Abstract
Objective
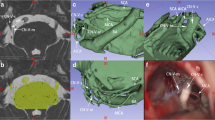
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a lightning bolt of violent, electrifying, and stinging pain, often secondary to the neurovascular conflict (NVC). The vessels involved in NVC are mostly arteries and rarely veins. Evaluation of NVC in the deep infratentorial region is inseparably connected with cranial imaging. We retrospectively analyzed the potential influence of three-dimensional (3D) virtual reality (VR) reconstructions compared to conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans on the evaluation of NVC for the surgical planning of microvascular decompression in patients with TN.
Methods
Medical files were retrospectively analyzed regarding patient- and disease-related data. Preoperative MRI scans were retrospectively visualized via VR software to detect the characteristics of NVC. A questionnaire of experienced neurosurgeons evaluated the influence of VR visualization technique on identification of anatomical structures involved in NVC and on surgical strategy.
Results
Twenty-four patients were included and 480 answer sheets were evaluated. Compared to conventional MRI, image presentation using 3D-VR modality significantly influenced the identification of the affected trigeminal nerve (p = 0.004), the vascular structure involved in the NVC (p = 0.0002), and the affected side of the trigeminal nerve (p = 0.005).
Conclusions
In patients with TN caused by NVC, the reconstruction of conventional preoperative MRI scans and the spatial and anatomical presentation in 3D-VR models offers the possibility of increased understanding of the anatomy and even more the underlying pathology, and thus influences operation planning and strategy.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data, material, and/or code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alaraj A, Luciano CJ, Bailey DP, Elsenousi A, Roitberg BZ, Bernardo A, Banerjee PP, Charbel FT (2015) Virtual reality cerebral aneurysm clipping simulation with real-time haptic feedback. Neurosurgery 11(Suppl 2):52–58. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000583
Alshukry A, Salburgo F, Jaloux L, Lavieille J-P, Montava M (2017) Trigeminal neuralgia (TN): A descriptive literature analysis on the diagnosis and management modalities. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg 118(4):251–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jormas.2017.06.010
Barker FG, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334(17):1077–1083. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199604253341701
Besta R, Shankar YU, Kumar A, Rajasekhar E, Prakash SB (2016) MRI 3D CISS-a novel imaging modality in diagnosing trigeminal neuralgia - a review. J Clin Diagn Res 10(3):ZE01–ZE03. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2016/14011.7348
Burtscher J, Kremser C, Seiwald M, Obwegeser A, Wagner M, Aichner F, Twerdy K, Felber S (1998) Three-dimensional computer assisted magnetic resonance imaging for neurosurgical planning in parasagittal and parafalcine central region tumors. Comput. Aided Surg. 3(1):27–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0150(1998)3:1<27:AID-IGS4>3.0.CO;2-N
Christiano LD, Singh R, Sukul V, Prestigiacomo CJ, Gandhi CD (2011) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: visualization of results in a 3D stereoscopic virtual reality environment. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 54(1):12–15. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1273731
Cohen-Gadol AA (2011) Microvascular decompression surgery for trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm: naunces of the technique based on experiences with 100 patients and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113(10):844–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.06.003
Cole CD, Liu JK, Apfelbaum RI (2005) Historical perspectives on the diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Focus 18(5):E4. https://doi.org/10.3171/foc.2005.18.5.5
Cruccu G (2017) Trigeminal neuralgia. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 23(2, Selected Topics in Outpatient Neurology):396–420. https://doi.org/10.1212/CON.0000000000000451
de Ribaupierre S, Eagleson R (2017) Editorial: Challenges for the usability of AR and VR for clinical neurosurgical procedures. Healthc Technol Lett 4(5):151. https://doi.org/10.1049/htl.2017.0077
Donahue JH, Ornan DA, Mukherjee S (2017) Imaging of vascular compression syndromes. Radiol Clin North Am 55(1):123–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcl.2016.08.001
Du Z-Y, Gao X, Zhang X-L, Wang Z-Q, Tang W-J (2010) Preoperative evaluation of neurovascular relationships for microvascular decompression in the cerebellopontine angle in a virtual reality environment. J Neurosurg 113(3):479–485. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.9.JNS091012
