Abstract
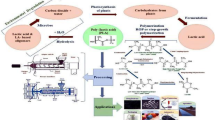
Imidazolium-based elastomeric ionomers (i-BIIR) were facilely synthesized by ionically modified brominated poly(isobutylene-co-isoprene) (BIIR) with different alkyl chain imidazole and thoroughly explored as novel toughening agents for poly(lactic acid) (PLA). The miscibility, thermal behavior, phase morphology and mechanical property of ionomers and blends were investigated through dynamic mechanical analyses (DMA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), tensile and impact testing. DMA and SEM results showed that better compatibility between the PLA and i-BIIR was achieved compared to the PLA/unmodified BIIR elastomer. A remarkable improvement in ductility with an optimum elongation at break up to 235% was achieved for the PLA/i-BIIR blends with 1-dodecylimidazole alkyl chain (i-BIIR-12), more than 10 times higher than that of pure PLA. The impact strengths of PLA were enhanced from 1.9 kJ/m2 to 4.1 kJ/m2 for the PLA/10 wt% i-BIIR-12 blend. Toughening mechanism had been established by systematical analysis of the compatibility, intermolecular interaction and phase structures of the blends. Interfacial cavitations initiated massive shear yielding of the PLA matrix owing to a suitable interfacial adhesion which played a key role in the enormous toughening effect in these blends. We believed that introducing imidazolium group into the BIIR elastomer was vital for the formation of a suitable interfacial adhesion.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Chen, G. Q.; Patel, M. K. Plastics derived from biological sources: present and future: a technical and environmental review. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112(4), 2082–2099
Zhang, X. Y.; Fevre, M.; Jones, G. O.; Waymouth, R. M. Catalysis as an enabling science for sustainable polymers. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118(2), 839–885
Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4(9), 835–864
Farah, S.; Anderson, D. G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications -a comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107(21), 367–392
Hou, J. Z.; Sun, X. P.; Zhang, W. X.; Li, L. L.; Teng, H. Preparation and characterization of electrospun fibers based on poly(L-lactic acid)/cellulose acetate. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 30(6), 916–922
Yao, C.; Li, X. S.; Neoh, K. G.; Shi, Z. L.; Kang, E. T. Antibacterial poly(D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) fibrous membranes modified with quaternary ammonium moieties. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 28(4), 581–588
Wu, N. J.; Zhang, H.; Fu, G. L. Super-tough poly(lactide) thermoplastic vulcanizates based on modified natural rubber. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5(1), 78–84
Wang, P.; Xu, P.; Wei, H. B.; Fang, H. G.; Ding, Y. S. Effect of block copolymer containing ionic liquid moiety on interfacial polarization in PLA/PCL blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 10.1002/APP.46161
Delgado, P. A.; Hillmyer, M. A. Combining block copolymers and hydrogen bonding for poly(lactide) toughening. RSC Adv. 2014, 4(26), 13266–13273
Hao, Y. P.; Ge, H. H.; Han, L. J.; Zhang, H. L.; Dong, L. S.; Sun, S. L. Thermal and mechanical properties of polylactide toughened with a butyl acrylate-ethyl acrylate-glysidyl methacrylate copolymer. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31(11), 1519–1527
Zhang, K. Toughened sustainable green composites from poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) based ternary blends and miscanthus biofiber. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2(10), 2345–2354
Yu, R. L.; Zhang, L. S.; Feng, Y. H.; Zhang, R. Y.; Zhu, J. Improvement in toughness of polylactide by melt blending with bio-based poly(ester)urethane. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 32(8), 1099–1110
Xing, Q.; Li, R. B.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X. Q.; Zhang, L. Y.; Wang, D. J. Phase morphology, crystallization behavior and mechanical properties of poly(L-lactide) toughened with biodegradable polyurethane: effect of composition and hard segment ratio. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33(9), 1294–1304
