Abstract
Background
Periodontal treatment in diabetic patients reduces systemic inflammatory burden and hence should be closely coordinated with the patient’s overall clinical diabetic management.
Objective
To evaluate the effectiveness of diode laser (DL) (Biolase EpicTM, 940 nm, Irvine, CA, USA) as an adjunct to scaling root and planing (SRP) on periodontal health and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients suffering from generalized chronic periodontitis (CP), currently, stage II or above/grade B or C periodontitis.
Materials and methodology
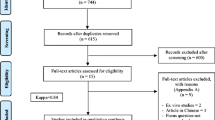
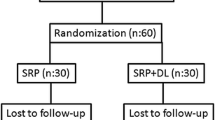
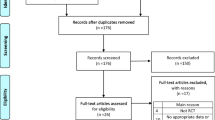
After initial screening of 55 T2DM patients, a total of 44 T2DM-CP patients (between the age group of 30 and 65 years) were selected and randomly assigned into two groups. The groups were divided into control group (n=22), treated with scaling and root planing alone (SRP alone), and experimental group (n=22), treated with scaling and root planing along with laser therapy (SRP + DL). Laser irradiation was accomplished at perio pocket setting of 0.8 W (average) in a pulse interval of 1.0 ms and pulse length of 1.0 ms delivering 24 J of energy using a 300-μm fiber optic delivery system.
Results
Thirty-seven out of 44 enrolled T2DM-CP patients completed the study. Both treatment modalities, i.e., SRP alone and SRP+DL resulted in mean significant (p < 0.001) improvement in periodontal health parameters (plaque index (PI), gingival index (GI), probing pocket depth (PPD) and clinical attachment loss (CAL)) and glycemic level (RBS, FBS, and HbA1c) in T2DM-CP patients after 6 months, and was higher in SRP+DL group in comparison to SRP alone. Among the periodontal health parameters, the mean PPD reduction and CAL gain were 51.78% and 48.26% in control as compared to 61.56% and 62.54% in experimental group respectively, whereas the mean significant reduction in HbA1c was 13.8% in SRP alone and 22.52% in SRP+DL group after 6 months (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Periodontal treatment involving SRP+DL contributes to improved periodontal health parameters and HbA1c level in T2DM-CP patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor GW (2001) Bidirectional interrelationships between diabetes and periodontal diseases: an epidemiologic perspective. Ann Periodntol 6(1):99–112
Koçak E, Sağlam M, Kayış SA, Dündar N, Kebapçılar L, Bruno G et al (2016) Nonsurgical periodontal therapy with/without diode laser modulates metabolic control of type 2 diabetics with periodontitis: a randomized clinical trial. Lasers Med Sci 31:343–353
Sanz M, Ceriello A, Buysschaert M, Chapple I, Demmer RT, Grazziani F et al (2017) Scientific evidence on the links between periodontal diseases and diabetes: consensus report and guidelines of the joint workshop on periodontal diseases and diabetes by the International Diabetes Federation and the European Federation of Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 00:1–12
American Diabetes Association (2018) Introduction: standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 41(1):S1–S2
Taylor GW, Borgnakke WS (2008) Periodontal disease: associations with diabetes, glycemic control and complications. Oral Dis 14:191–203
Awartini FA (2009) Evaluation of the relationship between type 2 diabetes and periodontal disease. Saudi Med J 30:902–906
Obradovic R, Kesic L, Mihailovic D, Jovanovic G, Antic S, Brkic Z (2012) Low-level laser therapy as an adjunct in periodontal therapy in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther 14:799–803
Abduljabbar T, Javed F, Shah A, Samer MS, Vohra F, Akram Z (2017) Role of lasers as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Lasers Med Sci 32:449–459
Barbosa FI, Araújo PV, Machado LJC, Magalhães CS, Guimarães MMM, Moreira AN (2018) Effect of photodynamic therapy as an adjuvant to non-surgical periodontal therapy: periodontal and metabolic evaluation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 22:245–250
Castro dos Santos NC, Andere NMRB, Araujo CF, de Marco AC, dos Santos LM, Jardini MAN et al (2016) Local adjunct effect of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for the treatment of chronic periodontitis in type 2 diabetics: split-mouth double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Lasers Med Sci 31:1633–1640
Bunjaku V, Popovska M, Grcev A, Mrasori S, Kameri A, Sllamniku Z et al (2017) Non-surgical periodontal treatment and low level laser therapy (LLLT) outcomes for patients suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity and chronic periodontitis. J Int Dent Med Res 10:214–221
Aoki A, Miyuki K, Sasaki, Watanabe H, Ishikawa I (2004) Lasers in nonsurgical periodontal therapy. Periodontol 36:59–97
