Abstract
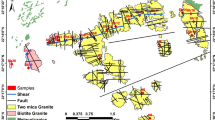
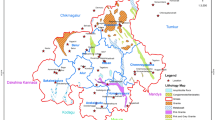
This study deals with natural radioactivity levels of the ten most important commercial granites from various districts currently being exploited as dimension stone in Turkey. Determining the level of radioactivity is important for human health, particularly for indoor use of granites. This study shows that the relationship between the natural radioactivity and the radiogenic mineralogical contents of the granites exploited for commercial utilization in Turkey is variable. The natural radioactivity levels (i.e., activity concentrations of radionuclides 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K) of granite samples were determined by high-resolution gamma-ray spectrometry. Using these activities, radiological hazard dose rates (absorbed and annual effective) and gamma-activity indexes were calculated using standard equations accepted by public health bodies, taking relevant international reports and guidelines into account. Three of the granites exploited in the Black Sea, Aegean, and Central Anatolia regions were found to be high in radium-equivalent activities and annual effective doses due to minerals bearing the radionuclides, including zircon, apatite, allanite, xenotime, uranothorite, K-feldspars, and biotite. Of those, uranothorite contains large amounts of radionuclides and is present in samples of granites collected from the Black Sea and Aegean regions. Radioactivity measurements using high-resolution gamma-ray spectroscopy serve as a rapid screening tool to evaluate natural radioactivity, whereas detailed petrographic, mineralogical, and elemental investigations can reveal the source of radioactive emissions in granites.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi A (2013) Calculation of gamma radiation dose rate and radon concentration due to granites used as building materials in Iran. Radiat Prot Dosim 155(3):335–342
Adams JAS, Osmond YK, Rogers JJW (1959) The geochemistry of uranium and thorium. Phys Chem Earth 3:298–343
Akal C (2013) Coeval Shoshonitic-ultrapotassic dyke emplacements within the Kestanbol pluton, Ezine–Biga peninsula (NW Anatolia). Turk J Earth Sci 22:220–238
Altschuler ZS, Clarke RS, Young EY (1958) Geochemistry of uranium in apatite and phosphorite. US Geological Survey Professional Paper, 314-D, pp 45–90
Altunkaynak Ş, Yılmaz Y (1999) The Kozak pluton and its emplacement. Geol J 34:257–274
Altunkaynak Ş, Sunal G, Aldanmaz E, Genç ŞC, Dilek Y, Furnes H, Foland KA, Yang J, Yıldız M (2012) Eocene granitic magmatism in NW Anatolia (Turkey) revisited: new implications from comparative zircon SHRIMP U–Pb and 40Ar–39Ar geochronology and isotope geochemistry on magma genesis and emplacement. Lithos 155:289–309
Amin RM (2012) Gamma radiation measurements of naturally occurring radioactive samples from commercial Egyptian granites. Environ Earth Sci 67(3):771–775
Amstrong JT (1988) Quantitative analysis of silicate and oxide materials: comparison of Monte Carlo, ZAF, and phi–rho-z procedures. Microbeam analysis, pp 239–246
Angı OS (2007) Aksaray Yaylak granitinin kaplama taşı yönünden özelliklerinin araştırılması. MSc thesis, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey, p 105
Anjos R, Veiga R, Soares T, Santos A, Aguiar J, Frascac M, Brage J, Uzêda D, Mangia L, Facure A, Mosquera B, Carvalho C, Gomes P (2005) Natural radionuclide distribution in Brazilian commercial granites. Radiat Meas 39:245–253
Ataman G (1974) Revue geochronologique, des massifs plutoniques et metamorphiques del’Anatolie. Hacettepe Bulletin of Natural Sciences and Engineering 3:518–523
Aykamış AŞ, Turhan Ş, Uğur FA, Baykan UN, Kılıç AM (2013) Radon exhalation rates and indoor radon concentration of some granite samples used as construction material in Turkey. J Radiat Prot Dosim 157:105–111
Aykol A, Tokel S (1991) The geochemistry and tectonic setting of the Demirkoy pluton of the Srednogorie–Strandja granitoid chain, NW Turkey. Mineral Mag 55:249–256
Beretka J, Matthew PJ (1985) Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrial wastes and by-products. Health Phys 48:87–95
Bingöl E (1989) 1:2000000 scaled geological map of Turkey. MTA Press, Ankara
Bingöl E, Delaloye M, Ataman G (1982) Granitic intrusion in Western Anatolia: a contribution to the geodynamic study of this area. Eclogae Geologische Helvetica 75(2):437–446
BS EN 12440 (2008) Natural stone—denomination criteria standard, UK
Canbaz B, Çam NF, Yaprak G, Candan O (2010) Natural radioactivity (226Ra, 232Th and 40K) and assessment of radiological hazards in the Kestanbol granitoid, Turkey. Radiat Prot Dosim 141(2):192–198
Carrera G, Garavaglia M, Magnoni S, Valli G, Vecchi R (1997) Natural radioactivity and radon exhalation in stony materials. J Environ Radioact 34:149–159