Zhang, K. Y.; Ran, X. H.; Wang, X. M.; Han, C. Y.; Han, L. J.; Wen, X.; Zhuang, Y. G.; Dong, L. S. Improvement in toughness and crystallization of poly(L-lactic acid) by melt blending with poly(epichlorohydrin-co-ethylene oxide). Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51(12), 2370–2380
Yuan, D. S.; Chen, Z. H.; Xu, C. H.; Chen, K. L.; Chen, Y. K. Fully biobased shape memory material based on novel cocontinuous structure in poly(lactic acid)/natural rubber TPVs fabricated via peroxide-induced dynamic vulcanization and in situ interfacial compatibilization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3(11), 2856–2865
Zhang, K. Y.; Nagarajan, V.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A. K. Supertoughened renewable PLA reactive multiphase blends system: phase morphology and performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6(15), 12436–12448
Dong, W. Y.; He, M. F.; Wang, H. T.; Ren, F. L.; Zhang, J. Q.; Zhao, X. W.; Li, Y. J. PLLA/ABS blends compatibilized by reactive comb polymers: double Tg depression and significantly improved toughness. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3(10), 2542–2550
Lin, Y.; Zhang, K. Y.; Dong, Z. M.; Dong, L. S.; Li, Y. S. Study of hydrogen-bonded blend of polylactide with biodegradable hyperbranched poly(ester amide). Macromolecules 2007, 40(17), 6257–6267
Han, S. I.; Yoo, Y. T; Kim, D. K.; Im, S. S. Biodegradable aliphatic polyester ionomers. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4(3), 199–207
Park, S. B.; Hwang, S. Y.; Moon, C. W.; Im, S. S. Plasticizer effect of novel PBS ionomer in PLA/PBS ionomer blends. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18(5), 463–471
Liu, H. Z.; Chen, F.; Liu, B.; Estep, G.; Zhang, J. W. Super toughened poly(lactic acid) ternary blends by simultaneous dynamic vulcanization and interfacial compatibilization. Macromolecules 2010, 43(14), 6058–6066
Liu, H. Z.; Song, W. J.; Chen, F.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J. W. Interaction of microstructure and interfacial adhesion on impact performance of polylactide (PLA) ternary blends. Macromolecules 2011, 44(6), 1513–1522
Liu, H. Z.; Guo, X. J.; Song, W. J.; Zhang, J. W. Effects of metal ion type on ionomer-assisted reactive toughening of poly(lactic acid). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52(13), 4787–4793
Megevand, B.; Pruvost, S.; Lins, L. C.; Livil, S.; Gérard, J. F.; Duchet-Rumeau, J. Probing nanomechanical properties with AFM to understand the structure and behavior of polymer blends compatibilized with ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6(98), 96421–96430
Lins, L. C.; Livi, S.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gérard, J. F. Phosphonium ionic liquids as new compatibilizing agents of biopolymer blends composed of poly(butylene-adipate-coterephtalate)/poly(lactic acid) (PBAT/PLA). RSC Adv. 2015, 5(73), 59082–59092
Wang, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, H. G.; Wei, H. B.; Ding, Y. S. A well-defined biodegradable 1,2,3-triazoliumfunctionalized PEG-è-PCL block copolymer: facile synthesis and its compatibilization for PLA/PCL blends. Ionics 2018, 10.1007/s11581-017-2234-3
Jérémy, O.; Jean-Marie, R.; Cédric, S.; Sophie, B.; Apostolos, E.; Dubois, P.; Giannelis, E. P. Shape-memory behavior of polylactide/silica ionic hybrids. Macromolecules 2017, 50(7), 2896–2905
Livi, S.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gérard, J. F.; Pham, T. N. Polymers and ionic liquids: a successful wedding. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216(4), 359–368
Chen, B. K.; Wu, T. Y.; Chang, Y. M.; Chen, A. F. Ductile polylactic acid prepared with ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 886–893
Gardella, L.; Furfaro, D.; Galimberti, M.; Monticelli, O. On the development of facile approach based on the use of ionic liquids: preparation of PLLA (sc-PLA)/high surface area nanographite systems. Green Chem. 2015, 17(7), 4082–4088
Cui, J.; Nie, F. M.; Yang, J. X.; Pan, L.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y. S. Novel imidazolium-Based poly(ionic liquid)s with different counter ions for self-healing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25220–25229
Le, H. H.; Das, A. Triggering the self-healing properties of modifed bromobutyl rubber by intrinsically electrical heating. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600385
