Abstract
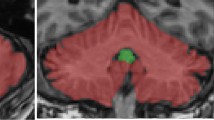
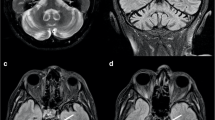
Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) studies have provided cumulative evidence of gray matter (GM) atrophy in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) relative to healthy controls (HC). However, not all findings have been entirely concordant. Herein, we performed a quantitative meta-analysis study in order to consistently quantify GM anomalies in PSP. We conducted a systematic search for VBM studies of PSP patients and HC using PubMed and Embase databases from January 2000 to May 2012. Meta-analysis of these VBM studies was performed using a newly improved voxel-based meta-analytic technique, effect-size signed differential mapping. A total of 9 cross-sectional VBM studies that involved 143 PSP patients and 216 HC subjects met the inclusion criteria. Considerable regional GM volume decrease was detected in the thalamus, basal ganglia, midbrain, insular cortex, and frontal cortex. These findings remained largely unchanged following jackknife sensitivity analyses. The present meta-analysis provided evidence of PSP-specific GM atrophy. This finding might help contribute to our understanding of the neurobiological basis underlying PSP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy: a heterogeneous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Morris HR, Gibb G, Katzenschlager R, Wood NW, Hanger DP, Strand C, Lashley T, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Anderton BH, Revesz T (2002) Pathological, clinical and genetic heterogeneity in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 125(Pt 5):969–975
Barsottini OG, Felicio AC, Aquino CC, Pedroso JL (2010) Progressive supranuclear palsy: new concepts. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 68(6):938–946
Burn DJ, Lees AJ (2002) Progressive supranuclear palsy: where are we now? Lancet Neurol 1(6):359–369
Williams DR, de Silva R, Paviour DC, Pittman A, Watt HC, Kilford L, Holton JL, Revesz T, Lees AJ (2005) Characteristics of two distinct clinical phenotypes in pathologically proven progressive supranuclear palsy: richardson’s syndrome and PSP-parkinsonism. Brain 128(Pt 6):1247–1258. doi:10.1093/brain/awh488
Williams DR, Lees AJ (2009) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinicopathological concepts and diagnostic challenges. Lancet Neurol 8(3):270–279. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70042-0
Hauw JJ, Daniel SE, Dickson D, Horoupian DS, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, McKee A, Tabaton M, Litvan I (1994) Preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology 44(11):2015–2019
Santacruz P, Uttl B, Litvan I, Grafman J (1998) Progressive supranuclear palsy: a survey of the disease course. Neurology 50(6):1637–1647
Josephs KA, Dickson DW (2003) Diagnostic accuracy of progressive supranuclear palsy in the society for progressive supranuclear palsy brain bank. Mov Disord 18(9):1018–1026. doi:10.1002/mds.10488
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 11(6 Pt 1):805–821. doi:10.1006/nimg.2000.0582
Brenneis C, Seppi K, Schocke M, Benke T, Wenning GK, Poewe W (2004) Voxel based morphometry reveals a distinct pattern of frontal atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(2):246–249
Price S, Paviour D, Scahill R, Stevens J, Rossor M, Lees A, Fox N (2004) Voxel-based morphometry detects patterns of atrophy that help differentiate progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 23(2):663–669. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.013
Cordato NJ, Duggins AJ, Halliday GM, Morris JG, Pantelis C (2005) Clinical deficits correlate with regional cerebral atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 128(Pt 6):1259–1266. doi:10.1093/brain/awh508
Boxer AL, Geschwind MD, Belfor N, Gorno-Tempini ML, Schauer GF, Miller BL, Weiner MW, Rosen HJ (2006) Patterns of brain atrophy that differentiate corticobasal degeneration syndrome from progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 63(1):81–86. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.1.81
Padovani A, Borroni B, Brambati SM, Agosti C, Broli M, Alonso R, Scifo P, Bellelli G, Alberici A, Gasparotti R, Perani D (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging and voxel based morphometry study in early progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77(4):457–463. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2005.075713
