Abstract
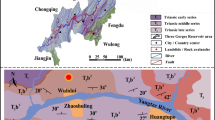
Jurassic strata prone to slope failure are widely distributed in the Three Gorges Reservoir region. The limit equilibrium method is generally used to analyze the stability of rock slopes that have a single failure plane. However, the stability of a stratified rock mass cannot be accurately estimated by this method because different bedding planes have variable shear strength parameters. A modified limit equilibrium method is presented with variable water pressure and shear strength used to estimate the stability coefficient of a sloping mass of stratified rock and to identify the potential sliding surface. Furthermore, an S-curve model is used to define the spatial variations of the shear strength parameters c and ϕ of the bedding plane and the tensile strength of the rock mass. This model can also describe the variation of strength parameters with distance from the slope surface, which depends on the reservoir water level. Also, it is used to evaluate the stability of the Qianjiangping landslide, located at Shazhenxi Town, Zigui County, Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. The results show the most probable sliding surface is the interface between a slightly weathered layer and subjacent bedrock. When reservoir water rises above the elevation of the slide mass toe, the stability coefficient of the slope declines sharply. When the reservoir water level is static at 135 m, the stability coefficient decreases gradually as the phreatic line changes as a result of heavy rainfall.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao L, Luo XQ (2007) Experimental study of dry-wet circulation of Qianjiangping Landslide’s unsaturated soil. Rock Soil Mech 28:93–97 (in Chinese)
Chen Z (2004) A generalized solution for tetrahedral rock wedge stability analysis. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:613–628
China Three Gorges Corporation. (2014) Title: Hydrologic situation, http://www.ctg.com.cn/inc/sqsk.php
Ching J, Yang ZY, Shiau JQ, Chen CJ (2013) Estimation of rock pressure during an excavation/cut in sedimentary rocks with inclined bedding planes. Struct Saf 41:11–19
Dong JJ, Tu CH, Lee WR, Jheng YJ (2012) Effects of hydraulic conductivity/strength anisotropy on the stability of stratified, poorly cemented rock slopes. Comput Geotech 40:147–159
Duncan CW, Christopher WM (2005) Rock slope engineering—civil and mining, 4th edn. Taylor & Francis e-Library, New York, pp 22–55
Eberhardt E, Stead D, Coggan JS (2004) Numerical analysis of initiation and progressive failure in natural rock slopes—the 1991 Randa rock slide. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:69–87
Eberhardt E, Thuro K, Luginbuehl M (2005) Slope instability mechanisms in dipping interbedded conglomerates and weathered marls—the 1999 Rufi landslide, Switzerland. Eng Geol 77:35–56
Fortsakis P, Nikas K, Marinos V, Marinos P (2012) Anisotropic behavior of stratified rock masses in tunnelling. Eng Geol 141–142:74–83
Fourniadis IG, Liu JG (2007) Landslides in the Wushan -Zigui region of the Three Gorges, China. Q J Eng Geol Hydroge 40:115–122
Gencer M (1985) Progressive failure in stratified and jointed rock mass. Rock Mech Rock Eng 18:267–292
Ghazvinian A, Vaneghi RG, Hadei MR, Azinfar MJ (2013) Shear behavior of inherently anisotropic rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 61:96–110
Gong WL, Wang J, Gong YX, Guo PY (2013) Thermography analysis of a roadway excavation experiment in 60° inclined stratified rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 60:134–147
Hammouri NA, Malkawi AIH, Yamin MM (2008) Stability analysis of slopes using the finite element method and limiting equilibrium approach. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67:471–478
Jian WX, Xu Q, Yang HF, Wang FW (2014) Mechanism and failure process of Qianjiangping landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Earth Sci 72(8):2999–3013
Jiang QH, Zhang ZH, Wei W, Xie N, Zhou CB (2012) Research on triggering mechanism and kinematic process of Qianjiangping landslide. Dis Adv 5(4):631–636
Johari A, Fazeli A, Javadi AA (2013) An investigation into application of jointly distributed random variables method in reliability assessment of rock slope stability. Comput Geotech 47:42–47
Li JJ, Xie SY, Kuang MS (2001) Geomorphic evolution of the Yangtze Gorges and the time of their formation. Geomorphology 41:125–135
