Abstract
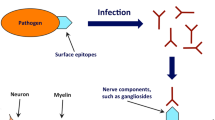
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a post-infectious disease in which the human peripheral nervous system is affected after infection by specific pathogenic bacteria, including Campylobacter jejuni. GBS is suggested to be provoked by molecular mimicry between sialylated lipooligosaccharide (LOS) structures on the cell envelope of these bacteria and ganglioside epitopes on the human peripheral nerves, resulting in autoimmune-driven nerve destruction. Earlier, the C. jejuni sialyltransferase (Cst-II) was found to be linked to GBS and demonstrated to be involved in the biosynthesis of the ganglioside-like LOS structures. Apart from a role in pathogenicity, we report here that Cst-II-generated ganglioside-like LOS structures confer efficient bacteriophage resistance in C. jejuni. By bioinformatic analysis, it is revealed that the presence of sialyltransferases in C. jejuni and other potential GBS-related pathogens correlated significantly with the apparent degeneration of an alternative anti-virus system: type II Clusters of Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat and associated genes (CRISPR-Cas). Molecular analysis of the C. jejuni CRISPR-Cas system confirmed the bioinformatic investigation. CRISPR degeneration and mutations in the cas genes cas2, cas1 and csn1 were found to correlate with Cst-II sialyltransferase presence (p < 0.0001). Remarkably, type II CRISPR-Cas systems are mainly found in mammalian pathogens. To study the potential involvement of this system in pathogenicity, we inactivated the type II CRISPR-Cas marker gene csn1, which effectively reduced virulence in primarily cst-II-positive C. jejuni isolates. Our findings indicate a novel link between viral defence, virulence and GBS in a pathogenic bacterium.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guerrant RL, Hughes JM, Lima NL, Crane J (1990) Diarrhea in developed and developing countries: magnitude, special settings, and etiologies. Rev Infect Dis 12(Suppl 1):S41–S50
Stephens DS (2009) Biology and pathogenesis of the evolutionarily successful, obligate human bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. Vaccine 27(Suppl 2):B71–B77
Harrison LH, Simonsen V, Waldman EA (2008) Emergence and disappearance of a virulent clone of Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius, cause of Brazilian purpuric fever. Clin Microbiol Rev 21(4):594–605
Nakwan N, Nakwan N, Atta T, Chokephaibulkit K (2009) Neonatal pasteurellosis: a review of reported cases. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 94(5):F373–F376
Severi E, Hood DW, Thomas GH (2007) Sialic acid utilization by bacterial pathogens. Microbiology 153(Pt 9):2817–2822
Guerry P, Ewing CP, Hickey TE, Prendergast MM, Moran AP (2000) Sialylation of lipooligosaccharide cores affects immunogenicity and serum resistance of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun 68(12):6656–6662
Fox KL, Cox AD, Gilbert M, Wakarchuk WW, Li J, Makepeace K, Richards JC, Moxon ER, Hood DW (2006) Identification of a bifunctional lipopolysaccharide sialyltransferase in Haemophilus influenzae: incorporation of disialic acid. J Biol Chem 281(52):40024–40032
Tatum FM, Tabatabai LB, Briggs RE (2009) Sialic acid uptake is necessary for virulence of Pasteurella multocida in turkeys. Microb Pathog 46(6):337–344
Habib I, Louwen R, Uyttendaele M, Houf K, Vandenberg O, Nieuwenhuis EE, Miller WG, van Belkum A, De Zutter L (2009) Correlation between genotypic diversity, lipooligosaccharide gene locus class variation, and caco-2 cell invasion potential of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from chicken meat and humans: contribution to virulotyping. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(13):4277–4288
Louwen R, Heikema A, van Belkum A, Ott A, Gilbert M, Ang W, Endtz HP, Bergman MP, Nieuwenhuis EE (2008) The sialylated lipooligosaccharide outer core in Campylobacter jejuni is an important determinant for epithelial cell invasion. Infect Immun 76(10):4431–4438
Perera VN, Nachamkin I, Ung H, Patterson JH, McConville MJ, Coloe PJ, Fry BN (2007) Molecular mimicry in Campylobacter jejuni: role of the lipo-oligosaccharide core oligosaccharide in inducing anti-ganglioside antibodies. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 50(1):27–36
