Abstract
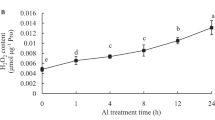
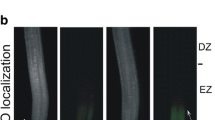
The objective of this study was to investigate the specific role of nitric oxide (NO) in the early response of hulless barley roots to copper (Cu) stress. We used the fluorescent probe diaminofluorescein-FM diacetate to establish NO localization, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-special labeling and histochemical procedures for the detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the root apex. An early production of NO was observed in Cu-treated root tips of hulless barley, but the detection of NO levels was decreased by supplementation with a NO scavenger, 2-phenyl-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide (c-PTIO). Application of sodium nitroprusside (a NO donor) relieved Cu-induced root inhibition, ROS accumulation and oxidative damage, while c-PTIO treatment had a synergistic effect with Cu and further enhanced ROS levels and oxidative stress. In addition, the Cu-dependent increase in activities of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and ascorbate peroxidase were further enhanced by exogenous NO, but application of c-PTIO decreased the activities of catalase and ascorbate peroxidase in Cu-treated roots. Subsequently, cell death was observed in root tips and was identified as a type of programed cell death (PCD) by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling assay. The addition of NO prevented the increase of cell death in root tips, whereas inhibiting NO accumulation further increased the number of cells undergoing PCD. These results revealed that NO production is an early response of hulless barley roots to Cu stress and that NO contributes to Cu tolerance in hulless barley possibly by modulating antioxidant defense, subsequently reducing oxidative stress and PCD in root tips.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASC:
-
Ascorbate
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Cu:
-
Copper
- c-PTIO:
-
2-(4-Carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzine
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DAF-FM:
-
DA 4-amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluorofluorescein diacetate
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- GPX:
-
Guaiacol peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NBT:
-
Nitro blue tetrazolium
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- NR:
-
Nitrate reductase
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- SNP:
-
Sodium nitroprusside
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
References
Adamakis ID, Panteris E, Eleftheriou EP (2011) The fatal effect of tungsten on Pisum sativum L. root cells: indications for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced programmed cell death. Planta 234:21–34
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Alemayehu A, Zelinova V, Bocova B, Huttova J, Mistrik I, Tamas L (2015) Enhanced nitric oxide generation in root transition zone during the early stage of cadmium stress is required for maintaining root growth in barley. Plant Soil 390:213–222
Balestrazzi A, Macovei A, Testoni C, Raimondi E, Dona M, Carbonera D (2009) Nitric oxide biosynthesis in white poplar (Populus alba L.) suspension cultures challenged with heavy metals. Plant Stress 3:1–6
Bellin D, Asai S, Delledonne M, Yoshioka H (2013) Nitric oxide as a mediator for defense responses. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:271–277
Benatti MR, Yookongkaew N, Meetam M, Guo WJ, Punyasuk N, AbuQamar S, Goldsbrough P (2014) Metallothionein deficiency impacts copper accumulation and redistribution in leaves and seeds of Arabidopsis. New Phytol 202:940–951
Besson-Bard A, Pugin A, Wendehenne D (2008) New insights into nitric oxide signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:21–39
Besson-Bard A, Gravot A, Richaud P, Auroy P, Duc C, Gaymard F, Taconnat L, Renou JP, Pugin A, Wendehenne D (2009) Nitric oxide contributes to cadmium toxicity in Arabidopsis by promoting cadmium accumulation in roots and by up-regulating genes related to iron uptake. Plant Physiol 149:1302–1315
Burkhead JL, Gogolin Reynolds KA, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Pilon M (2009) Copper homeostasis. New Phytol 182:799–816
