Abstract
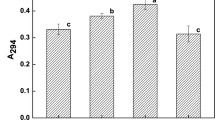
The primary purpose of this study was to analyze the ability of four peptidoglycan (PGN) from different lactic acid bacteria to bind acrylamide (AA) and to identify the binding mechanism. In this study, to clarify the possible binding interactions among AA and components of PGN, chemical components, surface structure, amino acids component, and functional groups of peptidoglycans were studied. It was found that PGN from Lactobacillus plantarum 1.0065 had the highest ability to bind AA with 87%. Furthermore, a significant positive relation was found between the carbohydrate content of PGN and percentage of bind AA, and the content of four specific amino acids of PGN and AA binding ability were also positive correlated. Thereinto, alanine of PGN had a significant impact on AA binding among four amino acids. Additionally, the C–O (carboxyl, polysaccharides, and arene), C=O amide, and N–H amines groups of PGN were involved in AA binding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baardseth P, Blom H, Skrede G, Mydland LT, Skrede A, Slinde E. Lactic acid fermentation reduces acrylamide formation and other maillard reactions in french fries. Food Chem. Toxicol. 71: 28–33 (2006)
Hariri E, Abboud MI, Demirdjian S, Korfali S, Mroueh M, Taleb RI. Carcinogenic and neurotoxic risks of acrylamide and heavy metals from potato and corn chips consumed by the lebanese population. J. Food Compos. Anal. 42: 91–97 (2015)
Oracz J, Nebesny E, yelewicz D. New treds in quantification of acrylamide in food products. Talanta 86: 23–24 (2011)
Anese M, Bortolomeazzi R, Manzocco L, Manzano M, Giusto C, Nicoli MC. Effect of chemical and biological dipping on acrylamide formation and sensory properties in deep-fried potatoes. Food Res. Int. 42: 142–147 (2009)
Hernandez-Mendoza A, Garcia HS, Steele JL. Screening of Lactobacillus casei strains for their ability to bind aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 47: 1064–1068 (2009)
Corthier G. The health benefits of probiotics. Danone Nutritopics 29: 1–18 (2004)
Hernandez-Mendoza A, Guzman-de-pena D, Garcia HS. Key role of teichoic acids on aflatoxin B1 binding by probiotic bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 107: 395–403 (2009)
El-Nezami H, Mikkänen H, Kankäänpää P, Salminen S, Ahokas J. Ability of Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium strains to remove Aflatoxin B1 from the chicken duodenum. J. Food Protect. 63: 549–552 (2000)
Fazeli MR, Hajimohammadali M, Mokshkani A, Samadi N, Jamalifar H, Khoshayand MR. Aflatoxin B1 binding capacity of autochthonous strains of Lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Protect. 72: 189–192 (2009)
Wang L, Yue TL, Yuan YH, Wang ZL, Ye MQ, Cai R. A new insight into the adsorption mechanism of patulin by the heat-inactive Lactic acid bacteria cells. Food Control 50: 104–110 (2015)
Hamidi A, Mirnejad R, Yahaghi E, Behnod V, Mirhosseini A, Amani S, Sattari S, Darian EK. The aflatoxin B1 isolating potential of two Lactic acid bacteria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 3: 732–736 (2013)
Hernandez-Mendoza A, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Córdoba B, García HS. Effect of oral supplementation of Lactobacillus reuteri in reduction of intestinal absorption of aflaoxin B1 in rats. J. Basic Microb. 51: 1–6 (2011)
Serrano-Niño JC, Cavazos-Garduño A, Cantú-Cornelio F, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Córdoba B, Hernández-Mendoza A, García HS. In vitro r edu ced availability of aflatoxin B1 and acrylamide by bonding interactions with teichoic acids from lactobacillus strains. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 64: 1334–1341 (2015)
Hwang KT, Lee W, Kim GY, Lee J, Jun W. The binding of aflatoxin B1 modulates the adhesion properties of Lactobacillus casei KCTC 3260 to HT29 colon cancer cell line. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 14: 866–870 (2005)
Tripathi P, Beaussart A, Andre G, Rolain T, Lebeer S, Vanderleyden J. Towards a nanoscale view of Lactic acid bacteria. Micron 43: 1323–1330 (2012)