Unkmeir A, Kämmerer U, Stade A, Hübner C, Haller S, Kolb-Mäurer A, Frosch M, Dietrich G (2002) Lipooligosaccharide and polysaccharide capsule: virulence factors of Neisseria meningitidis that determine meningococcal interaction with human dendritic cells. Infect Immun 70(5):2454–2462
Hammerschmidt S, Hilse R, van Putten JP, Gerardy-Schahn R, Unkmeir A, Frosch M (1996) Modulation of cell surface sialic acid expression in Neisseria meningitidis via a transposable genetic element. EMBO J 15(1):192–198
Chiu CP, Watts AG, Lairson LL, Gilbert M, Lim D, Wakarchuk WW, Withers SG, Strynadka NC (2004) Structural analysis of the sialyltransferase CstII from Campylobacter jejuni in complex with a substrate analog. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11(2):163–170
Gilbert M, Karwaski MF, Bernatchez S, Young NM, Taboada E, Michniewicz J, Cunningham AM, Wakarchuk WW (2002) The genetic bases for the variation in the lipo-oligosaccharide of the mucosal pathogen, Campylobacter jejuni. Biosynthesis of sialylated ganglioside mimics in the core oligosaccharide. J Biol Chem 277(1):327–337
Thon V, Lau K, Yu H, Tran BK, Chen X (2011) PmST2: a novel Pasteurella multocida glycolipid alpha2-3-sialyltransferase. Glycobiology 21(9):1206–1216
Packiam M, Shell DM, Liu SV, Liu YB, McGee DJ, Srivastava R, Seal S, Rest RF (2006) Differential expression and transcriptional analysis of the alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase gene in pathogenic Neisseria spp. Infect Immun 74(5):2637–2650
Sadler F, Fox A, Neal K, Dawson M, Cartwright K, Borrow R (2003) Genetic analysis of capsular status of meningococcal carrier isolates. Epidemiol Infect 130(1):59–70
Tsai CM (2001) Molecular mimicry of host structures by lipooligosaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis: characterization of sialylated and nonsialylated lacto-N-neotetraose (Galbeta1-4GlcNAcbeta1-3Galbeta1-4Glc) structures in lipooligosaccharides using monoclonal antibodies and specific lectins. Adv Exp Med Biol 491:525–542
Harvey HA, Swords WE, Apicella MA (2001) The mimicry of human glycolipids and glycosphingolipids by the lipooligosaccharides of pathogenic Neisseria and Haemophilus. J Autoimmun 16(3):257–262
Ang CW, Jacobs BC, Laman JD (2004) The Guillain–Barré syndrome: a true case of molecular mimicry. Trends Immunol 25(2):61–66
Brigham KS, Sandora TJ (2009) Neisseria meningitidis: epidemiology, treatment and prevention in adolescents. Curr Opin Pediatr 21(4):437–443
Yuki N (2007) Ganglioside mimicry and peripheral nerve disease. Muscle Nerve 35(6):691–711
Bennetto LP, Lyons P (2004) Miller Fisher syndrome associated with Pasteurella multocida infection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(12):1786–1787
Mori M, Kuwabara S, Miyake M, Noda M, Kuroki H, Kanno H, Ogawara K, Hattori T (2000) Haemophilus influenzae infection and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Brain 123(Pt 10):2171–2178
van Doorn PA, Ruts L, Jacobs BC (2008) Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment of Guillain–Barré syndrome. Lancet Neurol 7(10):939–950
Willison HJ, Kennedy PG (1993) Gangliosides and bacterial toxins in Guillain–Barré syndrome. J Neuroimmunol 46(1–2):105–112
Kiefer R, Kieseier BC, Stoll G, Hartung HP (2001) The role of macrophages in immune-mediated damage to the peripheral nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 64(2):109–127
van Belkum A, van den Braak N, Godschalk P, Ang W, Jacobs B, Gilbert M, Wakarchuk W, Verbrugh H, Endtz H (2001) A Campylobacter jejuni gene associated with immune-mediated neuropathy. Nat Med 7(7):752–753
Godschalk PC, Heikema AP, Gilbert M, Komagamine T, Ang CW, Glerum J, Brochu D, Li J, Yuki N, Jacobs BC, van Belkum A, Endtz HP (2004) The crucial role of Campylobacter jejuni genes in anti-ganglioside antibody induction in Guillain–Barré syndrome. J Clin Invest 114(11):1659–1665
Gilbert M, Godschalk PC, Karwaski MF, Ang CW, van Belkum A, Li J, Wakarchuk WW, Endtz HP (2004) Evidence for acquisition of the lipooligosaccharide biosynthesis locus in Campylobacter jejuni GB11, a strain isolated from a patient with Guillain–Barré syndrome, by horizontal exchange. Infect Immun 72(2):1162–1165
Phongsisay V, Perera VN, Fry BN (2006) Exchange of lipooligosaccharide synthesis genes creates potential Guillain–Barré syndrome-inducible strains of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun 74(2):1368–1372
Haft DH, Selengut J, Mongodin EF, Nelson KE (2005) A guild of 45 CRISPR-associated (Cas) protein families and multiple CRISPR/Cas subtypes exist in prokaryotic genomes. PLoS Comput Biol 1(6):e60
