Abstract
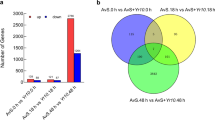
Green leaf volatiles (GLVs) play a vital role in enhancing herbivore-associated defense responses, but the mechanism by which they precisely regulate such responses is not well understood. (Z)-3-Hexenol (z3HOL), an important component of GLVs, effectively activates the defense of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) against a tea geometrid (TG) Ectropis obliqua Prout. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of defense activation by z3HOL, RNA-Sequencing was employed to investigate the effect of z3HOL on transcriptome responses to TG in tea plants. A total of 318 upregulated genes were identified, and expression of 10 unigenes was validated by quantitative real-time PCR. Among these 318 upregulated genes, 56 were defense-related, including 6 key enzyme genes in jasmonic acid, and ethylene biosynthesis, 24 signal transduction genes, and 12 insect-responsive transcription factors. Most of the defense-related genes are induced by JA, TG, or wounding treatments, suggesting that JA signaling plays a vital role in z3HOL-induced tea defense against TG.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- DGE:
-
Digital gene expression
- GC–MS:
-
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- GLVs:
-
Green leaf volatiles
- HIPVs:
-
Herbivore-induced plant volatiles
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- MPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- PIs:
-
Proteinase inhibitors
- PPO:
-
Polyphenol oxidase
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- RH:
-
Relative air humidity
- RLKs:
-
Receptor-like protein kinases
- RNA-seq:
-
RNA sequencing
- TFs:
-
Transcription factors
- TG:
-
Tea geometrid
- TPS:
-
Terpene synthase
- XIPs:
-
Xylanase inhibitor proteins
- z3HOL:
-
(Z)-3-Hexenol
References
Aljbory Z, Chen MS (2018) Indirect plant defense against insect herbivores: a review. Insect Sci 2018 25:2–23
Allmann S, Baldwin IT (2010) Insects betray themselves in nature to predators by rapid isomerization of green leaf volatiles. Science 329:1075–1078
Ameye M, Audenaert K, De Zutter N, Steppe K, Van Meulebroek L, Vanhaecke L, De Vleesschauwer D, Haesaert G, Smagghe G (2015) Priming of wheat with the green leaf volatile Z-3-hexenyl acetate enhances defense against Fusarium graminearum but boosts deoxynivalenol production. Plant Physiol 167:1671–1684
Arfaoui A, El Hadrami A, Daayf F (2018) Pre-treatment of soybean plants with calcium stimulates ROS responses and mitigates infection by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.. Plant Physiol Biochem 122:121–128
Beckers GJM, Jaskiewicz M, Liu Y, Underwood WR, He SY, Zhang S, Conrath U (2009) Mitogen-activated protein kinases 3 and 6 are required for full priming of stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21:944–953
Dicke M, Baldwin IT (2010) The evolutionary context for herbivore induced plant volatiles, beyond the cry for help. Trends Plant Sci 15:167–175
Dubrovina AS, Kiselev KV, Khristenko VS, Olga A, Aleynova OA (2017) The calcium-dependent protein kinase gene VaCPK29 is involved in grapevine responses to heat and osmotic stresses. Plant Growth Regul 82:79–89
Engelberth J, Alborn HT, Schmelz EA, Tumlinson JH (2004) Airborne signals prime plants against insect herbivore attack. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1781–1785
Engelberth J, Contreras CF, Dalvi C, Li T, Engelberth M (2013) Early transcriptome analyses of Z-3-hexenol-treated Zea mays revealed distinct transcriptional networks and anti-herbivore defense potential of green leaf volatiles. PLoS One 810:e77465
Farag MA, Fokar M, Zhang HA, Allen RD, Paré PW (2005) Z-3-Hexenol induces defense genes and downstream metabolites in maize. Planta 220:900–909
Frost CJ, Mescher MC, Dervinis C, Davis JM, Carlson JE, De Moraes CM (2008) Priming defense genes and metabolites in hybrid poplar by the green leaf volatile cis-3-hexenyl acetate. N Phytol 180:722–734
He XR, Chen X, Lin SB, Mo XC, Zhou PY, Zhang ZH, Lu YY, Gu HN, Shang ZC, Lou YG, Wu J (2017) Diversity-oriented synthesis as a tool for identifying new chemical elicitors. ChemistryOpen 6:102–111
Hu LF, Ye M, Zhang TF, Li R, Zhou GX, Wang Q, Lu J, Lou YG (2015) The rice transcription factor WRKY53 suppresses herbivore-induced defenses by acting as a negative feedback modulator of map kinase activity. Plant Physiol 169:2907–2921
