Abstract
Backgrounds
This retrospective study was conducted to compare the clinical outcomes of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) with those of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in patients with lung tumors.
Methods
Local tumor progression, adverse events, and overall survival were compared in patients who underwent either RFA or SBRT for a single lung tumor measuring 5 cm or smaller. This study was approved by the institutional review boards of two institutions. Informed consent was waived.
Results
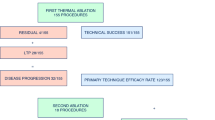
During September 2009 to June 2012, 48 patients [30 males and 18 females, with a mean age ± standard deviation (SD) of 75.0 ± 7.5 years] underwent RFA at one institution and 47 patients (21 males and 26 females, with a mean age ± SD of 77.0 ± 7.5 years) underwent SBRT in another. The mean maximum tumor diameter ± SD was 2.0 ± 0.8 cm (range 0.6−3.9 cm) in the RFA group, and 2.1 ± 0.9 cm (range 0.8–4.7 cm, p = 0.539) in the SBRT group. The RFA and SBRT groups showed similar 3-year local tumor progression [9.6 %, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 3.6–23.9 % vs. 7.0 %, 95 % CI 0.2–20.2 %, p = 0.746] and overall survival rates (86.4 %, 95 % CI 69.2–94.3 % vs. 79.6 %, 95 % CI 60.6–90.1 %, p = 0.738). No factor significantly affected local tumor progression. A maximum tumor size of 2 cm was identified as a prognostic factor in both univariate and multivariate analyses. No death was related to treatment procedures. Major complication rates (Grade 3 adverse events) of the RFA (10.4 %, 5/48) and SBRT (8.5 %, 4/47, p > 0.999) groups were similar.
Conclusion
For lung tumor patients, lung RFA provided local tumor control and survival that were similar to those achieved using SBRT, with equal safety.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Parkin DM (2001) Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2:533–543
Asamura H, Goya T, Koshiishi Y, Japanese Joint Committee of Lung Cancer Registry et al (2008) A Japanese lung cancer registry study: prognosis of 13,010 resected lung cancers. J Thorac Oncol 3:46–52
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer International Staging Committee, Participating Institutions et al (2007) The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714
Mery CM, Pappas AN, Bueno R et al (2005) Similar long-term survival of elderly patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with lobectomy or wedge resection within the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. Chest 128:237–245
Uematsu M, Shioda A, Suda A et al (2001) Computed tomography-guided frameless stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a 5-year experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:666–670
Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H et al (2004) Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: clinical outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer 101:1623–1631
Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M et al (2009) Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 27:3290–3296
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 303:1070–1076
Shibamoto Y, Hashizume C, Baba F et al (2012) Stereotactic body radiotherapy using a radiobiology-based regimen for stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer: a multicenter study. Cancer 118:2078–2084
Haasbeek CJA, Lagerwaard FJ, Antonisse ME et al (2010) Stage I non-small cell lung cancer in patients aged >75 years: outcomes after stereotactic radiotherapy. Cancer 116:406–414
Takeda A, Sanuki N, Kunieda E et al (2009) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary lung cancer at a dose of 50 Gy total in five fractions to the periphery of the planning target volume calculated using a superposition algorithm. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:442–448
Nagata Y, Takayama K, Matsuo Y et al (2005) Clinical outcomes of a phase I/II study of 48 Gy of stereotactic body radiotherapy in 4 fractions for primary lung cancer using a stereotactic body frame. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:1427–1431
Koto M, Takai Y, Ogawa Y et al (2007) A phase II study on stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 85:429–434
Grutters JP, Kessels AG, Pijls-Johannesma M et al (2010) Comparison of the effectiveness of radiotherapy with photons, protons and carbon-ions for non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol 95:32–40
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, DiPetrillo TA et al (2007) Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation: long-term safety and efficacy in 153 patients. Radiology 243:268–275
Hiraki T, Gobara H, Iishi T et al (2007) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer: results in 20 nonsurgical candidates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 134:1306–1312
Beland MD, Wasser EJ, Mayo-Smith WW et al (2010) Primary non-small cell lung cancer: review of frequency, location, and time of recurrence after radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 254:301–307
