Abstract
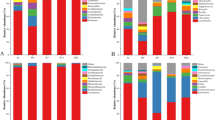
Chinese Tianshan tibico grains were collected from the rural area of Tianshan in Xinjiang province, China. Typical tibico grains are known to consist of polysaccharide matrix that embeds a variety of bacteria and yeasts. These grains are widely used in some rural regions to produce a beneficial sugary beverage that is slightly acidic and contains low level of alcohol. This work aimed to characterize the microbiota composition of Chinese Tianshan tibicos using the single molecule, real-time sequencing technology, which is advantageous in generating long reads. Our results revealed that the microbiota mainly comprised of the bacterial species of Lactobacillus hilgardii, Lactococcus raffinolactis, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Zymomonas mobilis, together with a Guehomyces pullulans-dominating fungal community. The data generated in this work helps identify beneficial microbes in Chinese Tianshan tibico grains.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boucher I, Vadeboncoeur C, Moineau S. Characterization of genes involved in the metabolism of alpha-galactosides by Lactococcus raffinolactis. Appl. Environ. Microb. 69: 4049–4056 (2003)
Chen X, Li J, Zhang L, Xu X, Wang A, Yang Y. Control of postharvest radish decay using a Cryptococcus albidus yeast coating formulation. Crop Prot. 41: 88–95 (2012)
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM. The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res. 35: D169–D172 (2007)
da Miguel MG, Cardoso PG, Magalhães KT, Schwan RF. Profile of microbial communities present in tibico (sugary kefir) grains from different Brazilian States. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27: 1875–1884 (2011)
Davidovic S, Miljkovic M, Antonovic D, Rajilic-Stojanovic M, Dimitrijevic-Brankovic S. Water Kefir grain as a source of potent dextran producing lactic acid bacteria. Hem. Ind. 69: 595–604 (2015)
Eid J, Fehr A, Gray J, Luong K, Lyle J, Otto G, Peluso P, Rank D, Baybayan P, Bettman B, Bibillo A, Bjornson K, Chaudhuri B, Christians F, Cicero R, Clark S, Dalal R, Dewinter A, Dixon J, Foquet M, Gaertner A, Hardenbol P, Heiner C, Hester K, Holden D, Kearns G, Kong X, Kuse R, Lacroix Y, Lin S, Lundquist P, Ma C, Marks P, Maxham M, Murphy D, Park I, Pham T, Phillips M, Roy J, Sebra R, Shen G, Sorenson J, Tomaney A, Travers K, Trulson M, Vieceli J, Wegener J, Wu D, Yang A, Zaccarin D, Zhao P, Zhong F, Korlach J, Turner S. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science. 323: 133–138 (2009)
Einsfeldt K, Baptista IC, Pereira JC, Costa-Amaral IC, Costa ES, Ribeiro MC, Land MG, Alves TL, Larentis AL, Almeida RV. Recombinant L-Asparaginase from Zymomonas mobilis: A potential new antileukemic agent produced in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 11: e0156692 (2016)
Gulitz A, Stadie J, Ehrmann MA, Ludwig W, Vogel RF. Comparative phylobiomic analysis of the bacterial community of water kefir by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing and ARDRA analysis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 114: 1082–1091 (2013)
Gulitz A, Stadie J, Wenning M, Ehrmann MA, Vogel RF. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 151: 284–288 (2011)
Hagi T, Hoshino T. Screening and characterization of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria from cultured common carp intestine. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 73: 1479–1483 (2009)
Hou Q, Xu H, Zheng Y, Xi X, Kwok LY, Sun Z, Zhang H, Zhang W. Evaluation of bacterial contamination in raw milk, ultra-high temperature milk and infant formula using single molecule, real-time sequencing technology. J. Dairy Sci. 98: 8464–8472 (2015)
Ikeda S, Fujimura T, Ytow N. Potential application of ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis to the microbial community analysis of agronomic products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53: 5604–5611 (2005)
Jany JL, Barbier G. Culture-independent methods for identifying microbial communities in cheese. Food Microbiol. 25: 839–848 (2008)
Kõljalg U, Nilsson RH, Abarenkov K, Tedersoo L, Taylor AFS, Bahram M, Bates ST, Bruns TD, Bengtsson-Palme J, Callaghan TM. Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Mol. Ecol. 22: 5271–5277 (2013)
Lee SH, Chang HC. Isolation of antifungal activity of Leuconostoc mesenteroides TA from kimchi and characterization of its antifungal compounds. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 25: 213–219 (2016)
Lee YG, Cho J-Y, Moon J-H. Isolation and antioxidative activity of amino acid derivatives produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 25: 329–334 (2016)