Kachroo A, Robin GP (2013) Systemic signaling during plant defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16:527–533
Kessler A, Halitschke R, Diezel C, Baldwin IT (2006) Priming of plant defense responses in nature by airborne signaling between Artemisia tridentata and Nicotiana attenuata. Oecologia 148:280–292
Kiep V, Vadassery J, Lattke J, Maass JP, Boland W, Peiter E, Mithofer A (2015) Systemic cytosolic Ca2+ elevation is activated upon wounding and herbivory in Arabidopsis. N Phytol 207:996–1004
Liu S, Han B (2010) Differential expression pattern of an acidic 9/13-lipoxygenase in flower opening and senescence and in leaf response to phloem feeders in the tea plant. BMC Plant Biol 10:228
Lu J, Ju HP, Zhou GX, Zhu CS, Erb M, Wang XP, Wang P, Lou YG (2011) An EAR-motif-containing ERF transcription factor affects herbivore-induced signaling, defense and resistance in rice. Plant J 68:583–596
Lu J, Li JC, Ju HP, Liu XL, Erb M, Wang X, Lou YG (2014) Contrasting effects of ethylene biosynthesis on induced plant resistance against a chewing and a piercing-sucking herbivore in rice. Mol Plant 7:1670–1682
Mauch-Mani B, Baccelli I, Luna E, Flors V (2017) Defense priming: an adaptive part of induced resistance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 68:485–512
Mazars C, Thuleau P, Lamotte O, Bourque S (2010) Cross-talk between ROS and calcium in regulation of nuclear activities. Mol Plant 3:706–718
Mithofer A, Wanner G, Boland W (2005) Effects of feeding Spodoptera littoralis on Lima bean leaves. II. Continuous mechanical wounding resembling insect feeding is sufficient to elicit herbivory-related volatile emission. Plant Physiol 137:1160–1168
Parry D, Spence JR, Volney WJA (1998) Budbreak phenology and natural enemies mediate survival of first-instar forest tent caterpillar (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae). Environ Entomol 27:1368–1374
Pieterse CMJ, Leon-Reyes A, Van der Ent S, Van Wees SCM (2009) Networking by small-molecule hormones in plant immunity. Nat Chem Biol 5:308–316
Scala A, Allmann S, Mirabella R, Haring MA, Schuurink RC (2013) Green leaf volatiles: A plant’s multifunctional weapon against herbivores and pathogens. Int J Mol Sci 14:17781–17811
Szczegielniak J, Borkiewicz L, Szurmak B, Lewandowska-Gnatowska E, Statkiewicz M, Klimecka M, Cieśla J, Muszyńska G (2012) Maize calcium-dependent protein kinase (ZmCPK11): local and systemic response to wounding, regulation by touch and components of jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol 146:1–14
Tamiru A, Bruce TJA, Woodcock CM, Caulfield JC, Midega CAO, Ogol CKPO, Mayon P, Birkett MA, Pickett JA, Khan ZR (2011) Maize landraces recruit egg and larval parasitoids in response to egg deposition by a herbivore. Ecol Lett 14:1075–1083
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10:57–63
Xin Z, Wang Q, Yu Z, Hu L, Li J, Xiang C, Wang B, Lou Y (2014) Overexpression of a xylanase inhibitor gene, OsHI-XIP, enhances resistance in rice to herbivores. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:465–475
Xin Z, Li X, Li J, Chen Z, Sun X (2016) Application of chemical elicitor (Z)-3-hexenol enhances direct and indirect plant defenses against tea geometrid Ectropis obliqua. Biocontrol 61:1–12
Yang ZW, Duan XN, Jin S, Li XW, Chen ZM, Ren BZ, Sun XL (2013) Regurgitant derived from the tea geometrid Ectropis obliqua suppresses wound-induced polyphenol oxidases activity in tea plants. J Chem Ecol 39:744–751
Ye GY, Xiao Q, Chen M, Chen XX, Yuan ZJ, Stanley DW, Hu C (2014) Tea: biological control of insect and mite pests in China. Biol Control 68:73–91
Zhao QY, Wang Y, Kong YM, Luo D, Li X, Hao P (2011) Optimizing de novo transcriptome assembly from short-read RNA-Seq data: a comparative study. BMC Bioinform 12:s2
Acknowledgements
The study was jointly sponsored by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201403030), the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (no. 1610212016019), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31401758), and the Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province (2016C32026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Z., Ge, L., Chen, S. et al. Enhanced transcriptome responses in herbivore-infested tea plants by the green leaf volatile (Z)-3-hexenol. J Plant Res 132, 285–293 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-019-01094-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-019-01094-x