Abstract
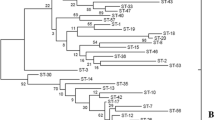
The objective of this study was to perform genetic diversity analysis of 13 strains isolated from South Korean foods by multilocus sequence typing (MLST). For typing, seven housekeeping loci (atpA, dnaA, dnaK, gyrB, pheS, pyrG, and rpoA) were selected, amplified and analyzed. Fifty-one polymorphic sites varying from 1 to 22 in each species were identified. Thirteen sequence types were generated with allele numbers ranged from 2 to 10. The overall relationship between strains was assessed by unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean dendrogram and minimum spanning tree. In addition, combined spits tree analysis revealed intragenic recombination. No clear relationship was observed between the isolation sources and strains. The developed MLST scheme enhanced our knowledge of the population diversity of Leu. citreum strains and will be used further for the selection of industrially important strain.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreani NA, Martino ME, Fasolato L, Carraro L, Montemurro F, Mioni R, Bordin P, Cardazzo B. Tracking the blue: A MLST approach to characterize the Pseudomonas fluorescens group. Food Microbiol. 39: 116–126 (2014)
Björkroth J, Holzapfel W. Genera Leuconostoc, Oenococcus and Weissella, pp. 267–319. In: The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria: Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria. Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E (eds). Springer, New York, NY, USA (2006)
Cai H, Rodriguez BT, Zhang W, Broadbent JR, Steele JL. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Lactobacillus casei strains isolated from different ecological niches suggests frequent recombination and niche specificity. Microbiology 153: 2655–2665 (2007)
Chang JY, Chang HC. Identification of a replicon from pCC3, a cryptic plasmid from Leuconostoc citreum C4 derived from kimchi, and development of a new host vector system. Biotechnol. Lett. 31: 685–696 (2009)
Chang JY, Chang HC. Improvements in the quality and shelf-life of kimchi by fermentation with the induced bacteriocin-producing strain, Leuconostoc citreum GJ7, as a starter. J. Food Sci. 75: 103–110 (2010)
Dan T, Liu W, Sun Z, Lv Q, Xu H, Song Y, Zhang H. A novel multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) protocol for Leuconostoc lactis isolates from traditional dairy products in China and Mongolia. BMC Microbiol. 14: 150 (2014)
De Bruyne K, Schillinger U, Caroline L, Boehringer B, Cleenwerck I, Vancanneyt M, De Vuyst, L, Franz CM, Vandamme P. Leuconostoc holzapfelii sp. nov., isolated from Ethiopian coffee fermentation and assessment of sequence analysis of housekeeping genes for delineation of Leuconostoc species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57: 2952–2959 (2007)
Hall TA. Bioedit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41: 95–98 (1999)
Huson DH, Bryant D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23: 254–267 (2006)
Kaur J, Lee S, Park YS, Sharma A. RAPD analysis of Leuconostoc mesenteroides strains associated with vegetables and food products from Korea. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 77: 383–388 (2017a)
Kaur J, Lee S, Sharma A, Park YS. Molecular typing of Leuconostoc citreum strains isolated from Korean fermented foods using a random amplified polymorphic DNA marker. Food Eng. Prog. 21: 174–179 (2017b)
Kaur J, Sharma A, Lee S, Park YS. DNA profiling of Leuconostoc citreum strains in fermented foods by repetitive element polymerase chain reaction. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27(10): 1778–1782 (2017c)
Korber B. HIV signature and sequence variation analysis, pp. 55–72. In: Computational Analysis of HIV Molecular Sequences. Rodrigo AG, Learn GH (eds). Dordrecht, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands (2000)
Kot W, Neve H, Heller KJ, Vogensen FK. Bacteriophages of Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, and Weissella. Front. Microbiol. 5: 186 (2014)
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic analysis 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33: 1870–1874. (2016)
Librado P, Rozas J. DnaSPv5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphisms data. Bioinformatics 25: 1451–1452 (2009)
Maiden MCJ, Bygraves JA, Feil E, Morelli G, Russell JE, Urwin R, Zhang Q, Zhou J, Zurth K, Caugant DA, Feavers IM, Achtman M, Spratt BG. Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 3140–3145 (1998)
Meslier V, Loux V, Renault P. Genome sequence of Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides strain 4882, isolated from a dairy starter culture. J. Bacteriol. 194: 696–712 (2012)
Picozzi C, Bonacina G, Vigentini I, Foschino R. Genetic diversity in Italian Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis strains assessed by Multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analyses. Microbiology 156: 2035–2045 (2010)
Sharma A, Kaur J, Lee S, Park Y-S. Genetic diversity analysis of Leuconostoc mesenteroides from Korean vegetables and food products by multilocus sequence typing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8942-4 (2018)
Zhang W, Liu W, Song Y, Xu H, Menghe B, Zhang H, Sun Z. Multilocus sequence typing of a dairy-associated Leuconostoc mesenteroides population reveals clonal structure with intragenic homologous recombination. J. Dairy Sci. 98: 1–10 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through High Value-added Food Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (Grant Number: 316051-03-2-HD020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Kaur, J., Lee, S. et al. Analysis of Leuconostoc citreum strains using multilocus sequence typing. Food Sci Biotechnol 27, 1755–1760 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0417-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0417-y