Leite AM, Mayo B, Rachid CT, Peixoto RS, Silva JT, Paschoalin VM, Delgado S. Assessment of the microbial diversity of Brazilian kefir grains by PCR-DGGE and pyrosequencing analysis. Food Microbiol. 31: 215–221 (2012)
Li X, Li J, Li M, Meng X. Screening and functional properties of cholesterol-degrading lactic acid bacteria from Jiangshui. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao = Acta microbiologica Sinica. 55: 1001–1009 (2015)
Lick S, Keller M, Bockelmann W, Heller KJ. Optimized DNA extraction method for starter cultures from yoghurt. Milchwissenschaft. 51: 183–186 (1995)
Liu W, Zheng Y, Kwok LY, Sun Z, Zhang J, Guo Z, Hou Q, Menhe B, Zhang H. High-throughput sequencing for the detection of the bacterial and fungal diversity in Mongolian naturally fermented cow’s milk in Russia. BMC Microbiol. 15: 45 (2015)
Lorenzetti MFS, Moro MR, García-Cruz CH. Alginate/PVA beads for levan production by Zymomonas mobilis. J. Food Process Eng. 38: 31–36 (2015)
Marsh AJ, O’Sullivan O, Hill C, Ross RP, Cotter PD. Sequence-based analysis of the microbial composition of water kefir from multiple sources. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 348: 79–85 (2013)
Meslier V, Loux V, Renault P. Genome sequence of Lactococcus raffinolactis strain 4877, isolated from natural dairy starter culture. J. Bacteriol. 194: 6364 (2012)
Mosher JJ, Bernberg EL, Shevchenko O, Kan J, Kaplan LA. Efficacy of a 3rd generation high-throughput sequencing platform for analyses of 16S rRNA genes from environmental samples. J. Microbiol. Meth. 95: 175–181 (2013)
Muhialdin BJ, Hassan Z, Abu Bakar F, Algboory HL, Saari N. Novel antifungal peptides produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides DU15 effectively inhibit growth of Aspergillus niger. J. Food Sci. 80: M1026–M1030 (2015)
Nakagawa T, Ikehata R, Uchino M, Miyaji T, Takano K, Tomizuka N. Cold-active acid beta-galactosidase activity of isolated psychrophilic-basidiomycetous yeast Guehomyces pullulans. Microbiol. Res. 161: 75–79 (2006)
Ning Y, Xu D, Zhang X, Bai Y, Ding J, Feng T, Wang S, Xu N, Qian K, Wang Y, Qi C. Beta-glucan restores tumor-educated dendritic cell maturation to enhance antitumor immune responses. Int. J. Cancer. 138: 2713–2723 (2016)
Rodina NN, Shutova VV, Revin VV. Effect of sucrose on the growth and dextransucrase activity of Leuconostoc mesenteroides. J. Biotechnol. 208: S117 (2015)
Shokri H, Asadi F, Khosravi AR. Isolation of β-glucan from the cell wall of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat. Prod. Res. 22: 414–421 (2008)
Terzic-Vidojevic A, Mihajlovic S, Uzelac G, Veljovic K, Tolinacki M, Nikolic M, Topisirovic L, Kojic M. Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from artisanal Travnik young cheeses, sweet creams and sweet kajmaks over four seasons. Food Microbiol. 39: 27–38 (2014)
Vardjan T, Mohar Lorbeg P, Rogelj I, Canzek Majhenic A. Characterization and stability of lactobacilli and yeast microbiota in kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 96: 2729–2736 (2013)
Wang H, Cao S, Wang WT, Wang KT, Jia X. Very high gravity ethanol and fatty acid production of Zymomonas mobilis without amino acid and vitamin. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 43: 861–871 (2016)
Yao G, Yu J, Hou Q, Hui W, Liu W, Kwok LY, Menghe B, Sun T, Zhang H, Zhang W. A perspective study of koumiss microbiome by metagenomics analysis based on single-cell amplification technique. Front. Microbiol. 8: 165 (2017)
Yoon EJ, Yoo SH, Cha J, Lee HG. Effect of levan’s branching structure on antitumor activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 34: 191–194 (2004)
Zhang A, Guo E, Qian L, Tang NY, Watt RM, Bartlam M. Purification, crystallization and X-ray crystallographic analysis of a putative exopolyphosphatase from Zymomonas mobilis. Acta Crystallogr. 72: 172–178 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank those who provided the tibico samples for use in this study and the National Natural Science Foundation of China for financial support of this research (Grant No. 31571815).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This paper does not contain any studies with human or animal subject.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, C., Hou, Q., Hui, W. et al. Assessment of the microbial diversity of Chinese Tianshan tibicos by single molecule, real-time sequencing technology. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 139–145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0460-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0460-8