50 gene assays. Radiology. 281(2):382–391, 2016
Ke N, Liming S, Qin C et al.: Rectal cancer: assessment of neoadjuvant chemoradiation outcome based on radiomics of multiparametric MRI. Clinical Cancer Research. 22(21):5256–5264, 2016
Jacob A, Satish V, Mirabela R et al.: Radiomics analysis on FLT-PET/MRI for characterization of early treatment response in renal cell carcinoma: a proof-of-concept study. Translational Oncology. 9(2):155–162, 2016
Szczypinski PM, Strzelecki M, Materka A et al.: MaZda—a software package for image texture analysis. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine. 94(1):66–76, 2009
Fang YHD, Lin CY, Shih MJ et al.: Development and evaluation of an open-source software package “CGITA” for quantifying tumor heterogeneity with molecular images. BioMed Research International.:248505, 2014
Deasy JO, Blanco AI, Clark VH: CERR: a computational environment for radiotherapy research. Medical Physics. 30(5):979–985, 2003
Apte A, Wang Y, Deasy J: SU-E-I-66: Radiomics and Image Registration Updates for the Computational Environment for Radiotherapy Research (CERR). Medical Physics. 41:145–145, 2014
Apte A, Veeraraghavan H, Oh J, Kijewski P, Deasy J: SU-E-J-253: The Radiomics Toolbox in the Computational Environment for Radiological Research (CERR). Medical Physics. 42:3324–3324, 2015
Computational Imaging & Bioinformatics Lab - Harvard Medical School (2018) Slicer-Radiomics. http://www.radiomics.io/slicerradiomics.html Accessed 25 February 2018
Pieper S., Halle M., Kikinis R. 3D Slicer. Biomedical Imaging: Nano to Macro, 2004. IEEE International Symposium on IEEE. 632–635, 2004
Zhang L, Fried DV, Fave XJ, Hunter LA, Yang J, Court LE: IBEX: an open infrastructure software platform to facilitate collaborative work in radiomics. Medical Physics. 42(3):1341–1353, 2015
Fave X, Mackin D, Lee J et al.: Computational resources for radiomics. Translational Cancer Research. 5(4):340–348, 2016
Yuan R, Luo M, Sun Z, Shi S, Xiao P, Xie Q: RayPlus: a Web-Based Platform for Medical Image Processing. Journal of Digital Imaging. 30(2):197–203, 2017
Mildenberger P, Eichelberg M, Martin E: Introduction to the DICOM standard. European Radiology. 12(4):920–927, 2002
Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S et al.: Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magnetic resonance imaging. 30(9):1234–1248, 2013
Danielsson PE: Euclidean distance mapping. Computer Graphics and Image Processing. 14(3):227–248, 1980
Otsu N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. 9(1): 62–66, 197S
Huertas A, Medioni G: Detection of intensity changes with subpixel accuracy using Laplacian-Gaussian masks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. PAMI-8(5):651–664, 1986
Xu Y, Weaver JB, Healy DM, Lu J: Wavelet transform domain filters: a spatially selective noise filtration technique. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 3(6):747–758, 1994
Weldon TP, Higgins WE, Dunn DF: Efficient Gabor filter design for texture segmentation. Pattern Recognition. 29(12):2005–2015, 1996
Ganeshan B, Abaleke S, Young RCD, Chatwin CR, Miles KA: Texture analysis of non-small cell lung cancer on unenhanced computed tomography: initial evidence for a relationship with tumour glucose metabolism and stage. Cancer Imaging. 10(1):137–143, 2010
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K: Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. SMC-3(6):610–621, 1973
Thibault G, Fertil B, Navarro C et al.: Shape and texture indexes application to cell nuclei classification. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence. 27(01):1357002, 2013
Galloway MM: Texture classification using gray level run length. Computer Graphic Image Process 4(2):172–179, 1975
Amadasun M, King R: Textural features corresponding to textural properties. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. 19(5):1264–1274, 1989
Tang X: Texture information in run-length matrices. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 7(11):1602–1609, 1998
Kitware Inc. (2018) The Visualization Toolkit (VTK). https://www.vtk.org/ Accessed 25 February 2018
Intel. (2018) Eigen. http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/ Accessed 25 February 2018
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our gratitude to Dr. Ruiguang Zhang and Dr. Quan Chen from the Department of Radiology, Wuhan Union Hospital, Wuhan, China, for all the inspiring discussions. And thanks to Mrs. Feifei Liu for the user interface design.
Funding
Dr. Rong Yuan acknowledges financial support from SZSM201612071.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, R., Shi, S., Chen, J. et al. Radiomics in RayPlus: a Web-Based Tool for Texture Analysis in Medical Images. J Digit Imaging 32, 269–275 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-018-0128-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-018-0128-1