Wu Z, Pan DD, Guo YX, Zeng XQ. Structure and anti-inflammatory capacity of peptidoglycan from Lactobacillus acidophilus in RAW-264.7 cells. Carbohyd. Polym. 96: 466–473 (2013)
Baik JE, Jang YO, Kang SS, Cho K, Yun CH, Han SH. Differential profiles of gastrointestinal proteins interacting with peptidoglycans from Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Immunol. 65: 77–85 (2015)
Chen KK, Liu C, He Y, Jiang HB, Lu ZQ. A short-type peptidoglycan recognition protein from the silkworm: Expression, characterization and involvement in the prophenoloxidase activation pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 45: 1–9 (2014)
Wu Z, Pan DD, Guo YX, Sun YY, Zeng XQ. Peptidoglycan diversity and antiinflammatory capacity in Lactobacillus strains. Carbohyd. Polym. 128: 130–137 (2015)
Vinderola CG, Bailo N, Reinheimer JA. Survival of probiotic microflora in Argentinian yogurts during refrigerated storage. Food Res. Int. 33: 97–102 (2000)
Vemula H, Ayon NJ, Gutheil WG. Cytoplasmic peptidoglycan intermediate levels in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochimie 121: 72–78 (2016)
Mei MAQ, Elbashir AA, Schmitz OJ. Determination of acrylamide in sudanese food by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with LTQ Qrbitrap mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 176: 342–349 (2015)
Marcotte L, Kegelaer G, Sandt C, Barbeau J, Lafleur M. An alternative infrared spectroscopy assay for the quantification of polysaccharides in bacterial samples. Anal. Biochem. 361: 7–14 (2007)
Hall MB. Efficacy of reducing sugar and phenol-sulfuric acid assays for analysis of soluble carbohydrates in feedstuffs. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 185: 94–100 (2013)
Lahtinen SJ, Haskard CA, Ouwehand AC, Salminen SJ, Ahokas JT. Binding of aflatoxin B1 to cell wall components of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Food Addit. Contam. 21: 158–164 (2004)
Zoghi A, Khosravi-Darani K, Sohrabvandi S. Surface binding of toxins and heavy metals by probiotics. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 14: 84–98 (2014)
Fuchs S, Sontag G, Stidl R, Ehrlich V, Kundi M, Knasmuller S. Detoxification of patulin and ochratoxin A, two abundant mycotoxins, by Lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem. Toxicol. 46: 1398–1407 (2008)
Turbic A, Ahokas JT, Haskard CA. Binding of mutagens to exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum mutant strain 301102S. J. Dairy Sci. 91: 2960–2966 (2002)
Zhao H F, Zhou F, Qi YQ, Piotr D, Bai FL, Piotr W, Zhang BL. Screening of Lactobacillus strains for their ability to bind Benzo(a)pyrene and the mechanism of the process. Food Chem. Toxicol. 59: 67–71 (2013)
Haskard C, Binnion C, Ahokas J. Factors affecting the sequestration of aflaoxin by Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 128: 39–49 (2000)
Hatab S, Yue T, Mohamad O. Removal of patulin from apple juice using inactivated Lactic acid bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 112: 892–899 (2012)
Guo C, Yuan Y, Yue T, Hatab S, Wang Z. Binding mechanism of patulin to heattreated yeast cell. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 55: 453–459 (2012)
Deng Y, Dixon JB, White N, Loeppert RH, Juo ASR. Bonding between polyacrylamide and smectite. Colloid. Surface A 281: 82–91 (2006)
Koutsidis G, Simons SPJ, Thong YH, Haldoupis Y, Mojica-Lazaro J, Wedzicha BL, Mottram DS. Investigations on the effect of amino acids on acrylamide, pyrazines, and Michael addition products in model systems. J. Agr. Food Chem. 57: 9011–9015 (2009)
Niderkorn V, Morgavi D, Aboab B, Lemaire M, Boudra H. Cell wall component and mycotoxin moieties involved in the binding of fumonisin B1 and B2 by Lactic acid bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 106: 977–985 (2009)
Zamora R, Delgado RM, Hidalgo FJ. Model reactions of acrylamide with selected amino compounds. J. Agr. Food Chem. 58: 1708–1713 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Liu, W., Li, L. et al. Key role of peptidoglycan on acrylamide binding by lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci Biotechnol 26, 271–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0036-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0036-z