Abstract
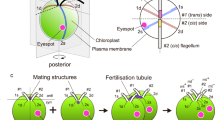
The sexual reproductive processes of some representative freshwater green algae are reviewed. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is a unicellular volvocine alga having two mating types: mating type plus (mt+) and mating type minus (mt−), which are controlled by a single, complex mating-type locus. Sexual adhesion between the gametes is mediated by sex-specific agglutinin molecules on their flagellar membranes. Cell fusion is initiated by an adhesive interaction between the mt+ and mt− mating structures, followed by localized membrane fusion. The loci of sex-limited genes and the conformation of sex-determining regions have been rearranged during the evolution of volvocine algae; however, the essential function of the sex-determining genes of the isogamous unicellular Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is conserved in the multicellular oogamous Volvox carteri. The sexual reproduction of the unicellular charophycean alga, Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex, is also focused on here. The sexual reproductive processes of heterothallic strains are controlled by two multifunctional sex pheromones, PR-IP and PR-IP Inducer, which independently promote multiple steps in conjugation at the appropriate times through different induction mechanisms. The molecules involved in sexual reproduction and sex determination have also been characterized.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe J, Hori S, Tsuchikane Y, Kitao N, Kato M, Sekimoto H (2011) Stable nuclear transformation of the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Cell Physiol 52:1676–1685. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcr103
Abe J, Hirano N, Komiya A, Kanda N, Fujiwara A, Hori S, Tsuchikane Y, Sekimoto H (2016a) Preparation of knockdown transformants of unicellular charophycean alga, Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Bio-protocol 6:e1813
Abe J, Hori S, Sato M, Sekimoto H (2016b) Concanavalin A disrupts the release of fibrous material necessary for zygote formation of a unicellular charophycean alga, Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Front Plant Sci 7:1040. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.01040
Akatsuka S, Sekimoto H, Iwai H, Fukumoto R, Fujii T (2003) Mucilage secretion regulated by sex pheromones in Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Cell Physiol 44:1081–1087
Akatsuka S, Tsuchikane Y, Fukumoto R, Fujii T, Sekimoto H (2006) Physiological characterization of the sex pheromone protoplast-release-inducing protein from the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex (Charophyta). Phycol Res 54:116–121
Buchanan MJ, Imam SH, Eskue WA, Snell WJ (1989) Activation of the cell wall degrading protease, lysin, during sexual signalling in Chlamydomonas: the enzyme is stored as an inactive, higher relative molecular mass precursor in the periplasm. J Cell Biol 108:199–207
Cook PA (1963) Variation in vegetative and sexual morphology among the small curved species of Closterium. Phycologia 3:1–18
Ferris PJ, Goodenough UW (1994) The Mating-type locus of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii contains highly rearranged DNA sequences. Cell 76:1135–1145
Ferris PJ, Goodenough UW (1997) Mating type in Chlamydomonas is specified by mid, the minus-dominance gene. Genetics 146:859–869
Ferris PJ, Woessner JP, Goodenough UW (1996) A sex recognition glycoprotein is encoded by the plus mating-type gene fus1 of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Biol Cell 7:1235–1248
Ferris P, Armbrust EV, Goodenough UW (2002) Genetic structure of the mating-type locus of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Genetics 160:181–200
Ferris P, Waffenschmidt S, Umen JG, Lin H, Lee J-H, Ishida K, Kubo T, Lau J, Goodenough UW (2005) Plus and minus sexual agglutinins from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell 17:597–615