Dumot C, Sindou M (2018) Veins of the cerebellopontine angle and specific complications of sacrifice, with special emphasis on microvascular decompression surgery. A review. World Neurosurg 117:422–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.06.160
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Finet J, Fillion-Robin J-C, Pujol S, Bauer C, Jennings D, Fennessy F, Sonka M, Buatti J, Aylward S, Miller JV, Pieper S, Kikinis R (2012) 3D slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn Reson Imaging 30(9):1323–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2012.05.001
Fisher RA (1922) On the interpretation of χ2 from contingency tables, and the calculation of P. J Royal Statistical Soc 85(1):87–94
González Sánchez JJ, Enseñat Nora J, Candela Canto S, Rumià Arboix J, Caral Pons LA, Oliver D, Ferrer Rodríguez E (2010) New stereoscopic virtual reality system application to cranial nerve microvascular decompression. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152(2):355–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0569-x
Gubian A, Rosahl SK (2017) Meta-analysis on safety and efficacy of microsurgical and radiosurgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg 103:757–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.04.085
Han K-W, Zhang D-F, Chen J-G, Hou L-J (2016) Presurgical visualization of the neurovascular relationship in trigeminal neuralgia with 3D modeling using free Slicer software. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 158(11):2195–2201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2936-8
Ibrahim TF, Garst JR, Burkett DJ, Toia GV, Braca JA, Hill JP, Anderson DE (2015) Microsurgical pontine descending tractotomy in cases of intractable trigeminal neuralgia. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 11(4):518–529. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000926
Jannetta PJ, Rand RW (1966) Transtentorial retrogasserian rhizotomy in trigeminal neuralgia by microneurosurgical technique. Bull Los Angeles Neurol Soc 31(3):93–99
Jannetta PJ, McLaughlin MR, Casey KF (2005) Technique of microvascular decompression. Technical note. Neurosurg Focus 18(5):E5
Jie H, Xuanchen Z, Deheng L, Kun G, Fengyang X, Xiang C, Xiaoting W, Guangxin Z, Yiqing L (2013) The long-term outcome of nerve combing for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 155(9):1703–1708; discussion 1707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1804-z
Kabatas S, Karasu A, Civelek E, Sabanci AP, Hepgul KT, Teng YD (2009) Microvascular decompression as a surgical management for trigeminal neuralgia: long-term follow-up and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev 32(1):87–93; discussion 93-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-008-0171-3
Kaufmann AM, Price AV (2019) A history of the Jannetta procedure. J Neurosurg 132:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.10.JNS181983
Kersten-Oertel M, Jannin P, Collins DL (2013) The state of the art of visualization in mixed reality image guided surgery. Comput Med Imaging Graph 37(2):98–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2013.01.009
Kin T, Nakatomi H, Shono N, Nomura S, Saito T, Oyama H, Saito N (2017) Neurosurgical virtual reality simulation for brain tumor using high-definition computer graphics: a review of the literature. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 57(10):513–520. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0320
Kockro RA, Stadie A, Schwandt E, Reisch R, Charalampaki C, Ng I, Yeo TT, Hwang P, Serra L, Perneczky A (2007) A collaborative virtual reality environment for neurosurgical planning and training. Neurosurgery 61(5 Suppl 2):379–391; discussion 391. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000303997.12645.26
Kontzialis M, Kocak M (2017) Imaging evaluation of trigeminal neuralgia. J Istanb Univ Fac Dent 51(3 Suppl 1):S62–S68. https://doi.org/10.17096/jiufd.27242
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529310
Lang E, Naraghi R, Tanrikulu L, Hastreiter P, Fahlbusch R, Neundörfer B, Tröscher-Weber R (2005) Neurovascular relationship at the trigeminal root entry zone in persistent idiopathic facial pain: findings from MRI 3D visualisation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(11):1506–1509. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2005.066084
Leidinger A, Muñoz-Hernandez F, Molet-Teixidó J (2018) Ausencia de conflicto neurovascular durante la microdescompresión vascular en el manejo de la neuralgia trigeminal esencial: ¿qué hacer? Revisión sistemática de la literatura (Absence of neurovascular conflict during microvascular decompression while treating essential trigeminal neuralgia. How to proceed? Systematic review of literature). Neurocirugia (Astur) 29(3):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucir.2018.02.001