Makarova KS, Haft DH, Barrangou R, Brouns SJ, Charpentier E, Horvath P, Moineau S, Mojica FJ, Wolf YI, Yakunin AF, van der Oost J, Koonin EV (2011) Evolution and classification of the CRISPR-Cas systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 9(6):467–477
Deveau H, Garneau JE, Moineau S (2010) CRISPR/Cas system and its role in phage–bacteria interactions. Annu Rev Microbiol 64:475–493
Horvath P, Barrangou R (2010) CRISPR/Cas, the immune system of bacteria and archaea. Science (New York, N.Y.) 327(5962):167–170
Stevens J, Chen LM, Carney PJ, Garten R, Foust A, Le J, Pokorny BA, Manojkumar R, Silverman J, Devis R, Rhea K, Xu X, Bucher DJ, Paulson JC, Cox NJ, Klimov A, Donis RO (2010) Receptor specificity of influenza A H3N2 viruses isolated in mammalian cells and embryonated chicken eggs. J Virol 84(16):8287–8299
Herrler G, Klenk HD (1987) The surface receptor is a major determinant of the cell tropism of influenza C virus. Virology 159(1):102–108
Superti F, Girmenta C, Seganti L, Orsi N (1986) Role of sialic acid in cell receptors for vesicular stomatitis virus. Acta Virol 30(1):10–18
Superti F, Hauttecoeur B, Morelec MJ, Goldoni P, Bizzini B, Tsiang H (1986) Involvement of gangliosides in rabies virus infection. J Gen Virol 67(Pt 1):47–56
Gilbert J, Dahl J, Riney C, You J, Cui C, Holmes R, Lencer W, Benjamin T (2005) Ganglioside GD1a restores infectibility to mouse cells lacking functional receptors for polyomavirus. J Virol 79(1):615–618
Superti F, Donelli G (1991) Gangliosides as binding sites in SA-11 rotavirus infection of LLC-MK2 cells. J Gen Virol 72(Pt 10):2467–2474
Markwell MA, Fredman P, Svennerholm L (1984) Receptor ganglioside content of three hosts for Sendai virus. MDBK, HeLa, and MDCK cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 775(1):7–16
Sinibaldi L, Goldoni P, Pietropaolo V, Longhi C, Orsi N (1990) Involvement of gangliosides in the interaction between BK virus and Vero cells. Arch Virol 113(3–4):291–296
Yao L, Korteweg C, Hsueh W, Gu J (2008) Avian influenza receptor expression in H5N1-infected and noninfected human tissues. FASEB J 22(3):733–740
Levin BR (2010) Nasty viruses, costly plasmids, population dynamics, and the conditions for establishing and maintaining CRISPR-mediated adaptive immunity in bacteria. PLoS Genet 6(10):e1001171
Coward C, Grant AJ, Swift C, Philp J, Towler R, Heydarian M, Frost JA, Maskell DJ (2006) Phase-variable surface structures are required for infection of Campylobacter jejuni by bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):4638–4647
Connerton PL, Loc Carrillo CM, Swift C, Dillon E, Scott A, Rees CE, Dodd CE, Frost J, Connerton IF (2004) Longitudinal study of Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophages and their hosts from broiler chickens. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(7):3877–3883
Godschalk PC, Kuijf ML, Li J, St Michael F, Ang CW, Jacobs BC, Karwaski MF, Brochu D, Moterassed A, Endtz HP, van Belkum A, Gilbert M (2007) Structural characterization of Campylobacter jejuni lipooligosaccharide outer cores associated with Guillain–Barré and Miller Fisher syndromes. Infect Immun 75(3):1245–1254
Dzieciatkowska M, Liu X, Heikema AP, Houliston RS, van Belkum A, Schweda EK, Gilbert M, Richards JC, Li J (2008) Rapid method for sensitive screening of oligosaccharide epitopes in the lipooligosaccharide from Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from Guillain–Barré syndrome and Miller Fisher syndrome patients. J Clin Microbiol 46(10):3429–3436
Grissa I, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C (2007) CRISPRFinder: a web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Web Server issue):W52–W57
Wren BW, Henderson J, Ketley JM (1994) A PCR-based strategy for the rapid construction of defined bacterial deletion mutants. Biotechniques 16(6):994–996
van Vliet AH, Wooldridge KG, Ketley JM (1998) Iron-responsive gene regulation in a Campylobacter jejuni fur mutant. J Bacteriol 180(20):5291–5298
Kim JS, Li J, Barnes IH, Baltzegar DA, Pajaniappan M, Cullen TW, Trent MS, Burns CM, Thompson SA (2008) Role of the Campylobacter jejuni Cj1461 DNA methyltransferase in regulating virulence characteristics. J Bacteriol 190(19):6524–6529
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol 7:214
MacCallum A, Hardy SP, Everest PH (2005) Campylobacter jejuni inhibits the absorptive transport functions of Caco-2 cells and disrupts cellular tight junctions. Microbiology 151(7):2451–2458