Ferris P, Olson BJ, De Hoff PL, Douglass S, Casero D, Prochnik S, Geng S, Rai R, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Nishii I, Hamaji T, Nozaki H, Pellegrini M, Umen JG (2010) Evolution of an expanded sex-determining locus in Volvox. Science 328:351–354
Geng S, De Hoff P, Umen JG (2014) Evolution of sexes from an ancestral mating-type specification pathway. PloS One 12:e1001904. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002055
Goodenough UW (1989) Cyclic AMP enhances the sexual agglutinability of Chlamydomonas flagella. J Cell Biol 109:247–252
Graham LE, Graham JE, Wilcox LW (2009) Algae 2nd edn. Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco
Hake S, Smith HM, Holtan H, Magnani E, Mele G, Ramirez J (2004) The role of knox genes in plant development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:125–151
Hamaji T, Ferris PJ, Coleman AW, Waffenschmidt S, Takahashi F, Nishii I, Nozaki H (2008) Identification of the minus-dominance gene ortholog in the mating-type locus of Gonium pectorale. Genetics 178:283–294
Hamaji T, Ferris PJ, Nishii I, Nishimura Y, Nozaki H (2013) Distribution of the sex-determining gene MID and molecular correspondence of mating types within the isogamous genus Gonium (Volvocales, Chlorophyta). PloS One 8:e64385. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064385
Hamaji T, Lopez D, Pellegrini M, Umen J (2016a) Identification and characterization of a cis-regulatory element for zygotic gene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. G3 (Bethesda) 6:1541–1548. doi:10.1534/g3.116.029181
Hamaji T, Mogi Y, Ferris PJ, Mori T, Miyagishima S, Kabeya Y, Nishimura Y, Toyoda A, Noguchi H, Fujiyama A, Olson BJ, Marriage TN, Nishii I, Umen JG, Nozaki H (2016b) Sequence of the Gonium pectorale mating locus reveals a complex and dynamic history of changes in volvocine algal mating haplotypes. G3 (Bethesda) 6:1179–1189 doi:10.1534/g3.115.026229
Hanschen ER, Marriage TN, Ferris PJ, Hamaji T, Toyoda A, Fujiyama A, Neme R, Noguchi H, Minakuchi Y, Suzuki M, Kawai-Toyooka H, Smith DR, Sparks H, Anderson J, Bakaric R, Luria V, Karger A, Kirschner MW, Durand PM, Michod RE, Nozaki H, Olson BJ (2016) The Gonium pectorale genome demonstrates co-option of cell cycle regulation during the evolution of multicellularity. Nat commun 7:11370. doi:10.1038/ncomms1137
Harris EH (1989) The Chlamydomonas Sourcebook: a comprehensive guide to biology and laboratory use. Academic Press, San Diego
Hirano N, Marukawa Y, Abe J, Hashiba S, Ichikawa M, Tanabe Y, Ito M, Nishii I, Tsuchikane Y, Sekimoto H (2015) A Receptor-like kinase, related with cell wall sensor of higher plants, is required for sexual reproduction in the unicellular charophycean alga, Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Cell Physiol 56:1456–1462
Hori S, Sekimoto H, Abe J (2012) Properties of cell surface carbohydrates in sexual reproduction of the Closterium peracerosum–strigosum–littorale complex (Zygnematophyceae, Charophyta). Phycol Res 60:254–260 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1835.2012.00656.x
Hori K, Maruyama F, Fujisawa T, Togashi T, Yamamoto N, Seo M, Sato S, Yamada T, Mori H, Tajima N, Moriyama T, Ikeuchi M, Watanabe M, Wada H, Kobayashi K, Saito M, Masuda T, Sasaki-Sekimoto Y, Mashiguchi K, Awai K, Shimojima M, Masuda S, Iwai M, Nobusawa T, Narise T, Kondo S, Saito H, Sato R, Murakawa M, Ihara Y, Oshima-Yamada Y, Ohtaka K, Satoh M, Sonobe K, Ishii M, Ohtani R, Kanamori-Sato M, Honoki R, Miyazaki D, Mochizuki H, Umetsu J, Higashi K, Shibata D, Kamiya Y, Sato N, Nakamura Y, Tabata S, Ida S, Kurokawa K, Ohta H (2014) Klebsormidium flaccidum genome reveals primary factors for plant terrestrial adaptation. Nat Commun 5:3978. doi:10.1038/ncomms4978
Hunnicutt GR, Kosfiszer MG, Snell WJ (1990) Cell body and flagellar agglutinins in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: the cell body plasma membrane is a reservoir for agglutinins whose migration to the flagella is regulated by a functional barrier. J Cell Biol 111:1605–1616
