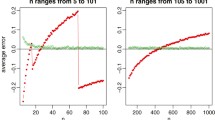
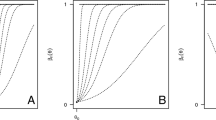
Abstract
This paper is devoted to robust Bayes sample size determination under the quadratic loss function. The idea behind the proposed approach is that the smaller a chosen posterior functional, the more robust the posterior inference. Such desired posterior functional has been taken, in the literature, as the range of posterior mean over a class of priors but we show that dealing with the posterior mean is not the only method leading to an optimal sample size. To provide an alternative approach, we propose implementing most stable rules into the context of sample size determination. We discuss properties of the desired most stable estimate and provide some examples in the normal model. We then compare the proposed approach with that of a recent global robustness study from both numerical and theoretical aspects. We illustrate the practical utility of our proposed method by analyzing a real data set.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adcock C (1997) Sample size determination: a review. J R Stat Soc Ser D (Stat) 46(2):261–283
Arias-Nicolás J, Martín J, Ruggeri F, Suárez-Llorens A (2009) Optimal actions in problems with convex loss functions. Int J Approx Reason 50(2):303–314
Berger JO (1985) Statistical decision theory and Bayesian analysis. Springer, Berlin
Berger JO (1990) Robust Bayesian analysis: sensitivity to the prior. J Stat Plan Inference 25(3):303–328
Berger JO, Moreno E, Pericchi LR, Bayarri MJ, Bernardo JM, Cano JA, De la Horra J, Martín J, Ríos-Insúa D, Betrò B et al (1994) An overview of robust Bayesian analysis. Test 3(1):5–124
Boratyńska A (1997) Stability of Bayesian inference in exponential families. Stat Prob Lett 36(2):173–178
Boratyńska A, Meczarski M (1994) Robust Bayesian estimation in the one-dimensional normal model. Stat Risk Model 12(3):221–230
Brutti P, De Santis F, Gubbiotti S (2014) Bayesian-frequentist sample size determination: a game of two priors. Metron 72(2):133–151
DasGupta A, Mukhopadhyay S (1994) Uniform and subuniform posterior robustness: the sample size problem. J Stat Plan Inference 40(2):189–204
De Santis F (2006) Sample size determination for robust Bayesian analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 101(473):278–291
De Santis F, Fasciolo MC, Gubbiotti S (2013) Predictive control of posterior robustness for sample size choice in a Bernoulli model. Stat Methods Appl 22(3):319–340
Golparvar L, Karimnezhad A, Parsian A (2016) Bayes and robust Bayes predictions in a subfamily of scale parameters under a precautionary loss function. Commun Stat Theory Methods 45(13):3970–3992
Inoue LY, Berry DA, Parmigiani G (2012) Relationship between Bayesian and frequentist sample size determination. Am Stat 59(1):79–87
Insua DR, Ruggeri F, Vidakovic B (1992) Some results on posterior regret $\Gamma $-minimax estimation. Stat Dec 13:315–351
Joseph L, Belisle P (1997) Bayesian sample size determination for normal means and differences between normal means. J R Stat Soc Ser D (Stat) 46(2):209–226
Joseph L, Wolfson DB (1997) Interval-based versus decision theoretic criteria for the choice of sample size. J R Stat Soc Ser D (Stat) 46(2):145–149
Karimnezhad A, Parsian A (2014) Robust Bayesian methodology with applications in credibility premium derivation and future claim size prediction. AStA Adv Stat Anal 98(3):287–303
Karimnezhad A, Niazi S, Parsian A (2014) Bayes and robust Bayes prediction with an application to a rainfall prediction problem. J Korean Stat Soc 43(2):275–291
Meczarski M (1993) Stability and conditional $\Gamma $-minimaxity in Bayesian inference. Appl Math 22:117–122
Meczarski M, Zieliński R (1991) Stability of the Bayesian estimator of the poisson mean under the inexactly specified gamma prior. Stat Probab Lett 12(4):329–333
Sahu S, Smith T (2006) A bayesian method of sample size determination with practical applications. J R Stat Soc Ser A (Stat Soc) 169(2):235–253
Sasahara AA (1973) The Urokinase Pulmonary Embolism Trial: a national cooperative study. American Heart Association, Dallas
Spiegelhalter DJ, Abrams KR, Myles JP (2004) Bayesian approaches to clinical trials and health-care evaluation, vol 13. Wiley, Hoboken
Wang F, Gelfand AE (2002) A simulation-based approach to Bayesian sample size determination for performance under a given model and for separating models. Stat Sci 17(2):193–208
Young DS, Gordon CM, Zhu S, Olin BD (2016) Sample size determination strategies for normal tolerance intervals using historical data. Qual Eng 28(3):337–351
Acknowledgements
The authors are cordially grateful to the Editor-in-Chief and two anonymous reviewers for making several valuable comments and improvements on an earlier version of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimnezhad, A., Parsian, A. Most stable sample size determination in clinical trials. Stat Methods Appl 27, 437–454 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-017-0419-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-017-0419-6