Abstract
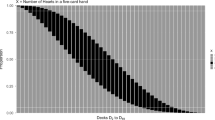
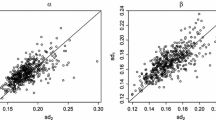
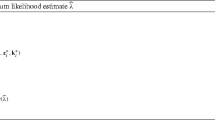
In this paper, the likelihood ratio approach is applied for measuring evidence provided by record data in favor of a hypothesis against an alternative under a random sampling scheme. Explicit expressions for probabilities of observing strong and weak evidences are derived. Asymptotic behaviors of these probabilities are investigated in a greater detail. Optimal sample size in which the substantial evidence reaches a desired level is determined. An illustrative example concerning records of times between consecutive telephone calls to a company’s switchboard is also analyzed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsanullah M (1980) Linear prediction of record values for the two parameter exponential distribution. Ann Inst Stat Math 32:363–368
Arnold BC, Balakrishnan N, Nagaraja HN (1998) Records. Wiley, New York
Blume JD (2002) Likelihood methods for measuring statistical evidence. Stat Med 21(17):2563–2599
Blume JD (2011) Likelihood and its evidential framework. In: Gabbay DM, Woods J (eds) Handbook of the philosophy of science: philosophy of statistics. North Holland, San Diego, pp 493–511
Carlin P, Gelfand AE (1993) Parametric likelihood inference for record breaking problems. Biometrika 80(3):507–515
Castillo E, Hadi AS, Balakrishnan N, Sarabia JM (2005) Extreme value and related models with applications in engineering and science. Wiley, Hoboken
De Santis F (2004) Statistical evidence and sample size determination for Bayesian hypothesis testing. J Stat Plan Inference 124:121–144
Doostparast M (2009) A note on estimation based on record data. Metrika 69:69–80
Doostparast M, Balakrishnan N (2010) Optimal sample size for record data and associated cost analysis for exponential distribution. J Stat Comput Simul 80(12):1389–1401
Doostparast M, Balakrishnan N (2011) Optimal statistical procedures on the basis of records in a two-parameter exponential distribution. J Stat Comput Simul 81(12):2003–2019
Doostparast M, Emadi M (2006) Statistical evidence methodology for model acceptance based on record values. J Korean Stat Soc 35(2):167–177
Emadi M, Arghami NR (2003) Some measures of support for statistical hypotheses. J Stat Theory Appl 2:165–176
Nevzorov V (2001) Records: mathematical theory. Translation of mathematical monographs. Am Math Soc Providence 194:RI USA
Royall R (1997) Statistical evidence: a likelihood paradigm. Chapman & Hall, New York
Royall R (2000) On the probability of observing misleading statistical evidence. J Am Stat Assoc 95:760–780
Samaniego FJ, Whitaker LR (1986) On estimating popular characteristics from record breaking observations I. Parametric results. Nav Res Logist Q 33:531–543
Wang SJ, Blume JD (2011) An evidential approach to non-inferiority clinical trials. Pharm Stat 10:440–447
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to anonymous referees and the Associate Editor for their useful suggestions and comments on an earlier version of this paper, which resulted in this improved version of the manuscript. Doostparast’s research was partially supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doostparast, M., Emadi, M. Evidential inference and optimal sample size determination on the basis of record values and record times under random sampling scheme. Stat Methods Appl 23, 41–50 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-012-0228-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-012-0228-x