Ichimura T (1973) The life cycle and its control in some species of Closterium, with special reference to the biological species problem. D. Sci. thesis, University of Tokyo, Tokyo
Ju C, Van de Poel B, Cooper ED, Thierer JH, Gibbons TR, Delwiche CF, Chang C (2015) Conservation of ethylene as a plant hormone over 450 million years of evolution. Nat Plant 1:14004. doi:10.1038/nplants.2014.4
Kanaoka MM, Higashiyama T (2015) Peptide signaling in pollen tube guidance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 28:127–136. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2015.10.006
Karol KG, McCourt RM, Cimino MT, Delwiche CF (2001) The closest living relatives of land plants. Science 294:2351–2353. doi:10.1126/science.1065156
Kinoshita T, Fukuzawa H, Shimada T, Saito T, Matsuda Y (1992) Primary structure and expression of a gamete lytic enzyme in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: similarity of functional domains to matrix metalloproteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4693–4697
Lee JH, Huawen L, Joo S, Goodenough UW (2008) Early sexual origins of homeoprotein heterodimerization and evolution of the plant KNOX/BELL family. Cell 133:829–840
Lin H, Goodenough UW (2007) Gametogenesis in the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii minus mating type is controlled by two genes, MID and MTD1. Genetics 176:913–925
Lippert BE (1967) Sexual reproduction in Closterium moniliferum and Closterium ehrenbergii. J Phycol 3:182–198
Liu Y, Tewari R, Ning J, Blagborough AM, Garbom S, Pei J, Grishin NV, Steele RE, Sinden RE, Snell WJ, Billker O (2008) The conserved plant sterility gene HAP2 functions after attachment of fusogenic membranes in Chlamydomonas and Plasmodium gametes. Genes Dev 22:1051–1068. doi:10.1101/gad.1656508
Liu Y, Misamore MJ, Snell WJ (2010) Membrane fusion triggers rapid degradation of two gamete-specific, fusion-essential proteins in a membrane block to polygamy in Chlamydomonas. Development 137:1473–1481. doi:10.1242/dev.044743
Merchant SS, Prochnik SE, Vallon O, Harris EH, Karpowicz SJ, Witman GB, Terry A, Salamov A, Fritz-Laylin LK, Marechal-Drouard L, Marshall WF, Qu LH, Nelson DR, Sanderfoot AA, Spalding MH, Kapitonov VV, Ren Q, Ferris P, Lindquist E, Shapiro H, Lucas SM, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Cardol P, Cerutti H, Chanfreau G, Chen CL, Cognat V, Croft MT, Dent R, Dutcher S, Fernandez E, Fukuzawa H, Gonzalez-Ballester D, Gonzalez-Halphen D, Hallmann A, Hanikenne M, Hippler M, Inwood W, Jabbari K, Kalanon M, Kuras R, Lefebvre PA, Lemaire SD, Lobanov AV, Lohr M, Manuell A, Meier I, Mets L, Mittag M, Mittelmeier T, Moroney JV, Moseley J, Napoli C, Nedelcu AM, Niyogi K, Novoselov SV, Paulsen IT, Pazour G, Purton S, Ral JP, Riano-Pachon DM, Riekhof W, Rymarquis L, Schroda M, Stern D, Umen J, Willows R, Wilson N, Zimmer SL, Allmer J, Balk J, Bisova K, Chen CJ, Elias M, Gendler K, Hauser C, Lamb MR, Ledford H, Long JC, Minagawa J, Page MD, Pan J, Pootakham W, Roje S, Rose A, Stahlberg E, Terauchi AM, Yang P, Ball S, Bowler C, Dieckmann CL, Gladyshev VN, Green P, Jorgensen R, Mayfield S, Mueller-Roeber B, Rajamani S, Sayre RT, Brokstein P, Dubchak I, Goodstein D, Hornick L, Huang YW, Jhaveri J, Luo Y, Martinez D, Ngau WC, Otillar B, Poliakov A, Porter A, Szajkowski L, Werner G, Zhou K, Grigoriev IV, Rokhsar DS, Grossman AR (2007) The Chlamydomonas genome reveals the evolution of key animal and plant functions. Science 318:245–250. doi:10.1126/science.1143609
Misamore MJ, Gupta S, Snell WJ (2002) FUS1, the cell surface protein required for Chlamydomonas fertilization, contains invasin-like internal repeats and requires actin for its localization. Mol Biol Cell 13:625
Misamore MJ, Gupta S, Snell WJ (2003) The Chlamydomonas Fus1 protein is present on the mating type plus fusion organelle and required for a critical membrane adhesion event during fusion with minus gametes. Mol Biol Cell 14:2530–2542
Mori T, Kuroiwa H, Higashiyama T, Kuroiwa T (2006) GENERATIVE CELL SPECIFIC 1 is essential for angiosperm fertilization. Nat Cell Biol 8:64–71. doi:10.1038/ncb1345