Agosta F, Kostic VS, Galantucci S, Mesaros S, Svetel M, Pagani E, Stefanova E, Filippi M (2010) The in vivo distribution of brain tissue loss in Richardson’s syndrome and PSP-parkinsonism: a VBM-DARTEL study. Eur J Neurosci 32(4):640–647. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07304.x
Lehericy S, Hartmann A, Lannuzel A, Galanaud D, Delmaire C, Bienaimee MJ, Jodoin N, Roze E, Gaymard B, Vidailhet M (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging lesion pattern in Guadeloupean parkinsonism is distinct from progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 133(Pt 8):2410–2425. doi:10.1093/brain/awq162
Takahashi R, Ishii K, Kakigi T, Yokoyama K, Mori E, Murakami T (2011) Brain alterations and mini-mental state examination in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy: voxel-based investigations using f-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 1(1):381–392. doi:10.1159/000333368
Ghosh BC, Calder AJ, Peers PV, Lawrence AD, Acosta-Cabronero J, Pereira JM, Hodges JR, Rowe JB (2012) Social cognitive deficits and their neural correlates in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain. doi:10.1093/brain/aws128
Whitwell JL, Avula R, Master A, Vemuri P, Senjem ML, Jones DT, Jack CR Jr, Josephs KA (2011) Disrupted thalamocortical connectivity in PSP: a resting-state fMRI, DTI, and VBM study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17(8):599–605. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.05.013
Saini J, Bagepally BS, Sandhya M, Pasha SA, Yadav R, Pal PK (2011) In vivo evaluation of white matter pathology in patients of progressive supranuclear palsy using TBSS. Neuroradiology. doi:10.1007/s00234-011-0983-7
Radua J, Mataix-Cols D (2009) Voxel-wise meta-analysis of grey matter changes in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Br J Psychiatry 195(5):393–402. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.108.055046
Radua J, Mataix-Cols D, Phillips ML, El-Hage W, Kronhaus DM, Cardoner N, Surguladze S (2011) A new meta-analytic method for neuroimaging studies that combines reported peak coordinates and statistical parametric maps. Eur Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2011.04.001
Li J, Pan P, Huang R, Shang H (2012) A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies of white matter volume alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(2):757–763. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.12.001
Pan PL, Song W, Shang HF (2012) Voxel-wise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 19(2):199–206. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03474.x
Via E, Radua J, Cardoner N, Happe F, Mataix-Cols D (2011) Meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in autism spectrum disorder: should Asperger disorder be subsumed under a broader umbrella of autistic spectrum disorder? Arch Gen Psychiatry 68(4):409–418. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.27
Li J, Pan P, Song W, Huang R, Chen K, Shang H (2011) A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.04.007
Bora E, Fornito A, Yucel M, Pantelis C (2010) Voxelwise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 67(11):1097–1105. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.01.020
Pan P, Song W, Yang J, Huang R, Chen K, Gong QY, Zhong JG, Shi HC, Shang HF (2012) Gray matter atrophy in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 33(2–3):141–148
Litvan I, Agid Y, Calne D, Campbell G, Dubois B, Duvoisin RC, Goetz CG, Golbe LI, Grafman J, Growdon JH, Hallett M, Jankovic J, Quinn NP, Tolosa E, Zee DS (1996) Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology 47(1):1–9
Litvan I, Bhatia KP, Burn DJ, Goetz CG, Lang AE, McKeith I, Quinn N, Sethi KD, Shults C, Wenning GK (2003) Movement disorders society scientific issues committee report: SIC task force appraisal of clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinsonian disorders. Mov Disord 18(5):467–486. doi:10.1002/mds.10459
Herrero MT, Barcia C, Navarro JM (2002) Functional anatomy of thalamus and basal ganglia. Childs Nerv Syst 18(8):386–404. doi:10.1007/s00381-002-0604-1
Warren NM, Piggott MA, Perry EK, Burn DJ (2005) Cholinergic systems in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 128(Pt 2):239–249. doi:10.1093/brain/awh391
Matsumoto R, Nakano I, Arai N, Suda M, Oda M (1996) Progressive supranuclear palsy with asymmetric lesions in the thalamus and cerebellum, with special reference to the unilateral predominance of many torpedoes. Acta Neuropathol 92(6):640–644
Dickson DW, Rademakers R, Hutton ML (2007) Progressive supranuclear palsy: pathology and genetics. Brain Pathol 17(1):74–82. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00054.x