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182
Correa-Aragunde N, Foresi N, Lamattina L (2013) Structure diversity of nitric oxide synthases (NOS): the emergence of new forms in photosynthetic organisms. Front Plant Sci. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00232
Curtis M, Hays J (2007) Tolerance of dividing cells to replication stress in UVB-irradiated Arabidopsis roots: requirements for DNA translesion polymerases h and z. DNA Repair 6:1341–1358
Cuypers A, Smeets K, Ruytinx J, Opdenakker K, Keunen E, Remans T, Horemans N, Vanhoudt N, Van Sanden S, Van Belleghem F, Guisez Y, Colpaert J, Vangronsveld J (2011) The cellular redox state as a modulator in cadmium and copper responses in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. J Plant Physiol 168:309–316
De Michele R, Vurro E, Rigo C, Costa A, Elviri L, Di Valentin M, Careri M, Zottini M, Sanità di Toppi L, Lo Schiavo F (2009) Nitric oxide is involved in cadmium-induced programmed cell death in Arabidopsis suspension cultures. Plant Physiol 150:217–228
Domingos P, Prado AM, Wong A, Gehring C, Feijo JA (2015) Nitric oxide: a multitasked signaling gas in plants. Mol Plant 8:506–520
Doyle SM, McCabe PF (2010) Type and cellular location of reactive oxygen species determine activation or suppression of programmed cell death in Arabidopsis suspension cultures. Plant Signal Behav 5:467–468
Duan YF, Zhang WS, Li B, Wang YN, Li KX, Sodmergen Han C, Zhang Y, Li X (2010) An endoplasmic reticulum response pathway mediates programmed cell death of root tip induced by water stress in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 186:681–695
Feigl G, Kumar D, Lehotai N, Tugyi N, Molnar A, Ordog A, Szepesi A, Gemes K, Laskay G, Erdei L, Kolbert Z (2012) Physiological and morphological responses of the root system of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.) and rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) to copper stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 94:179–189
Foresi N, Correa-Aragunde N, Parisi G, Caló G, Salerno G, Lamattina L (2010) Characterization of a nitric oxide synthase from the plant kingdom: NO generation from the green alga Ostreococcus tauri is light irradiance and growth phase dependent. Plant Cell 22:3816–3830
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2005) Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: a metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 17:1866–1875
González A, Cabrera Mde L, Henriquez MJ, Contreras RA, Morales B, Moenne A (2012) Cross talk among calcium, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide and activation of gene expression involving calmodulins and calcium-dependent protein kinases in U. compressa exposed to copper excess. Plant Physiol 158:1451–1462
He H, He L, Gu M (2014) The diversity of nitric oxide function in plant responses to metal stress. Biometals 27:219–228
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts.I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Helmersson A, VonArnold S, Bozhkov PV (2008) The level of free intracellular zinc mediates programmed cell death/cell survival decisions in plant embryos. Plant Physiol 147:1158–1167
Hu KD, Hu LY, Li YH, Zhang FQ, Zhang H (2007) Protective roles of nitric oxide on germination and antioxidative metabolism in wheat seeds under copper stress. Plant Growth Regul 53:173–183
Hu Y, Li J, Yang L, Yang L, Nan W, Cao X, Bi Y (2014) Inhibition of root growth by narciclasine is caused by DNA damage-Induced cell cycle arrest in Lettuce seedlings. Protoplasma 251:1113–1124
Hu Y, You J, Liang X (2015) Nitrate reductase-mediated nitric oxide production is involved in copper tolerance in shoots of hulless barley. Plant Cell Rep 34:367–379
Huang W, Yang X, Yao S, Lwinoo T, He H, Wang A et al (2014) Reactive oxygen species burst induced by aluminum stress triggers mitochondria-dependent programmed cell death in peanut root tip cells. Plant Physiol Biochem 82:76–84
İşeri OD, Korpe DA, Yurtcu E, Sahin FI, Haberal M (2011) Copper induced oxidative damage, antioxidant response and genotoxicity in Lycopersicum esculentum Mill. and Cucumis sativus L. Plant Cell Rep 30:1713–1721
Janda T, Szalai G, Tari I, Paldi E (1999) Hydroponic treatment with salicylic acid decreases the effects of chilling in maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Planta 208:175–180