Noguchi T (1988) Numerical and structural changes in dictyosomes during zygospore germination of Closterium ehrenbergii. Protoplasma 147:135–142
Noguchi T, Ueda K (1985) Cell walls, plasma membranes, and dictyosomes during zygote maturation of Closterium ehrenbergii. Protoplasma 128:64–71
Nojiri T, Fujii T, Sekimoto H (1995) Purification and characterization of a novel sex pheromone that induces the release of another sex pheromone during sexual reproduction of the heterothallic Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Cell Physiol 36:79–84
Nozaki H, Mori T, Misumi O, Matsunaga S, Kuroiwa T (2006) Males evolved from the dominant isogametic mating type. Curr Biol 16:R1018–R1020
Pan J, Snell WJ (2002) Kinesin-II is required for flagellar sensory transduction during fertilization in Chlamydomonas. Mol Biol Cell 13:1417–1426
Pasquale SM, Goodenough UW (1987) Cyclic AMP functions as a primary sexual signal in gametes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol 105:2279–2292
Pickett-Heaps JD, Fowke LC (1971) Conjugation in the desmid Closterium littorale. J Phycol 7:37–50
Prochnik SE, Umen J, Nedelcu AM, Hallmann A, Miller SM, Nishii I, Ferris P, Kuo A, Mitros T, Fritz-Laylin LK, Hellsten U, Chapman J, Simakov O, Rensing SA, Terry A, Pangilinan J, Kapitonov V, Jurka J, Salamov A, Shapiro H, Schmutz J, Grimwood J, Lindquist E, Lucas S, Grigoriev IV, Schmitt R, Kirk D, Rokhsar DS (2010) Genomic analysis of organismal complexity in the multicellular green alga Volvox carteri. Science 329:223–226
Saito T, Tsubo Y, Matsuda Y (1985) Synthesis and turnover of cell body agglutinin as a pool of flagellar surface agglutinin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii gamete. Arch Microbiol 142:207–210
Saito T, Small L, Goodenough UW (1993) Activation of adenylyl cyclase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by adhesion and by heat. J Cell Biol 122:137–147
Scofield S, Murray AH (2006) KNOX gene function in plant stem cell niches. Plant Mol Biol 60:929–946
Sekimoto H (2002) Production and secretion of a biologically active Closterium sex pheromone by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:789–794
Sekimoto H, Satoh S, Fujii T (1990) Biochemical and physiological properties of a protein inducing protoplast release during conjugation in the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Planta 182:348–354
Sekimoto H, Satoh S, Fujii T (1992) Biochemical and physiological properties of a gametic protoplast-release-inducing protein in Closterium. Korean. J Phycol 7:121–129
Sekimoto H, Inoki Y, Fujii T (1993a) Detection and evaluation of an inducer of diffusible mating pheromone of heterothallic Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Cell Physiol 37:991–996
Sekimoto H, Satoh S, Fujii T (1993b) Analysis of binding of biotinylated protoplast-release-inducing protein that induces release of gametic protoplasts in the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Planta 189:468–474
Sekimoto H, Sone Y, Fujii T (1994a) cDNA cloning of a 42-kilodalton subunit of protoplast-release-inducing protein from Closterium. Plant Physiol 104:1095–1096
Sekimoto H, Sone Y, Fujii T (1994b) A cDNA encoding a 19-kilodalton subunit of protoplast-release-inducing protein from Closterium. Plant Physiol 105:447
Sekimoto H, Sone Y, Fujii T (1994c) Regulation of expression of the genes for a sex pheromone by an inducer of the sex pheromone in the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Planta 193:137–144
Sekimoto H, Fukumoto R, Dohmae N, Takio K, Fujii T, Kamiya Y (1998) Molecular cloning of a novel sex pheromone responsible for the release of a different sex pheromone in Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Cell Physiol 39:1169–1175
Sekimoto H, Tanabe Y, Takizawa M, Ito N, Fukumoto R, Ito M (2003) Expressed sequence tags from the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex, a unicellular charophycean alga, in the sexual reproduction process. DNA Res 10:147–153