Kodama H, Yamakado K, Takaki H et al (2012) Lung radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of unresectable recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer after surgical intervention. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:563–569
Fernando HC, De Hoyos A, Landreneau RJ et al (2005) Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer in marginal surgical candidates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 129:639–644
Dupuy DE (2013) Treatment of medically inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer with stereotactic body radiation therapy versus image-guided tumor ablation: can interventional radiology compete? J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:1139–1145
Donington J, Ferguson M, Mazzone P, Thoracic Oncology Network of American College of Chest Physicians; Workforce on Evidence-Based Surgery of Society of Thoracic Surgeons et al (2012) American college of chest physicians and society of thoracic surgeons consensus statement for evaluation and management for high-risk patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 142:1620–1635
Howington JA, Blum MG, Chang AC et al (2013) Treatment of stage I and II non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American college of chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 143(5 Suppl):e278S–e313S
Dunlap NE, Larner JM, Read PW et al (2010) Size matters: a comparison of T1 and T2 peripheral non-small-cell lung cancers treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 140:583–589
Huang L, Han Y, Zhao J et al (2011) Is radiofrequency thermal ablation a safe and effective procedure in the treatment of pulmonary malignancies? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 39:348–351
de Baère T, Palussière J, Aupérin A et al (2006) Midterm local efficacy and survival after radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors with minimum follow-up of 1 year: prospective evaluation. Radiology 240:587–596
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C et al (2006) Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:4833–4839
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, Society of Interventional Radiology Technology Assessment Committee; International Working Group on Image-Guided Tumor Ablation et al (2005) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology 235:728–739
Kashima M, Yamakado K, Takaki H et al (2011) Complications after 1000 lung radiofrequency ablation sessions in 420 patients: a single center’s experiences. Am J Roentgenol 197:W576–W580
Lee JM, Jin GY, Goldberg SN et al (2003) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for inoperable non-small cell lung cancer and metastases: preliminary report. Radiology 230:125–134
Zhu JC, Yan TD, Glenn D et al (2009) Radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors: feasibility and safety. Ann Thorac Surg 87:1023–1028
Hiraki T, Tajiri N, Mimura H et al (2006) Pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and chest tube placement after radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors: incidence and risk factors. Radiology 241:275–283
Yamakado K, Akeboshi M, Nakatsuka A et al (2005) Tumor seeding following lung radiofrequency ablation: a case report. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28:530–532
Sakurai J, Hiraki T, Mukai T et al (2007) Intractable pneumothorax due to bronchopleural fistula after radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 8:141–145
Nomura M, Yamakado K, Nomoto Y et al (2008) Complications after lung radiofrequency ablation: risk factors for lung inflammation. Br J Radiol 81:244–249
Okuma T, Matsuoka T, Hamamoto S et al (2009) Percutaneous computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors complicated with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Ann Thorac Surg 87:948–950
Steinke K, Sewell PE, Dupuy D et al (2004) Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation—an international study survey. Anticancer Res 24:339–343
Sano Y, Kanazawa S, Gobara H et al (2007) Feasibility of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for intrathoracic malignancies: a large single-center experience. Cancer 109:1397–1405
Pennathur A, Abbas G, Gooding WE et al (2009) Image-guided radiofrequency ablation of lung neoplasm in 100 consecutive patients by a thoracic surgical service. Ann Thorac Surg 88:1601–1606
Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Mizowaki T et al (2009) Survey of stereotactic body radiation therapy in Japan by the Japan 3-D conformal external beam radiotherapy group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75:343–347
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest, grant or any other assistance to be disclosed in any authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ochiai, S., Yamakado, K., Kodama, H. et al. Comparison of therapeutic results from radiofrequency ablation and stereotactic body radiotherapy in solitary lung tumors measuring 5 cm or smaller. Int J Clin Oncol 20, 499–507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0741-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0741-z