Kazemi N (2012) Effect of exogenous nitric oxide alleviating nickel-induced oxidative stress in leaves of tomato plants. Int J Agric Sci 2:799–809
Ke W, Xiong ZT, Chen S, Chen J (2007) Effects of copper and mineral nutrition on growth, copper accumulation and mineral element uptake in two Rumex japonicus populations from a copper mine and an uncontaminated field sites. Environ Exp Bot 59:59–67
Lee SA, Yoon EK, Heo JO, Lee MH, Hwang I, Cheong H, Lee WS, Hwang YS, Lim J (2012) Analysis of Arabidopsis glucose insensitive growth mutants reveals the involvement of the plastidial copper transporter PAA1 in glucose-induced intracellular signaling. Plant Physiol 159:1001–1012
Lehotai N, Pető A, Bajkán S, Erdei L, Tari I, Kolbert Z (2011) In vivo and in situ visualization of early physiological events induced by heavy metals in pea root meristem. Acta Physiol Plant 33:2199–2207
Lequeux H, Hermans C, Lutts S, Verbruggen N (2010) Response to copper excess in Arabidopsis thaliana: impact on the root system architecture, hormone distribution, lignin accumulation and mineral profile. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:673–682
Liu KL, Shen L, Sheng JP (2008) Improvement in cadmium tolerance of tomato seedlings with an antisense DNA for 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase. J Plant Nutr 31:809–827
Ma WW, Xu WZ, Xu H, Chen YS, He ZY, Ma M (2010) Nitric oxide modulates cadmium influx during cadmium-induced programmed cell death in tobacco BY-2 cells. Planta 232:325–335
Mackintosh C, Douglas D, Lillo C (1995) Identification of a protein that inhibits the phosphorylated form of nitrate reductase from spinach (Spinacia oleracea) leaves. Plant Physiol 107:451–457
Murphy AS, Eisinger WR, Shaff JE, Kochian LV, Taiz L (1999) Early copper induced leakage of K+ from Arabidopsis seedlings is mediated by ion channels and coupled to citrate efflux. Plant Physiol 121:1375–1382
Ouzounidou G, Ciamporova M, Moustakas M, Karataglis S (1995) Responses of maize (Zea mays L.) plants to copper stress. I. Growth, mineral content and ultrastructure of roots. Environ Exp Bot 35:167–176
Pető A, Lehotai N, Feigl G, Tugyi N, Ördög A, Gémes K, Tari I, Erdei L, Kolbert Z (2013) Nitric oxide contributes to copper tolerance by influencing ROS metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 32:1913–1923
Petrov V, Hille J, Mueller-Roeber B, Gechev TS (2015) ROS-mediated abiotic stress-induced programmed cell death in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:69. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00069
Prochazkova D, Sairam RK, Srivastava GC, Singh DV (2001) Oxidative stress and antioxidant activity as the basis of senescence in maize leaves. Plant Sci 161:765–771
Reape TJ, McCabe PF (2008) Apoptotic-like programmed cell death in plants. New Phytol 180:13–26
Schiavon M, Zhang L, Abdel-Ghany SE, Pilon M, Malagoli M, PilonSmits EAH (2007) Variation in copper tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana accessions Columbia, Landsberg erecta and Wassilewskija. Physiol Plant 129:342–350
Shin LJ, Lo JC, Yeh KC (2012) Copper chaperone antioxidant protein1 is essential for copper homeostasis. Plant Physiol 159:1099–1110
Simontacchi M, Galatro A, Ramos-Artuso F, Santa-María GE (2015) Plant survival in a changing environment: the role of nitric oxide in plant responses to abiotic stress. Front Plant Sci 6:977. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00977
Singh HP, Kaur S, Batish DR, Sharma VP, Sharma N, Kohli R (2009) Nitric oxide alleviates arsenic toxicity by reducing oxidative damage in the roots of Oryza sativa (rice). Nitric Oxide 20:289–297
Sun L, Lu W, Zhang J, Zhang W (1999) Investigation of barley germplasm in China. Genet Resour Crop Evol 46:361–369
Sun C, Lu L, Liu L, Liu W, Yu Y, Liu X, Hu Y, Jin C, Lin X (2014) Nitrate reductase-mediated early nitric oxide burst alleviates oxidative damage induced by aluminum through enhancement of antioxidant defenses in roots of wheat (Triticum aestivum). New Phytol 201:1240–1250
Sun C, Liu L, Yu Y, Liu W, Lu L, Jin C, Lin X (2015) Nitric oxide alleviates aluminum-induced oxidative damage through regulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in roots of wheat. J Integr Plant Biol 57:550–561