Das, A.; Sallat, A.; Böhme, F.; Suckow, M.; Basu, D.; Wießner, S.; Stöckelhuber, K. W.; Voit, B.; Heirich, G. Ionic modification turns commercial rubber into a self-healing material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7(37), 20623–20630
Suckow, M.; Mordvinkin, A.; Roy, M.; Singha, N. K.; Heinrich, G.; Voit, B.; Saalwächter, K.; Böhme, F. Tuning the properties and self-healing behavior of ionically modified poly(isobutylene-co-isoprene) rubber. Macromolecules 2018, 51(2), 468–479
Meng, Q. Q.; Wang, B.; Pan, L.; Li, Y. S.; Ma, Z. Synthesis and properties of isotactic polypropylene ionomers containing ammonium Ions. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2017, 11, 1762–1772
Lee, M.; Choi, U. H.; Wi, S.; Slebodnick, C.; Colby, R. H.; Gibson, H. W. 1,2-Bis[iV-(iV′-alkylimidazolium)] ethane salts: a new class of organic ionic plastic crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21(33), 12280–12287
Dakin, J. M.; Shanmugam, K. V. S.; Twigg, C.; Whitney, R. A.; Parent, J. S. Isobutylene-rich macromonomers: dynamics and yields of peroxide-initiated crosslinking. Polym. Chem. 2015, 53(1), 123–132
Parent, J. S.; Porter, A. M. J.; Kleczek, M. R.; Whitney, R. A. Imidazolium bromide derivatives of poly(isobutylene-coisoprene): a new class of elastomeric ionomers. Polymer 2011, 52(24), 5410–5418
Kim, A.; Miller, K. M. Synthesis and thermal analysis of crosslinked imidazolium-containing polyester networks prepared by Michael addition polymerization. Polymer 2012, 53(25), 5666–5674
Ye, Y. S.; Sharick, S.; Davis, E. M.; Winey, K. I.; Elabd, Y. A. High hydroxide conductivity in polymerized ionic liquid block copolymers. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2(7), 575–580
Nykaza, J. R.; Ye, Y. S.; Elabd, Y. A. Polymerized ionic liquid diblock copolymers with long alkyl side-chain length. Polymer 2014, 55(16), 3360–3369
Wu, J. R.; Huang, G. S.; Pan, Q. Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Y. C.; Wang, B. An investigation on the molecular mobility through the glass transition of chlorinated butyl rubber. Polymer 2007, 48(26), 7653–7659
Mora-Barrantes, I.; Malmierica, M. A.; Valentin, J. L.; Rodriguez, A.; Ibarra, L. Effect of covalent cross-links on the network structure of thermo-reversible ionic elastomers. Soft Matter 2012, 8(19), 5201–5213
Marin, N.; Favis, B. D. Co-continuous morphology development in partially miscible PMMA/PC blends. Polymer 2002, 43(17), 4723–4731
Harrats, C.; Thomas, S. and Groeninckx, G. "Micro-and nanostructured multiphase polymer blends system", CRC Press, 2006, p. 4-33
Phetwarotai, W.; Tanrattanakul, V.; Phusunti, N. Synergistic effect of nucleation and compatibilization on the polylactide and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend films. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34(9), 1129–1140
Nagarajan, V. Overcoming the fundamental challenges in improving the impact strength and crystallinity of PLA biocomposites: influence of nucleating agent and mold temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7(21), 11203–11214
Yu, F.; Huang, H. X. Simultaneously toughening and reinforcing poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic polyurethane blend via enhancing interfacial adhesion by hydrophobic silica nanoparticles. Polym. Test. 2015, 45, 107–113
Zhang, K. Y.; Mohanty, A. K.; Misra, M. Fully biodegradable and biorenewable ternary blends from polylactide, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(butylene succinate) with balanced properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4(6), 3091–3101
Zhang, K. Y.; Nagarajan, V.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A. K. Super toughened renewable PLA reactive multiphase blends system: phase morphology and performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6(15), 12436–12448.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51573130).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Hu, K., Sun, ST. et al. Toughening Poly(lactic acid) with Imidazolium-based Elastomeric Ionomers. Chin J Polym Sci 36, 1342–1352 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-018-2143-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-018-2143-6