Çetin E, Altınsoy N, Örgün Y (2012) Natural radioactivity levels of granites used in Turkey. Radiat Prot Dosim 151:299–305
Clark SP, Peterman ZE, Heier KS (1966) Abundance of U, Th and K. In: Handbook of physical constants. Geol. Soc. Am. Mere., vol 97, pp 521–541
Cuney M, Friederich M (1987) Physicochemical and crystal-chemical controls on accessory paragenesis in granitoids: implications for uranium metallogenesis. Bull Minéral 110:235–247
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J (1997) Rock-Forming Minerals Volume 1A: Orthosilicates, 2nd edn. Geological Society, London
Delaloye M, Bingöl E (2000) Granitoids from western and northwestern Anatolia: geochemistry and modeling of geodynamic evolution. Int Geol Rev 42(3):241–268
EC (European Commission) (2011) Draft presented under Article 31 Euratom Treaty for the opinion of the European Economic and Social Committee: laying down basic safety standards for protection against the dangers arising from exposure to ionising radiation. COM(2011) 593, Brussels, Belgium
El-Arabi AM (2007) Ra, Th, K concentrations in igneous rocks from eastern desert Egypt and its radiological implications. Radiat Meas 42:94–100
Erkül-Tatar S, Özmen SF, Erkül F, Boztosun İ (2016) Comparison between natural radioactivity levels and geochemistry of some granitoids in western Turkey. Turk J Earth Sci 25:242–255
Faure G (1986) Principles of isotope geology. Wiley, Chichester
Goldschmidt VM (1954) Geochemistry (edited by Alex Muir). Clarendon Press, Oxford, p 730
Guillén J, Tejado JJ, Baeza A, Corbacho JA, Muñoz JG (2014) Assessment of radiological hazard of commercial granites from Extremadura (Spain). J Environ Radioact 132:81–88
Heinrich WME (1958) Mineralogy and geology of radioactive raw materials. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency) (1987) Preparation of gamma-ray spectroscopy reference materials RGU-1, RGTh-1 and RGK-1 report-IAEA/RL/148, Vienna, Austria
Ilbeyli N (1998) Petrogenesis of collision-related plutonic rocks, central Anatolia (Turkey). PhD thesis, Durham University, UK, p 279
Kadıoğlu YK, Dilek Y, Güleç N, Foland KA (2003) Tectonomagmatic evolution of bimodal plutons in the Central Anatolian Crystalline Complex, Turkey. Geol J 111:671–690
Karacık Z, Yılmaz Y (1998) Geology of the ignimbrites and the associated volcano–plutonic complex of the Ezine area, northwestern Anatolia. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 85:251–264
Karadeniz Ö, Akal C (2014) Radiological mapping in the granodiorite area of Bergama (Pergamon)–Kozak, Turkey. Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:361–373
Karadeniz Ö, Çıyrak N, Yaprak G, Akal C (2011) Terrestrial gamma exposure in the granodiorite area of Bergama (Pergamon)–Kozak, Turkey. Radioanal Nucl Chem 288(3):919–926
Karadeniz Ö, Yaprak G, Akal C, Emen İ (2012) Indoor radon measurements in the granodiorite area of Bergama (Pergamon)–Kozak, Turkey. Radiat Prot Dosim 149(2):147–154
Kerur BR, Kumar A, Narayani S, Lagare MT, Abani MC (2003) Study of radioactivity levels in granites of North Karnataka region of India. Radiat Prot Environ 26(1–2):446–449
Köksal S, Göncüoğlu MC, Toksoy-Köksal F, Möller A, Kemnitz H (2008) Zircon typologies and internal structures as petrogenetic indicators in contrasting granitoid types from Central Anatolia. Mineral Petrogr 93:185–211
Le Bas MJ, Streckeisen AL (1991) The IUGS systematics of igneous rocks. J Geol Soc Lond 148:825–833
Le Maitre RW (ed) (2002) Igneous rocks. A classification and glossary of terms. Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, UK, p 236
MacKenzie WS, Donaldson CH, Guilford C (1995) Atlas of igneous rocks and their textures. Longman, Harlow Press, London
Marocchi M, Righi S, Bargossi GM, Gasparotto G (2011) Natural radionuclides content and radiological hazard of commercial ornamental stones: an integrated radiometric and mineralogical-petrographic study. Radiat Meas 46:538–545
Moore WJ, McKeey EH, Akıncı Ö (1980) Chemistry and chronology of plutonic rocks in the Pontid mountains, northern Turkey. European copper deposits congress book, Belgrade, pp 209–216
NEA-OECD (1979) Exposure to radiation from the natural radioactivity in building materials. Report by a group of experts of the OECD, Nuclear Energy Agency, Paris, France
Onargan T, Gür F, Kaya E, Güneri S (2012) Assessment of natural radioactivity in commercial granites used in Turkey. J Environ Sci Health Part A 47(12):1825–1830
Örgun Y, Altınsoy N, Yılmaz-Şahin S, Güngör Y, Gültekin AH, Karahan G, Karacık Z (2007) Natural and anthropogenic radionuclides in rocks and beach sands from Ezine region (Çanakkale), Western Anatolia, Turkey. Appl Radiat Isot 65:739–747
Osmanlıoğlu AE (2006) Natural radioactivity and evaluation of effective dose equivalent of granites in Turkey. Radiat Prot Dosim 121:325–329
