Abstract
Background
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of switch maintenance erlotinib and bevacizumab after induction therapy with carboplatin/pemetrexed/bevacizumab for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with wild-type EGFR.
Methods
Enrolled patients had treatment-naïve, advanced non-squamous NSCLC with wild-type EGFR. Carboplatin [area under the curve (AUC) 5.0], pemetrexed (500 mg/m2) and bevacizumab (15 mg/kg) were administered on day 1 every 3 weeks for 4–6 cycles. Maintenance therapy with erlotinib (150 mg/body) on day 1 through 21 plus bevacizumab on day 1 every 3 weeks was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was 6-month progression-free survival (PFS); secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), overall response rate (ORR), toxicity, and quality of life (QOL).
Results
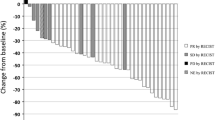
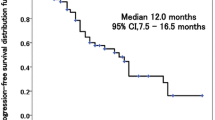
Fifty-one patients were enrolled between September 2011 and June 2014. The median number of cycles for induction and maintenance therapy was 4 (range 1–6) and 4 (range 1–20). Twenty-nine patients (58%) received maintenance therapy. The 6-month PFS rate was 59.5% [95% confidence interval (CI) 45.0–72.6%]. The ORR was 48.0% (95% CI 34.8–61.5%), and disease control rate was 86.0% (95% CI 73.8–93.0%). The median PFS and OS were 6.5 months (95% CI 5.8–7.2 months) and 21.4 months (95% CI 15.9–26.9 months), respectively. Although grades ≥ 3 adverse events were observed in 33 patients (66.0%), most were hematologic; there was no febrile neutropenia. QOL was maintained throughout treatment.
Conclusions
Carboplatin/pemetrexed/bevacizumab followed by erlotinib and bevacizumab maintenance showed modest efficacy and was well tolerated in non-squamous NSCLC patients with wild-type EGFR.
Trial registration
UMIN000005872.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J et al (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60:277–300
Parkin DM (2001) Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol 2:533–543
Lee CK, Wu YL, Ding PN et al (2015) Impact of specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations and clinical characteristics on outcomes after treatment with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 33:1958–1965
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K et al (2013) Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 368:2385–2394
Facchinetti F, Rossi G, Bria E et al (2017) Oncogene addiction in non-small cell lung cancer: focus on ROS1 inhibition. Cancer Treat Rev 55:83–95
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375:1823–1833
Sun JM, Park JO, Won YW et al (2010) Who are less likely to receive subsequent chemotherapy beyond first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer? Implications for selection of patients for maintenance therapy. J Thorac Oncol 5:540–545
Gerber DE, Rasco DW, Le P et al (2011) Predictors and impact of second-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the United States: real-world considerations for maintenance therapy. J Thorac Oncol 6:365–371
Fidias PM, Dakhil SR, Lyss AP et al (2009) Phase III study of immediate compared with delayed docetaxel after front-line therapy with gemcitabine plus carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:591–598
Pérol M, Chouaid C, Pérol D et al (2012) Randomized, phase III study of gemcitabine or erlotinib maintenance therapy versus observation, with predefined second-line treatment, after cisplatin-gemcitabine induction chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 30:3516–3524
Socinski MA, Schell MJ, Peterman A et al (2002) Phase III trial comparing a defined duration of therapy versus continuous therapy followed by second-line therapy in advanced-stage IIIB/IV non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 20:1335–1343
Ciuleanu T, Brodowicz T, Zielinski C et al (2009) Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet 374:1432–1440
Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L et al (2010) Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 11:521–529
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC et al (2006) Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355:2542–2550
Johnson ML, Patel JD (2014) Chemotherapy and targeted therapeutics as maintenance of response in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Oncol 41:93–100
Paz-Ares LG, de Marinis F, Dediu M et al (2013) PARAMOUNT: final overall survival results of the phase III study of maintenance pemetrexed versus placebo immediately after induction treatment with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:2895–2902
Johnson BE, Kabbinavar F, Fehrenbacher L et al (2013) ATLAS: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIIB trial comparing bevacizumab therapy with or without erlotinib, after completion of chemotherapy, with bevacizumab for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:3926–3934