Gaasbeek EJ, Wagenaar JA, Guilhabert MR, van Putten JP, Parker CT, van der Wal FJ (2010) Nucleases encoded by the integrated elements CJIE2 and CJIE4 inhibit natural transformation of Campylobacter jejuni. J Bacteriol 192(4):936–941
Gaasbeek EJ, Wagenaar JA, Guilhabert MR, Wösten MM, van Putten JP, van der Graaf-van Bloois L, Parker CT, van der Wal FJ (2009) A DNase encoded by integrated element CJIE1 inhibits natural transformation of Campylobacter jejuni. J Bacteriol 191(7):2296–2306
Mortensen NP, Kuijf ML, Ang CW, Schiellerup P, Krogfelt KA, Jacobs BC, van Belkum A, Endtz HP, Bergman MP (2009) Sialylation of Campylobacter jejuni lipo-oligosaccharides is associated with severe gastro-enteritis and reactive arthritis. Microbes Infect 11(12):988–994
Lindenstrauss AG, Pavlovic M, Bringmann A, Behr J, Ehrmann MA, Vogel RF (2011) Comparison of genotypic and phenotypic cluster analyses of virulence determinants and possible role of CRISPR elements towards their incidence in Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. Syst Appl Microbiol 34(8):553–560
Delaney NF, Balenger S, Bonneaud C, Marx CJ, Hill GE, Ferguson-Noel N, Tsai P, Rodrigo A, Edwards SV (2012) Ultrafast evolution and loss of CRISPRs following a host shift in a novel wildlife pathogen, Mycoplasma gallisepticum. PLoS Genet 8(2):e1002511
Palmer KL, Gilmore MS (2010) Multidrug-resistant enterococci lack CRISPR-cas. MBio 1(4). Pii: e00227-10
Nozawa T, Furukawa N, Aikawa C, Watanabe T, Haobam B, Kurokawa K, Maruyama F, Nakagawa I (2011) CRISPR inhibition of prophage acquisition in Streptococcus pyogenes. PLoS One 6(5):e19543
Fricke WF, Mammel MK, McDermott PF, Tartera C, White DG, Leclerc JE, Ravel J, Cebula TA (2011) Comparative genomics of 28 Salmonella enterica isolates: evidence for CRISPR-mediated adaptive sublineage evolution. J Bacteriol 193(14):3556–3568
Palmer KL, Whiteley M (2011) DMS3-42: the secret to CRISPR-dependent biofilm inhibition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 193(14):3431–2
Zegans ME, Wagner JC, Cady KC, Murphy DM, Hammond JH, O’Toole GA (2009) Interaction between bacteriophage DMS3 and host CRISPR region inhibits group behaviors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 191(1):210–219
Deltcheva E, Chylinski K, Sharma CM, Gonzales K, Chao Y, Pirzada ZA, Eckert MR, Vogel J, Charpentier E (2011) CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor RNase III. Nature 471(7340):602–607
Ho TW, Willison HJ, Nachamkin I, Li CY, Veitch J, Ung H, Wang GR, Liu RC, Cornblath DR, Asbury AK, Griffin JW, McKhann GM (1999) Anti-GD1a antibody is associated with axonal but not demyelinating forms of Guillain–Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol 45(2):168–173
Sinha S, Prasad KN, Jain D, Pandey CM, Jha S, Pradhan S (2007) Preceding infections and anti-ganglioside antibodies in patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome: a single centre prospective case–control study. Clin Microbiol Infect 13(3):334–337
Perez-Rodriguez R, Haitjema C, Huang Q, Nam KH, Bernardis S, Ke A, DeLisa MP (2011) Envelope stress is a trigger of CRISPR RNA-mediated DNA silencing in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 79(3):584–599
Raivio T (2011) Identifying your enemies—could envelope stress trigger microbial immunity? Mol Microbiol 79(3):557–561
Jerome JP, Bell JA, Plovanich-Jones AE, Barrick JE, Brown CT, Mansfield LS (2011) Standing genetic variation in contingency loci drives the rapid adaptation of Campylobacter jejuni to a novel host. PLoS One 6(1):e16399
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Human Frontier Science Program (RGP 38/2003) and by the BBSRC Institute Strategic Programme Grant to the IFR. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. We would like to thank Theo Hoogenboezem (Erasmus MC) for the mass spectrometry analysis of the recombinant Csn1 protein for polyclonal antibody production and Ian Connerton for bacteriophage CP28.
Conflicts of interest
Alex van Belkum is an employee of bioMérieux. There are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louwen, R., Horst-Kreft, D., de Boer, A.G. et al. A novel link between Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophage defence, virulence and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32, 207–226 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1733-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1733-4