Sekimoto H, Tanabe Y, Tsuchikane Y, Shirosaki H, Fukuda H, Demura T, Ito M (2006) Gene expression profiling using cDNA microarray analysis of the sexual reproduction stage of the unicellular charophycean alga Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Physiol 141:271–279
Sekimoto H, Abe J, Tsuchikane Y (2012) New insights into the regulation of sexual reproduction in Closterium. Int Rev. Cell Mol Biol 297:309–338. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-394308-8.00014-5
Sekimoto H, Abe J, Tsuchikane Y (2014) Mechanism of sexual reproduction in fresh water microalgae. In: Ramawat KG, Merillon JM, Shivanna KR (eds.) Reproductive biology of plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 29–56
Snell WJ, Eskue WA, Buchanan MJ (1989) Regulated secretion of a serine protease that activates an extracellular matrix-degrading metalloprotease during fertilization in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol 109:1689–1694
Steele RE, Dana CE (2009) Evolutionary history of the HAP2/GCS1 gene and sexual reproduction in metazoans. PloS one 4:e7680. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007680
Timme RE, Bachvaroff TR, Delwiche CF (2012) Broad phylogenomic sampling and the sister lineage of land plants. PloS one 7:e29696. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029696
Tsuchikane Y, Ito M, Fujii T, Sekimoto H (2005) A sex pheromone, protoplast-release-inducing protein (PR-IP) Inducer, induces sexual cell division and production of PR-IP in Closterium. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1472–1476
Tsuchikane Y, Kokubun Y, Sekimoto H (2010a) Characterization and molecular cloning of conjugation-regulating sex pheromones in homothallic Closterium. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1515–1523
Tsuchikane Y, Sato M, Ootaki T, Kokubun Y, Nozaki H, Ito M, Sekimoto H (2010b) Sexual processes and phylogenetic relationships of a homothallic strain in the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex (Zygnematales, Charophyceae). J Phycol 46:278–284
Tsuchikane Y, Tsuchiya M, Hindak F, Nozaki H, Sekimoto H (2012) Zygospore formation between homothallic and heterothallic strains of Closterium. Sex Plant Reprod 25:1–9. doi:10.1007/s00497-011-0174-z
von Besser K, Frank AC, Johnson MA, Preuss D (2006) Arabidopsis HAP2 (GCS1) is a sperm-specific gene required for pollen tube guidance and fertilization. Development 133:4761–4769. doi:10.1242/dev.02683
Wickett NJ, Mirarab S, Nguyen N, Warnow T, Carpenter E, Matasci N, Ayyampalayam S, Barker MS, Burleigh JG, Gitzendanner MA, Ruhfel BR, Wafula E, Der JP, Graham SW, Mathews S, Melkonian M, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Miles NW, Rothfels CJ, Pokorny L, Shaw AJ, DeGironimo L, Stevenson DW, Surek B, Villarreal JC, Roure B, Philippe H, dePamphilis CW, Chen T, Deyholos MK, Baucom RS, Kutchan TM, Augustin MM, Wang J, Zhang Y, Tian Z, Yan Z, Wu X, Sun X, Wong GK, Leebens-Mack J (2014) Phylotranscriptomic analysis of the origin and early diversification of land plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E4859–E4868
Wong JL, Johnson MA (2010) Is HAP2-GCS1 an ancestral gamete fusogen? Trends Cell Biol 20:134–141. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2009.12.007
Zhang YH, Snell WJ (1994) Flagellar adhesion-dependent regulation of Chlamydomonas adenylyl cyclase in vitro—a possible role for protein kinases in sexual signaling. J Cell Biol 125:617–624
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (nos. 24370038, 25304012, 26650147, 15H05237, and 16H04836) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas “Elucidating common mechanisms of allogenic authentication” (no. 24112713 to H.S.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan. The work was also partly supprted by MEXT KAKENHI (221S0002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekimoto, H. Sexual reproduction and sex determination in green algae. J Plant Res 130, 423–431 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-017-0908-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-017-0908-6