Papadopoulos A, Christofides G, Koroneos A, Papado-poulou L, Papastefanou C, Stoulos S (2013) Natural radioactivity and radiation index of the major granitic plutons in Greece. J Environ Radioact 124:227–238
Pavlidou S, Koroneos A, Papastefanou C, Christofides G, Stoulos S, Vavelides M (2006) Natural radioactivity of granites used as building materials. J Environ Radioact 89:48–60
Pereira D, Neves L, Pereira A, Peinado M, Blanco JA, Tejado JJ (2012) A radiological study of some ornamental stones: the bluish granites from Extremadura (Spain). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12:395–401
Pivko D (2004) World’s quarries of commercial granites—localization and geology. In: Proceedings of the international conference in dimension stone, Prague, vol 1, pp 147–152
Pollack HN (1982) The heat flow from the continents. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 10:459–481
Puccini A, Xhixha G, Cuccuru S, Oggiano G, Xhixha M, Mantovani F, Alvarez C, Casini L (2014) Radiological characterization of granitoid outcrops and dimension stones of the Variscan Corsica–Sardinia batholith. Environ Earth Sci 71(1):393–405
Rollinson H (1993) Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation. Longman Group UK Ltd., Oxford
Şahin-Yılmaz S, Güngör Y, Boztuğ D (2004) Comparative petrogenetic investigation of composite Kaçkar batholith granitoids in eastern Pontide magmatic arc—northern Turkey. Earth Planets Space 56:429–446
Salas HT, Nalini HA Jr, Mendes JC (2006) Radioactivity dosage evaluation of Brazilian ornamental granitic rocks based on chemical data, with mineralogical and lithological characterization. Environ Geol 49:520–526
Sayın N (2013) Radioactive element contents of some granites used as building materials: insights into the radiological hazards. Bull Eng Geol Environ 72:579–587
Staatz MH, Conklin NM, Brownfield IK (1977) Rare earths, thorium, and other minor elements in sphene from some plutonic rocks in west-central Alaska. J Res USGS Surv 5:623–628
Stanley SM (2004) Earth system history, 2nd edn. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York
Stoulos S, Manolopoulou M, Papastefanou C (2003) Assessment of natural radiation exposure and radon exhalation from building materials in Greece. J Environ Radioact 69:225–240
Stranden E (1976) Some aspects on radioactivity of building materials. Physica Norvegica 8:167–173
Turhan S (2012) Estimation of possible radiological hazards from natural radioactivity in commercially-utilized ornamental and countertops granite tiles. Ann Nucl Energy 44:34–39
Turtiainen T, Weltner A (2007) Assessment of dose during the life cycle of natural stone production. Radiat Prot Dosim 124(2):167–171
Tzortzis M, Tsertos H, Christofides S, Christodoulides G (2003) Gamma measurements and dose rates in commercially used tiling rocks (granites). J Environ Radioact 70:223–235
UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the effects of Atomic Radiation) (2000) Sources and effects of Ionizing radiation, exposures from natural radiation sources, annex B. United Nations, New York
Vanderhaeghe O, Cecile F, Jean-François M, Anne-Sylvie A-M, Pierre B, Michel C (2011) Cratons radioactivity, crustal growth, paleogeotherms and metallogenic provinces. In: Geophysical research abstracts, vol 13, EGU2011-4101. EGU General Assembly 2011
Whitfield JM, Rogers JJW, Adams JAS (1959) The relationship between the petrology and the thorium and uranium contents of some granitic rocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 17:248–271
Whitney DL, Evans BW (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 95:185–187
Xinwei L, Lingqing W, Xiaodan J (2006) Radiometric analysis of Chinese commercial granites. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267(3):669–673
Acknowledgments
This paper was prepared using the radioactivity data and their research methods of commercial granites exploited in Aksaray region (Turkey) in the PhD thesis of O. Serkan ANGI [in preparation, to be submitted to Istanbul Technical University (ITU) Institute of Science and Technology]. The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. Paul A. Schroeder and Dr. Christopher J. Fleisher from University of Georgia Department of Geology (USA), and Prof. Dr. Yusuf Kağan Kadıoğlu from Ankara University Department of Geological Engineering (Turkey) for their generous and valuable contributions that significantly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angı, O.S., Yavuz, O., Yalçın, T. et al. Mineralogy-induced radiological aspects with characterization of commercial granites exploited in Turkey. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76, 507–522 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0894-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0894-2