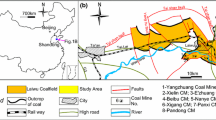
Abstract
Shallow coal seams are actively excavated in western China, which can adversely affect groundwater availability. We analyzed the failure mode in the mining of a shallow coal seam, and demonstrated that its fracture zone was directly exposed to an unconsolidated aquifer. Two numerical models (steady and unsteady state models) were used in which the fractured overburden was considered as the first boundary and the aquifer-contacting zone was considered as a drainage boundary. We applied this numerical model to analyze the groundwater system of the Daliuta coal mine in the Shendong area of western China. Simulation results showed that the mining cause groundwater level to decline > 50 m in 2012; the groundwater loss amounted to 2.12 × 104 m3/day.
Zusammenfassung
Oberflächennahe Kohleflöze werden in Westchina aktiv abgebaut, wobei jedoch die Beeinflussung des Grundwassers durch den Bergbau unzureichend erforscht ist. In der vorliegenden Studie haben wir eine Auswirkungsanalyse für den Abbau oberflächennaher Kohleflöze durchgeführt und gezeigt, dass die Bruchzone des Kohleflözes unmittelbar dem schwebenden Grundwasserleiter angrenzt. Wir haben zwei numerische Modelle angewendet, in welchen die gebrochenen, wasserleitenden Deckgesteine als erste Randbedingung und die Aquifer-Kontaktzone als Drainagegraben-Randbedingung angenommen wurden. Das numerische Modell wurde angewendet, um die Beeinflussung des Grundwassersystems der Daliuta Kohlemiene im Shendong-Gebiet in Westchina durch bergbauliche Aktivitäten zu untersuchen. Die Simulationsergebnisse zeigen, dass aufgrund der Kohlegewinnung der Grundwasserspiegel in 2012 um über 50 m absank und der Grundwasserverlust 2,12 x 10^4 m3/d umfasste.
Resumen
Las vetas poco profundas de carbón son excavadas activamente en el oeste de China, pero la perturbación de los proyectos mineros sobre las aguas subterráneas permanece aún sin ser adecuadamente estudiada. En este trabajo, analizamos el modo de falla en la extracción de la veta de carbón superficial y demostramos que la zona de fractura de la veta de carbón está directamente expuesta al acuífero. Se propusieron dos modelos numéricos en los cuales se consideró que la roca agrietada conductora de agua era el primer límite y que la zona de contacto con el acuífero se consideraba el límite de la zanja de drenaje. Aplicamos este modelo numérico para analizar la perturbación de la minería sobre el sistema de agua subterránea de la mina de carbón Daliuta en el área de Shendong en el oeste de China. Los resultados de la simulación mostraron que debido a la extracción de carbón, el nivel del agua subterránea disminuyó en más de 50 m en 2012 y la pérdida de agua subterránea fue de 2,12×104 m3/d.
抽象
中国西部浅埋煤层开采对地下水系统的扰动仍研究不足。我们分析了浅埋煤层开采的岩层破断模式,认为煤层顶板裂隙带会直接连通松散含水层。提出了两个数值模型,破裂的导水覆岩被视为一类边界,含水层接触带被视为排水沟渠边界。我们应用该数值模型分析了采矿对中国西部神东矿区大柳塔煤矿地下水系统的影响。模拟结果表明,煤炭开采使地下水位2012年下降超过50m,地下水漏失达2.12 × 104m3/d。








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen JN, Yue ZX (2013) The system of soil management in the coal mining collapse area. Appl Mech Mater 361–363:871–874
Chen YX, Zhou ZH (2016) Analysis on the hydraulic conductivity of DRAIN module in MODFLOW. Pearl River 37(4):80–83 (in Chinese)
Chugh YP, Behum PT (2014) Coal waste management practices in the USA: an overview. Int J Coal Sci Technol 1(2):163–176
Fan ZZ, Yu L, Yu HY, Li CR (2012) Movement behavior of overlying strata in shallow seam high cutting height fully mechanized mining. Saf Coal Mines 43(1):186–189 (in Chinese)
Fu MC, Zeng H, Zhang HJ, Shi LP (2009) Land reclamation and ecological reconstruction in resource-exhausted mining areas. Sci Technol Rev 27(17):38–43 (in Chinese)
He Y (2014) Research on rainfall infiltration intensity in Shendong mining area. J Xian Univ Sci Technol 34(4):473–478 (in Chinese)
Li Y (2008) The hydrological and ecological effects caused by groundwater resources and coal mining in the coal distribution area of northern Shaanxi Province, Ph.D. Dissertation. Chang’an University, Xi’an (in Chinese)
Li Q, Li YC, Chen DY, Liu HP (2013) The water resource utilization in Shendong mining area. J Arid Land Resour Environ 27(9):141–147 (in Chinese)
Liu HZ (2011) Quantitative evaluation of groundwater system disturbance in mining area. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Qian MG, Miao XX, Xu JL (1996) Theoretical study of key stratum in ground control. J China Coal Soc 21(3):225–230 (in Chinese)
Qian MG, Shi PW, Xu JL (2010) Mining pressure and strata control. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou, pp 98–101 (in Chinese)
Skousen J, Zipper CE (2014) Post-mining policies and practices in the Eastern USA coal region. Int J Coal Sci Technol 1(2):135–151
Tshivhandekano AN (2005) Documenting reclamation and closure of Ermelo coal mines: implications for developing a national strategy for mine reclamation in South Africa. University of Pretoria, Pretoria
Wang L, Wei SP, Wang QJ (2008) Effect of coal exploitation on groundwater and vegetation in the Yushenfu coal mine. J Chin Coal Soc 33(12):1408–1414 (in Chinese)
Wu XJ (2013) Study on river runoff change and ecological base flow in coal mining area, Ph.D. Dissertation. Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an (in Chinese)
Xiao P, Li SG, Lin H, Zhao P (2014) Distribution characteristics of stope support pressure for different main key layer position. Safe Coal Mines 45(12):211–213 (in Chinese)
Yang RM, Chen CH, Song JL, Gao YY (2013) Detection study of overlying strata failure types in Shendong mining area. Safe Coal Mines 25–27 (in Chinese)
Zhang FG, Liu WS (2002) A numerical simulation on the influence of underground water flow regime caused by coal mining—a case study in Daliuta. J Safe Environ 4:30–33 (in Chinese)
Zhang C, Liu S, Hu Y, Huang Y, Xu L (2006) A study on types and causes of land desertification in the coal mining area of Shanxi Province. In: Proceedings of the international specialty conference on science and technology for desertification control, vol 242(s1–2), pp 517–519 (in Chinese)
Zhang S, Ma C, Zhang L (2011) The regulators of runoff of the Ulan Moron River in the Daliuta mine area: the effects of mine coal. Acta Sci Circ 5(12):889–896 (in Chinese)
Zhao GZ (2011) Study on transformation mechanism of vadose zone water-groundwater in the wind-blown sand area of the Ordos Basin. Chang’an University, Xi’an (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Chinese 13th Five-Year Key Research and Development Program (No. 2016YFC0501102 and 2017YFC0804103) and China Coal Technology and Engineering Group Co., Ltd. Technology Innovation Fund (No. 2013ZD002-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Jin, D., Geng, J. et al. Numerical Simulation of the Groundwater System for Mining Shallow Buried Coal Seams in the Ecologically Fragile Areas of Western China. Mine Water Environ 38, 158–165 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-0551-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-0551-z