Barlesi F, Scherpereel A, Rittmeyer A et al (2013) Randomized phase III trial of maintenance bevacizumab with or without pemetrexed after first-line induction with bevacizumab, cisplatin, and pemetrexed in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAPERL (MO22089). J Clin Oncol 31:3004–3011
Patel JD, Socinski MA, Garon EB et al (2013) PointBreak: a randomized phase III study of pemetrexed plus carboplatin and bevacizumab followed by maintenance pemetrexed and bevacizumab versus paclitaxel plus carboplatin and bevacizumab followed by maintenance bevacizumab in patients with stage IIIB or IV nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:4349–4357
Zinner RG, Obasaju CK, Spigel DR et al (2015) PRONOUNCE: randomized, open-label, phase III study of first-line pemetrexed + carboplatin followed by maintenance pemetrexed versus paclitaxel + carboplatin + bevacizumab followed by maintenance bevacizumab in patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 10:134–142
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T et al (2005) Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353:123–132
Pennell NA, Lynch TJ (2009) Combined inhibition of the VEGFR and EGFR signaling pathways in the treatment of NSCLC. Oncologist 14:399–411
Rolff J, Becker M, Merk J et al (2016) Preclinical study of a combination of erlotinib and bevacizumab in early stages of unselected non-small cell lung cancer patient-derived xenografts. Target Oncol 11:507–514
Herbst RS, Ansari R, Bustin F et al (2011) Efficacy of bevacizumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of standard first-line chemotherapy (BeTa): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 377:1846–1854
Kanazawa K, Yokouchi H, Wang X et al (2014) Phase II trial of carboplatin and pemetrexed as first-line chemotherapy for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer, and correlation between the efficacy/toxicity and genetic polymorphisms associated with pemetrexed metabolism: Hokkaido Lung Cancer Clinical Study Group Trial (HOT) 0902. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74:1149–1157
Takagi Y, Toriihara A, Nakahara Y et al (2013) Eligibility for bevacizumab as an independent prognostic factor for patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS One 8:e59700
Nakashima K, Murakami H, Omori S et al (2016) Doublet chemotherapy with cisplatin and pemetrexed is associated with a favorable outcome in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer who are eligible for bevacizumab and maintenance therapy. Mol Clin Oncol 5:575–578
Weiss JM, Villaruz LC, O’Brien J et al (2016) Results of a phase II trial of carboplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab for the treatment of never or former/light smoking patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 17:128–132
Yokoi T, Torii Y, Katashiba Y et al (2014) Phase II study of pemetrexed and carboplatin plus bevacizumab, followed by maintenance pemetrexed and bevacizumab in Japanese patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 8:2453–2457
Karayama M, Inui N, Fujisawa T et al (2016) Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed and bevacizumab versus pemetrexed monotherapy after induction therapy with carboplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 58:30–37
Kawaguchi T, Ando M, Asami K et al (2014) Randomized phase III trial of erlotinib versus docetaxel as second- or third-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: docetaxel and erlotinib lung cancer trial (DELTA). J Clin Oncol 32:1902–1908
Garassino MC, Martelli O, Broggini M et al (2013) Erlotinib versus docetaxel as second-line treatment of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and wild-type EGFR tumours (TAILOR): a randomized controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 14:981–988
Morise M, Taniguchi H, Saka H et al (2014) Phase II study of erlotinib for previously treated patients with EGFR wild-type non-small-cell lung cancer, following EGFR mutation status reevaluation with the scorpion amplified refractory mutation system. Mol Clin Oncol 2:991–996
Langer CJ, Gadgeel SM, Borghaei H et al (2017) Carboplatin and pemetrexed with or without pembrolizumab for advanced, non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, phase 2 cohort of the open-label KEYNOTE-021 study. Lancet Oncol 17:1497–1508
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S et al (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:2078–2092
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients, their families, and investigators who participated in this study.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Takashina, T., Asahina, H., Oizumi, S. et al. A phase II study of carboplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab followed by erlotinib and bevacizumab maintenance for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer with wild-type EGFR (HOT1101). Int J Clin Oncol 23, 1060–1069 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1318-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1318-z