Li AJ, Merified RS, Lvamin AV (2008) Stability charts for rock slopes based on the Hoek-Brown failure criterion. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45:689–700
Li CD, Hu XL, Tang HM, Fan FS, Wang LQ (2012) Evaluation and control study on reservoir bank landslide in the Three Gorges reservoir region, China. Disa Adv 5(4):8–135
Li YR, Wen BP, Aydin A, Ju NP (2013) Ring shear tests on slip zone soil zone soils of the three giant landslides in the Three Gorges Project area. Eng Geol 154:106–115
Liu JG, Mason PJ, Clerici N, Chen S, Davis A, Miao F, Deng H, Liang L (2004) Landslide hazard assessment in the Three Gorges area of the Yangtze river using ASTER imagery: Zigui-Badong. Geomorphology 61:171–187
Liu CH, Jaksa MB, Meyers AG (2008) Improved analytical solution for toppling stability analysis of rock slopes. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45:1361–1372
Lu ZD (2010) Experimental and theoretical analysis on mechanical properties of fractured rock under water-rock interaction. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan China
Luo XQ, Xu KX, Xiao SR, Wang ZJ, Zhang ZH (2007) The formation mechanism of Qianjiangping landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Research report, pp 13–69 (in Chinese)
Pantelidis L (2009) Rock slope stability assessment through rock mass classification systems. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46:315–325
Qin S, Jiao JJ, Wang S, Long H (2001) A nonlinear catastrophe model of instability of planar-slip slope and chaotic dynamical mechanisms of its evolutionary process. Int J Solids Str 38:8093–8109
Taghavi M, Dovoudi MH, Amiri-Tokaldany E, Darby SE (2010) An analytical method to estimate failure plane angle and tension crack depth for use in riverbank stability analyses. Geomorphology 123:74–83
Tang HM, Zou ZX, Xiong CR, Wu YP, Hu XL, Wang LQ, Lu S, Criss RE, Li CD (2015) An evolution model of large consequent bedding rockslides, with particular reference to the Jiweishan rockslide in Southwest China. Eng Geol 186(24):17–27
Tiwari R (2015) Simplified numerical implementation in slope stability modeling. Int J Geomech 15(3):1–19
Wang FW, Zhang YM, Huo ZT, Peng XM, Wang SM, Yamasaki S (2008) Mechanism for the rapid motion of the Qianjiangping landslide during reactivation by the first impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam reservoir, China. Landslides 5:379–396
Wen B, Shen J, Tan J (2008) The influence of water on the occurrence of Qianjiangping landslide. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 3:3–18
Wu Q, Tang HM, Wang LQ, Lin ZH (2009) Analytic solutions for phreatic line in reservoir slope with inclined impervious bed under rainfall and reservoir water level fluctuation. Rock Soil Mech 30(10):3025–3031
Xu B, Wang Y (2015) Stability analysis of the Lingshan gold mine tailings dam under conditions of a raised dam height. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74:151–161
Yang XL, Yin JH (2006) Linear Mohr-Coulomb strength parameters from the non-linear Hoek-Brown rock masses. Int J Nonlin Mech 41:1000–1005
Yang XL, Zou J (2006) Stability factors for rock slopes subjected to pore water pressure based on Hoek-Brown failure criterion. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 43:1146–1152
Zhou XP, Cheng H (2013) Analysis of stability of three-dimensional slopes using the rigorous limit equilibrium method. Eng Geol 160:21–33
Zou ZX, Tang HM, Xiong CR, Wu YP, Liu X, Liao SB (2012) Geomechanical Model of progressive failure for large consequent bedding rockslide and its stability analysis. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(11):2222–2230 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study is financially supported by the National Basic Research Program 973 Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (2011CB710604), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41272305), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41502300), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. Q16D020005). The authors appreciate the help provided by Harkiran Kaur, who made the careful English language editing on this manuscript before submitting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Yong, R. & Ez Eldin, M.A.M. Stability analysis of stratified rock slopes with spatially variable strength parameters: the case of Qianjiangping landslide. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76, 839–853 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0876-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0876-4