Teune LK, Bartels AL, de Jong BM, Willemsen AT, Eshuis SA, de Vries JJ, van Oostrom JC, Leenders KL (2010) Typical cerebral metabolic patterns in neurodegenerative brain diseases. Mov Disord 25(14):2395–2404. doi:10.1002/mds.23291
Messina D, Cerasa A, Condino F, Arabia G, Novellino F, Nicoletti G, Salsone M, Morelli M, Lanza PL, Quattrone A (2011) Patterns of brain atrophy in Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17(3):172–176. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2010.12.010
Hanyu H, Asano T, Sakurai H, Takasaki M, Shindo H, Abe K (2001) Magnetisation transfer measurements of the subcortical grey and white matter in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia and in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neuroradiology 43(7):542–546
Schulz JB, Skalej M, Wedekind D, Luft AR, Abele M, Voigt K, Dichgans J, Klockgether T (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging-based volumetry differentiates idiopathic Parkinson’s syndrome from multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 45(1):65–74
Srulijes K, Reimold M, Liscic RM, Bauer S, Dietzel E, Liepelt-Scarfone I, Berg D, Maetzler W (2012) Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in Richardson’s syndrome and progressive supranuclear palsy-parkinsonism. Mov Disord 27(1):151–155
Zwergal A, la Fougere C, Lorenzl S, Rominger A, Xiong G, Deutschenbaur L, Linn J, Krafczyk S, Dieterich M, Brandt T, Strupp M, Bartenstein P, Jahn K (2011) Postural imbalance and falls in PSP correlate with functional pathology of the thalamus. Neurology 77(2):101–109. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318223c79d
Goffinet AM, De Volder AG, Gillain C, Rectem D, Bol A, Michel C, Cogneau M, Labar D, Laterre C (1989) Positron tomography demonstrates frontal lobe hypometabolism in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 25(2):131–139. doi:10.1002/ana.410250205
Karbe H, Grond M, Huber M, Herholz K, Kessler J, Heiss WD (1992) Subcortical damage and cortical dysfunction in progressive supranuclear palsy demonstrated by positron emission tomography. J Neurol 239(2):98–102
Foster NL, Gilman S, Berent S, Morin EM, Brown MB, Koeppe RA (1988) Cerebral hypometabolism in progressive supranuclear palsy studied with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 24(3):399–406. doi:10.1002/ana.410240308
Juh R, Pae CU, Kim TS, Lee CU, Choe B, Suh T (2005) Cerebral glucose metabolism in corticobasal degeneration comparison with progressive supranuclear palsy using statistical mapping analysis. Neurosci Lett 383(1–2):22–27. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.03.057
Hosaka K, Ishii K, Sakamoto S, Mori T, Sasaki M, Hirono N, Mori E (2002) Voxel-based comparison of regional cerebral glucose metabolism between PSP and corticobasal degeneration. J Neurol Sci 199(1–2):67–71
Mishina M, Ishii K, Mitani K, Ohyama M, Yamazaki M, Ishiwata K, Senda M, Kobayashi S, Kitamura S, Katayama Y (2004) Midbrain hypometabolism as early diagnostic sign for progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neurol Scand 110(2):128–135. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2004.00293.x
Augustine JR (1996) Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 22(3):229–244
Liakakis G, Nickel J, Seitz RJ (2011) Diversity of the inferior frontal gyrus—a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Behav Brain Res 225(1):341–347. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.06.022
Colosimo C, Morgante L, Antonini A, Barone P, Avarello TP, Bottacchi E, Cannas A, Ceravolo MG, Ceravolo R, Cicarelli G, Gaglio RM, Giglia L, Iemolo F, Manfredi M, Meco G, Nicoletti A, Pederzoli M, Petrone A, Pisani A, Pontieri FE, Quatrale R, Ramat S, Scala R, Volpe G, Zappulla S, Bentivoglio AR, Stocchi F, Trianni G, Del Dotto P, Simoni L, Marconi R (2010) Non-motor symptoms in atypical and secondary parkinsonism: the PRIAMO study. J Neurol 257(1):5–14. doi:10.1007/s00415-009-5255-7
Acknowledgments
We thank all the authors of the included studies. We especially thank Dr. Joaquim Radua for his kind help and suggestings.
Conflict of interest
There is no actual or potential financial and other conflict of interest related to the submitted manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, H.C., Zhong, J.G., Pan, P.L. et al. Gray matter atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy: meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Neurol Sci 34, 1049–1055 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1406-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1406-9