Lovely TJ, Jannetta PJ (1997) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Surgical technique and long-term results. Neurosurg Clin N Am 8(1):11–29
Lutz J, Thon N, Stahl R, Lummel N, Tonn J-C, Linn J, Mehrkens J-H (2016) Microstructural alterations in trigeminal neuralgia determined by diffusion tensor imaging are independent of symptom duration, severity, and type of neurovascular conflict. J Neurosurg 124(3):823–830. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.2.JNS142587
Merskey H (2002) Clarifying definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 96(3):408–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3959(01)00423-7
Ohtani K, Mashiko T, Oguro K, Takemura A, Hatayama T, Sasaki T, Watanabe E (2016) Preoperative three-dimensional diagnosis of neurovascular relationships at the root exit zones during microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. World Neurosurg 92:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.05.005
Oishi M, Fukuda M, Ishida G, Saito A, Hiraishi T, Fujii Y (2011) Presurgical simulation with advanced 3-dimensional multifusion volumetric imaging in patients with skull base tumors. Neurosurgery 68(1 Suppl Operative):188–199; discussion 199. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e318207b3ad
Ong CS, Deib G, Yesantharao P, Qiao Y, Pakpoor J, Hibino N, Hui F, Garcia JR (2018) Virtual reality in neurointervention. J Vasc Interv Neurol 10(1):17–22
Sandhu SK, Lee JYK (2016) Measurement of trigeminal neuralgia pain: Penn Facial Pain Scale. Neurosurg Clin N Am 27(3):327–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2016.02.003
Stadie AT, Kockro RA, Reisch R, Tropine A, Boor S, Stoeter P, Perneczky A (2008) Virtual reality system for planning minimally invasive neurosurgery. Technical note. J Neurosurg 108(2):382–394. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/108/2/0382
Yao S, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Hou Y, Xu X, Zhang Z, Kikinis R, Chen X (2018) Multimodal image-based virtual reality presurgical simulation and evaluation for trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm. World Neurosurg 113:e499–e507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.02.069
Zanier ER, Zoerle T, Di Lernia D, Riva G (2018) Virtual reality for traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol 9:345. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00345
Zawy Alsofy S, Sakellaropoulou I, Stroop R (2020) Evaluation of surgical approaches for tumor resection in the deep infratentorial region and impact of virtual reality technique for the surgical planning and strategy. J Craniofac Surg 31(7):1865–1869. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000006525
Zeng Q, Zhou Q, Liu Z, Li C, Ni S, Xue F (2013) Preoperative detection of the neurovascular relationship in trigeminal neuralgia using three-dimensional fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition (FIESTA) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). J Clin Neurosci 20(1):107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2012.01.046
Zhong J, Zhu J, Sun H, Dou N-N, Wang Y-N, Ying T-T, Xia L, Liu M-X, Tao B-B, Li S-T (2014) Microvascular decompression surgery: surgical principles and technical nuances based on 4000 cases. Neurol Res 36(10):882–893. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743132814Y.0000000344
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Lidmila Fuskova for assistance with statistical analysis. The manuscript was proofread for English language by Deborah Nock (Medical WriteAway, Norwich, UK).
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Samer Zawy Alsofy, Heinz Welzel Saravia, and Ioanna Sakellaropoulou. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Samer Zawy Alsofy, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the ethics commission of the Medical Faculty, Witten/Herdecke University (Ref-Nr. 201/2018).
Human and animal experiments
This article does not contain any studies with humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate/for publication
The ethics commission of the Medical Faculty, Witten/Herdecke University (Ref-Nr. 201/2018) confirmed that formal consent is not required for this retrospective study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zawy Alsofy, S., Welzel Saravia, H., Nakamura, M. et al. Virtual reality-based evaluation of neurovascular conflict for the surgical planning of microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia patients. Neurosurg Rev 44, 3309–3321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01500-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01500-w