Abstract
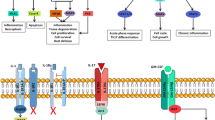
Interleukin (IL)-27 is a novel member of the IL-6/IL-12 family of cytokines with a broad range of pro- and anti-inflammatory properties. Recently, accumulating evidence has shown that IL-27 can play either a pathogenic or a protective role in animal models of inflammatory arthritis, depending upon the model and underlying pathogenic mechanisms. As to human system, elevated expression of IL-27 has clearly been detected in the synovial membranes and fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Moreover, stimulation of IL-27 receptor with IL-27 of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from RA had a suppressive effect on the production of proinflammatory cytokines in vitro. All these findings suggest that IL-27 may have promise as a potential therapeutic target for RA. In this review, we will discuss the biological features of IL-27 and summarize recent advances on both pathogenic and protective roles of IL-27 in RA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN (1996) Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell 85:307–310
Taga T, Kishimoto T (1997) Gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 15:797–819
Pope RM, Shahrara S (2013) Possible roles of IL-12-family cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9:252–256
Pflanz S, Timans JC, Cheung J, Rosales R, Kanzler H, Gilbert J, Hibbert L, Churakova T, Travis M, Vaisberg E, Blumenschein WM, Mattson JD, Wagner JL, To W, Zurawski S, McClanahan TK, Gorman DM, Bazan JF, de Waal Malefyt R, Rennick D, Kastelein RA (2002) IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells. Immunity 16:779–790
Yoshida H, Nakaya M, Miyazaki Y (2009) Interleukin 27: a double-edged sword for offense and defense. J Leukoc Biol 86:1295–1303
Takeda A, Hamano S, Yamanaka A, Hanada T, Ishibashi T, Mak TW, Yoshimura A, Yoshida H (2003) Cutting edge: role of IL-27/WSX-1 signaling for induction of T-bet through activation of STAT1 during initial Th1 commitment. J Immunol 170:4886–4890
Rosario AP F d, Lamb T, Spence P, Stephens R, Lang A, Roers A, Muller W, O’Garra A, Langhorne J (2012) IL-27 promotes IL-10 production by effector Th1 CD4+ T cells: a critical mechanism for protection from severe immunopathology during malaria infection. J Immunol 188:1178–1190
Wojno ED, Hunter CA (2012) New directions in the basic and translational biology of interleukin-27. Trends Immunol 33:91–97
Niedbala W, Cai B, Wei X, Patakas A, Leung BP, McInnes IB, Liew FY (2008) Interleukin 27 attenuates collagen-induced arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1474–1479
Cao Y, Doodes PD, Glant TT, Finnegan A (2008) IL-27 induces a Th1 immune response and susceptibility to experimental arthritis. J Immunol 180:922–930
Wong CK, da Chen P, Tam LS, Li EK, Yin YB, Lam CW (2010) Effects of inflammatory cytokine IL-27 on the activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R129
Tanida S, Yoshitomi H, Ishikawa M, Kasahara T, Murata K, Shibuya H, Ito H, Nakamura T (2011) IL-27-producing CD14(+) cells infiltrate inflamed joints of rheumatoid arthritis and regulate inflammation and chemotactic migration. Cytokine 55:237–244
Pflanz S, Hibbert L, Mattson J, Rosales R, Vaisberg E, Bazan JF, Phillips JH, McClanahan TK, de Waal MR, Kastelein RA (2004) WSX-1 and glycoprotein 130 constitute a signal-transducing receptor for IL-27. J Immunol 172:2225–2231
Miyazaki Y, Inoue H, Matsumura M, Matsumoto K, Nakano T, Tsuda M, Hamano S, Yoshimura A, Yoshida H (2005) Exacerbation of experimental allergic asthma by augmented Th2 responses in WSX-1-deficient mice. J Immunol 175:2401–2407
Owaki T, Asakawa M, Fukai F, Mizuguchi J, Yoshimoto T (2006) IL-27 induces Th1 differentiation via p38 MAPK/T-bet- and intercellular adhesion molecule-1/LFA-1/ERK1/2-dependent pathways. J Immunol 177:7579–7587
Villarino AV, Stumhofer JS, Saris CJ, Kastelein RA, de Sauvage FJ, Hunter CA (2006) IL-27 limits IL-2 production during Th1 differentiation. J Immunol 176:237–247
Lucas S, Ghilardi N, Li J, de Sauvage FJ (2003) IL-27 regulates IL-12 responsiveness of naive CD4+ T cells through Stat1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15047–15052
Yoshimura T, Takeda A, Hamano S, Miyazaki Y, Kinjyo I, Ishibashi T, Yoshimura A, Yoshida H (2006) Two-sided roles of IL-27: induction of Th1 differentiation on naive CD4+ T cells versus suppression of proinflammatory cytokine production including IL-23-induced IL-17 on activated CD4+ T cells partially through STAT3-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 177:5377–5385
Tesmer LA, Lundy SK, Sarkar S, Fox DA (2008) Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol Rev 223:87–113
Shen H, Xia L, Xiao W, Lu J (2011) Increased levels of interleukin-27 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 63:860–861
Pickens SR, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Mandelin AM 2nd, Agrawal H, Matsui M, Yoshimoto T, Shahrara S (2011) Local expression of interleukin-27 ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 63:2289–2298
Rajaiah R, Puttabyatappa M, Polumuri SK, Moudgil KD (2011) Interleukin-27 and interferon-gamma are involved in regulation of autoimmune arthritis. J Biol Chem 286:2817–2825
Furukawa M, Takaishi H, Takito J, Yoda M, Sakai S, Hikata T, Hakozaki A, Uchikawa S, Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Kimura T, Okada Y, Matsuo K, Yoshida H, Toyama Y (2009) IL-27 abrogates receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand-mediated osteoclastogenesis of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-forming unit cells through STAT1-dependent inhibition of c-Fos. J Immunol 183:2397–2406
Kalliolias GD, Zhao B, Triantafyllopoulou A, Park-Min KH, Ivashkiv LB (2010) Interleukin-27 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis by abrogating RANKL-mediated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 and suppressing proximal RANK signaling. Arthritis Rheum 62:402–413
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, F., Pan, YH., Huang, X. et al. Interleukin-27 as a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis: has the time come?. Clin Rheumatol 32, 1425–1428 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2341-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2341-0