Sgolastra F, Severino M, Gatto R, Monaco A (2013) Effectiveness of diode laser as adjunctive therapy to scaling root planning in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: a meta-analysis. Lasers Med Sci 28:1393–1402
Chandra S, Shashikumar P (2019) Diode laser - a novel therapeutic approach in the treatment of chronic periodontitis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. J Lasers Med Sci 10:56–63
Saglam M, Kantarci A, Dundar N, Hakki SS (2014) Clinical and biochemical effects of diode laser as an adjunct to nonsurgical treatment of chronic periodontitis: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Lasers Med Sci 29:37–46
Crispino A, Figliuzzi MM, Iovane C, Giudice TD, Lomanno S, Pacifico D et al (2015) Effectiveness of a diode laser in addition to non-surgical periodontal therapy: study of intervention. Ann Stomatol VI:15–20
Paul P, Bilichodmath S, Sameera U (2018) Clinical and glycemic level evaluation of the efficacy of diode laser and antibiotics with scaling and root planing in treating chronic periodontitis patients with diabetes. J Dent Lasers 12:24–30
Cao R, Li Q, Wu Q, Yao M, Chen Y, Zhou H (2019) Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on glycemic control of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 19:176
Löe H, Silness J (1963) Periodontal disease in pregnancy. I. Prevalence and severity. Acta Odontol Scand 21:533–551
Silness J, Löe H (1964) Periodontal disease in pregnancy. II. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odontol Scand 22:121–135
Mohan M, Jhingran R, Bains VK, Gupta V, Madan R, Rizvi I et al (2014) Impact of scaling and root planing on C-reactive protein levels in gingival crevicular fluid and serum in chronic periodontitis patients with or without diabetes mellitus. J Periodontal Implant Sci 44:158–168
Qadri T, Javed F, Johannsen G, Gustaffson A (2015) Role of diode lasers (800–980Nm) as adjuncts to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: a systematic review. Photomed Laser Surg 33:568–575
Convissar RA (2016) Principles and practice of laser dentistry, 2nd edn. Elsevier, New York
Kocak E, Sağlam M, Arslan U et al (2020) Effect of diode laser application as an adjunct to nonsurgical periodontal therapy on the reduction of red complex microorganisms in type 2 diabetics with chronic periodontitis. Lasers Med Sci 35:1403–1410
Le R, Zhe Z, Daxu L, Chunni D, Hong T (2018) Clinical efficacy of semiconductor laser-assisted minocycline in moderate-to-severe chronic periodontitis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trop J Pharm Res 17:1165–1170
Janket SJ, Wightman A, Baird AE, Van Dyke TE, Jones JA (2005) Does periodontal treatment improve glycemic control in diabetic patients? A meta-analysis of intervention studies. J Dent Res 84:1154–1159
Takeda M, Ojima M, Yoshioka H, Inaba H, Kogo M, Shizukuishi S et al (2006) Relationship of serum advanced glycation end products with deterioration of periodontitis in type 2 diabetes patients. J Periodontol 77:15–20
Lalla E, Lamster IB, Stern DM, Schmidt AM (2001) Receptor for advanced glycation end products, inflammation, and accelerated periodontal disease in diabetics: mechanisms and insights into therapeutic modalities. Ann Periodontol 6:113–118
Kolbe MF, Ribeiro FV, Luchesi VH, Casarin RC, Sallum EA, Nociti FH Jr et al (2014) Photodynamic therapy during supportive periodontal care: clinical, microbiologic, immune inflammatory, and patient centered performance in a split-mouth randomized clinical trial. J Periodontol 85:e277–e286
Singh M, Bains VK, Jhingran R, Srivastava R, Madan R, Maurya SC et al (2019) Prevalence of periodontal disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross-sectional study. Contemp Clin Dent 10:349–357
ICMR Guidelines for management of type 2 diabetes 2018. https://medulletin.com. Accessed 28 Jan 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Study is financed by the authors themselves. Infrastructural support provided by the Institute.
Ethics approval
Research protocol and study design approved by Institutional Human Ethics Committee and Institutional Research & Development Committee. Written informed consent obtained from human participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key messages
Diode laser as adjunct to SRP showed additional benefits in T2DM-CP patients in terms of their periodontal and systemic health parameters.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soi, S., Bains, V.K., Srivastava, R. et al. Comparative evaluation of improvement in periodontal and glycemic health status of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients after scaling and root planing with or without adjunctive use of diode laser. Lasers Med Sci 36, 1307–1315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-021-03261-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-021-03261-w