Tarnowsk BI, Spinale FG, Nicholson JH (1991) DAPI as a useful stain for nuclear quantitation. Biotech Histochem 66:297–302
Tewari RK, Hahn EJ, Paek KY (2008) Modulation of copper toxicity-induced oxidative damage by nitric oxide supply in the adventitious roots of Panax ginseng. Plant Cell Rep 27:171–181
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39
Upadhyaya A, Sankhla D, Davis TD, Sankhla N, Smith B (1985) Effect of paclobutrazol on the activities of some enzymes of activated oxygen metabolism and lipid peroxidation in senescing soybean leaves. J Plant Physiol 121:453–461
Valentovicova K, Haluskova L, Huttova J, Mistrık I, Tamas L (2010) Effect of cadmium on diaphorase activity and nitric oxide production in barley root tips. J Plant Physiol 167:10–14
VanBreusegem F, Dat JF (2006) Reactive oxygen species in plant cell death. Plant Physiol 141:384–390
Wang C, Zhang SH, Wang PF, Hou J, Zhang WJ, Li W, Lin ZP (2009) The effect of excess Zn on mineral nutrition and antioxidative response in rapeseed seedlings. Chemosphere 75:1468–1476
Wang L, Yang L, Yang F, Li X, Song Y, Wang X, Hu X (2010) Involvements of H2O2 and metallothionein in NO-mediated tomato tolerance to copper toxicity. J Plant Physiol 167:1298–1306
Wintz H, Fox T, Wu YY, Feng V, Chen WQ, Chang HS, Zhu T, Vulpe C (2003) Expression profiles of Arabidopsis thaliana in mineral deficiencies reveal novel transporters involved in metal homeostasis. J Biol Chem 278:47644–47653
Xiong J, An L, Lu H, Zhu C (2009) Exogenous nitric oxide enhances cadmium tolerance of rice by increasing pectin and hemicellulose contents in root cell wall. Planta 230:755–765
Xu J, Wang W, Yin H, Liu X, Sun H, Mi Q (2010a) Exogenous nitric oxide improves antioxidative capacity and reduces auxin degradation in roots of Medicago truncatula seedlings under cadmium stress. Plant Soil 326:321–330
Xu J, Yin H, Li Y, Liu X (2010b) Nitric oxide is associated with long-term zinc tolerance in Solanum nigrum. Plant Physiol 154:1319–1334
Xu X, Shi G, Ding C, Xu Y, Zhao J, Yang H, Pan Q (2011) Regulation of exogenous spermidine on the reactive oxygen species level and polyamine metabolism in Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) griseb under copper stress. Plant Growth Regul 63:251–258
Xu H, Xu W, Xi H, Ma W, He Z, Ma M (2013) The ER luminal binding protein (BiP) alleviates Cd2+-induced programmed cell death through endoplasmic reticulum stress-cell death signaling pathway in tobacco cells. J Plant Physiol 170:1434–1441
Ye Y, Li Z, Xing D (2013) Nitric oxide promotes MPK6-mediated caspase-3-like activation in cadmium-induced Arabidopsis thaliana programmed cell death. Plant Cell Environ 36:1–15
Yin YQ, Ma DQ, Ding Y (2003) Analysis of genetic diversity of hordein in wild close relatives of barley from Tibet. Theor Appl Genet 107:837–842
Yruela I (2009) Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct Plant Biol 36:409–430
Yu CC, Hung KT, Kao CH (2005) Nitric oxide reduces Cu toxicity and Cu-induced NH4 + accumulation in rice leaves. J Plant Physiol 162:319–330
Yu Q, Sun L, Jin H, Chen Q, Chen Z, Xu M (2012) Lead-induced nitric oxide generation plays a critical role in lead uptake by Pogonatherum crinitum root cells. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1728–1736
Zeng X, Long H, Wang Z, Zhao S, Tang Y, Huang Z, Wang Y (2015) The draft genome of Tibetan hulless barley reveals adaptive patterns to the high stressful Tibetan Plateau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:1095–1100
Zhou T, Zheng LP, Yuan HY, Yuan YF, Wang JW (2012) The nitric oxide production and NADPH-diaphorase activity in root tips of Vicia faba L. under copper toxicity. Plant Omics J 5:115–121
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Open Funds for Key Laboratory of Mollisols Agroecology of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Heilongjiang Province Science Foundation for Youths (QC2015036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y. Early generation of nitric oxide contributes to copper tolerance through reducing oxidative stress and cell death in hulless barley roots. J Plant Res 129, 963–978 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0841-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0841-0